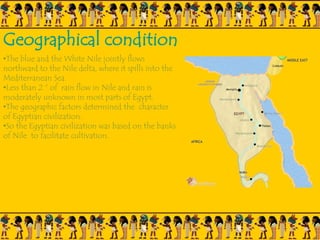
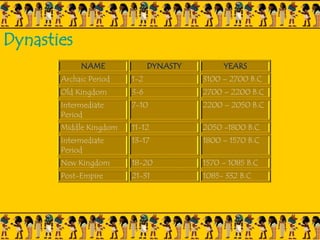
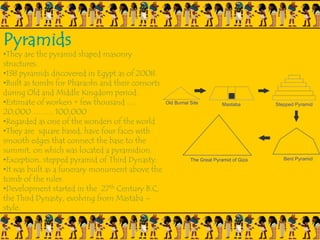
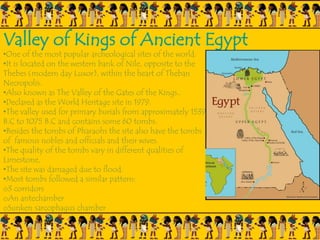
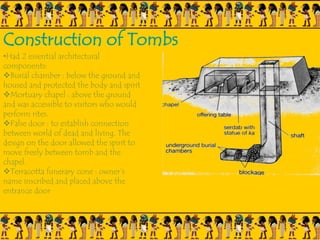
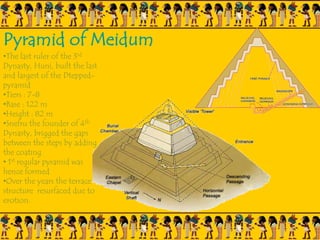
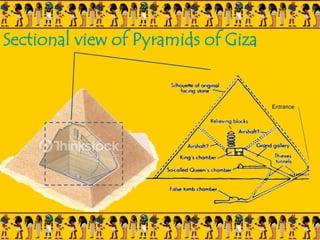
The document provides information on Egyptian civilization and its architecture. It discusses the geography of Egypt along the Nile River which determined the character of Egyptian civilization. It then outlines the different dynasties of ancient Egypt and describes the predominant materials used in architecture such as sun-baked bricks, stone, and limestone. Some key architectural features are discussed such as the use of symbolic motifs, hieroglyphics, and alignment with astronomical events. Different structures are summarized such as pyramids, which served as tombs for pharaohs; sphinxes which guarded tombs; and obelisks which symbolized the sun god. The document also covers the Valley of Kings and different types of tombs including mastabas