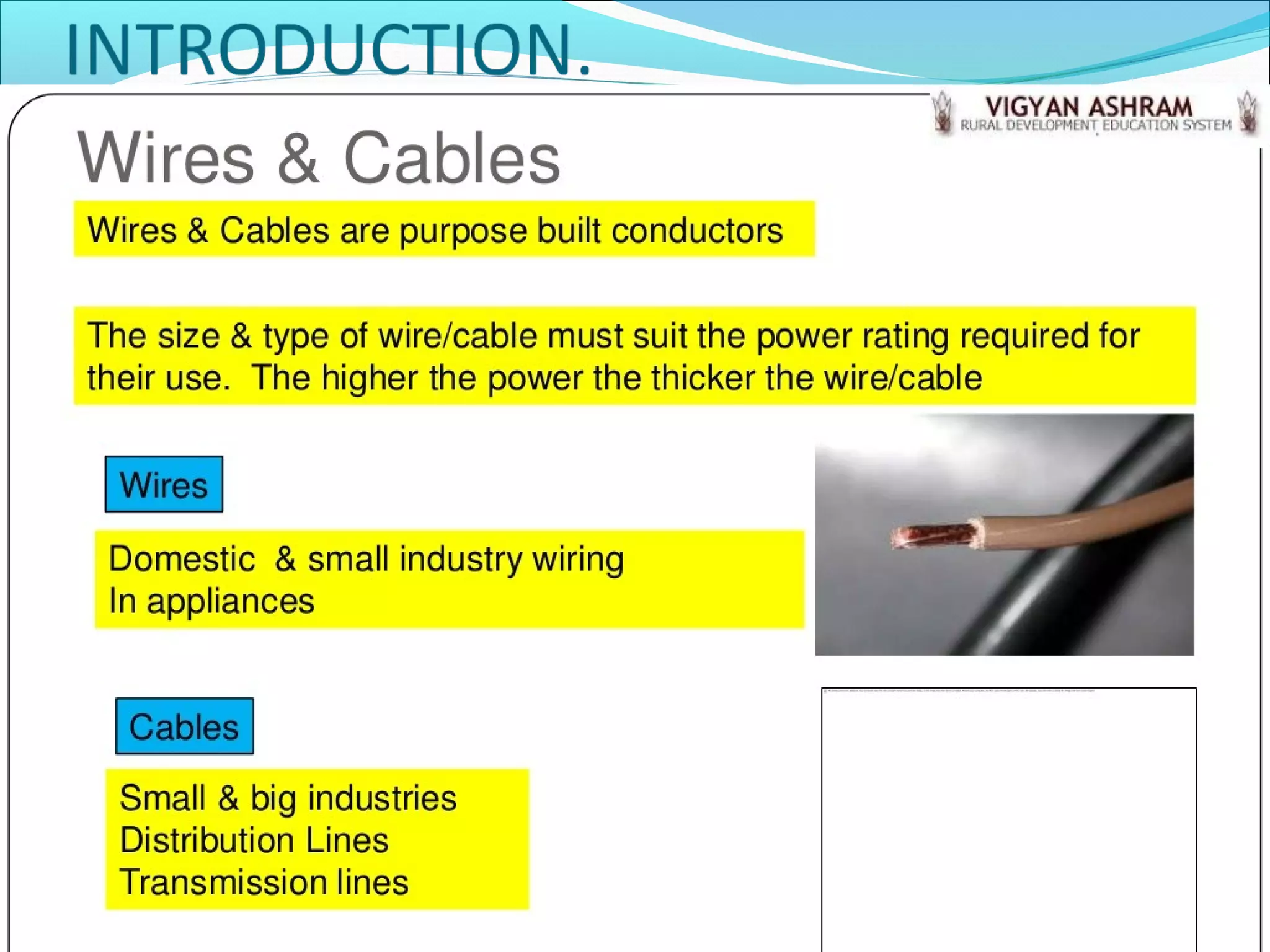
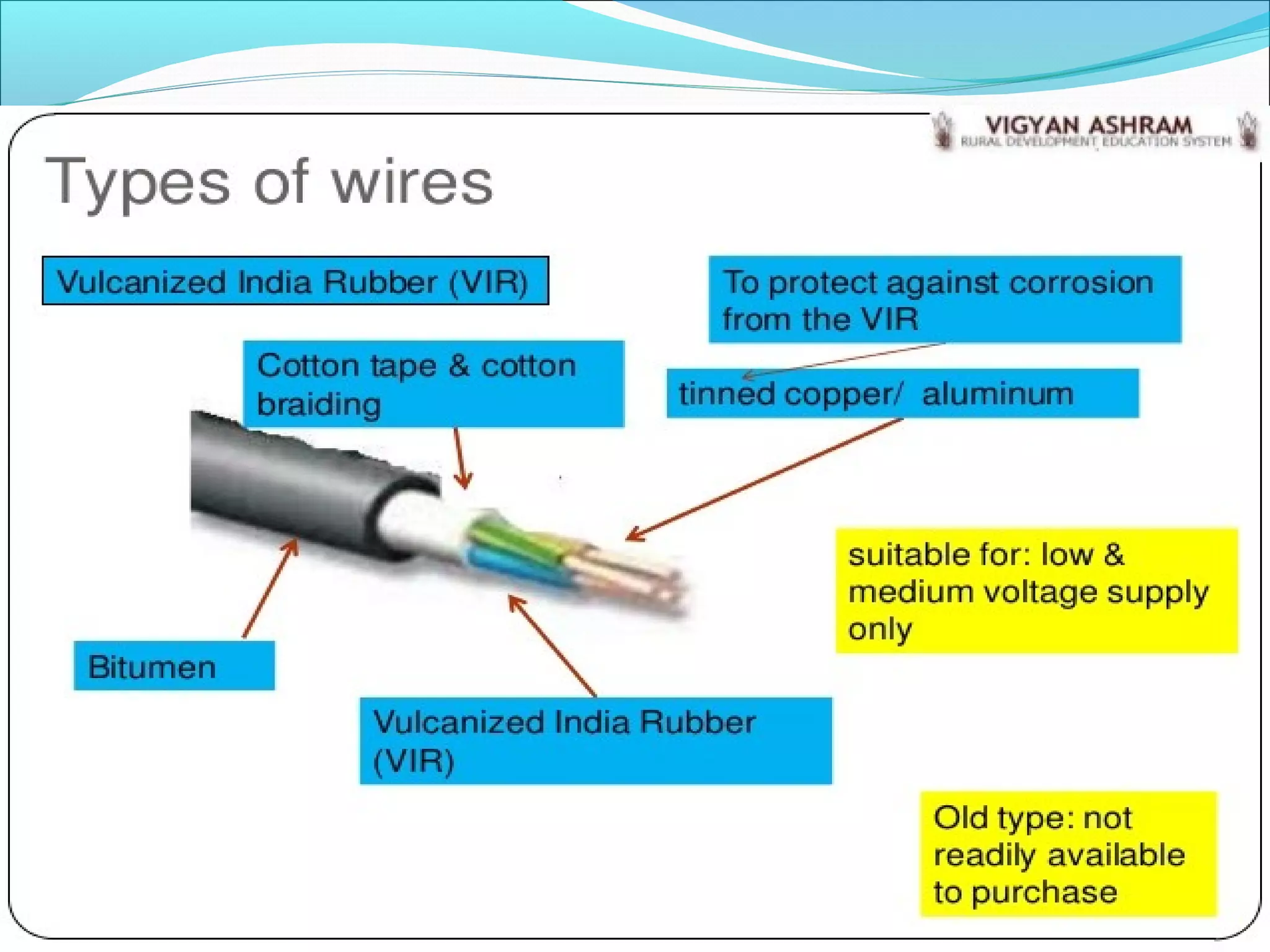
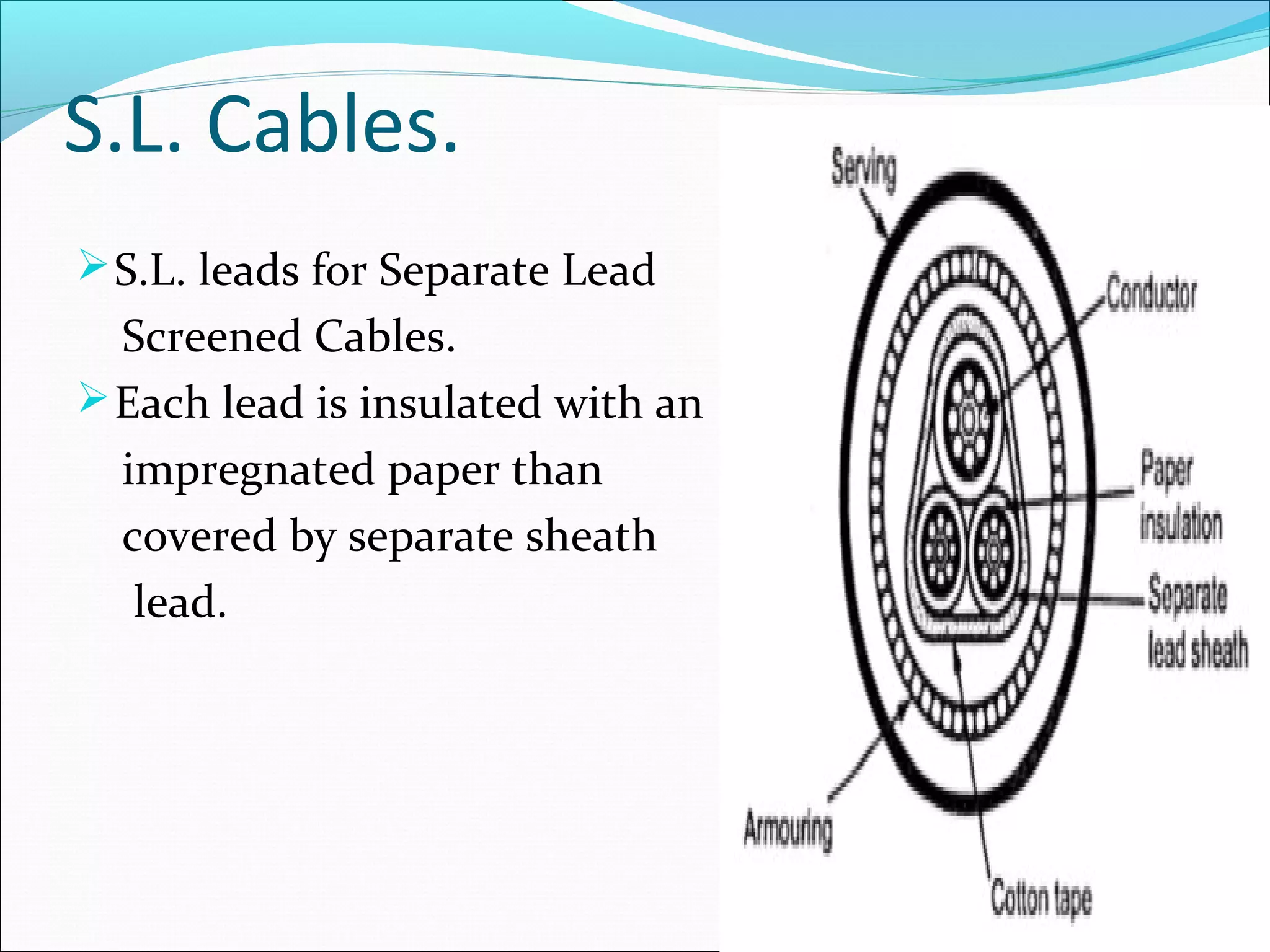
This document discusses different types of wires and cables used in electrical installations. It describes six main types of wires: VIR, TRS, PVC, lead alloy sheathed, weather proof, and flexible wires. PVC wire is most commonly used due to its moisture proof, tough, and durable properties. Cables are assemblies of two or more conductors held together with an overall sheath. Cables are classified based on voltage level and insulation material into low tension, medium/high tension, belted, screened, super tension, oil filled, and gas pressure cables.