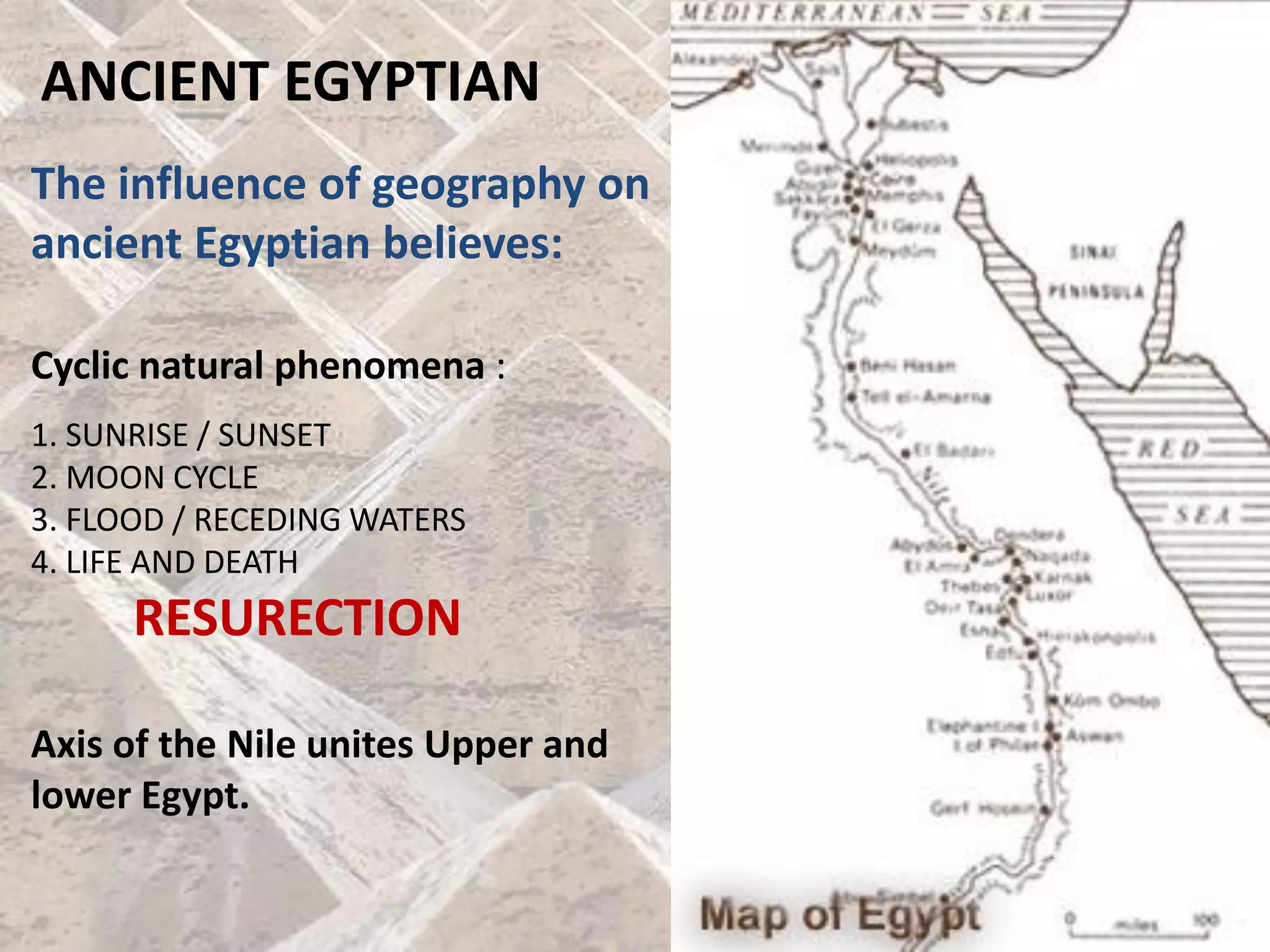
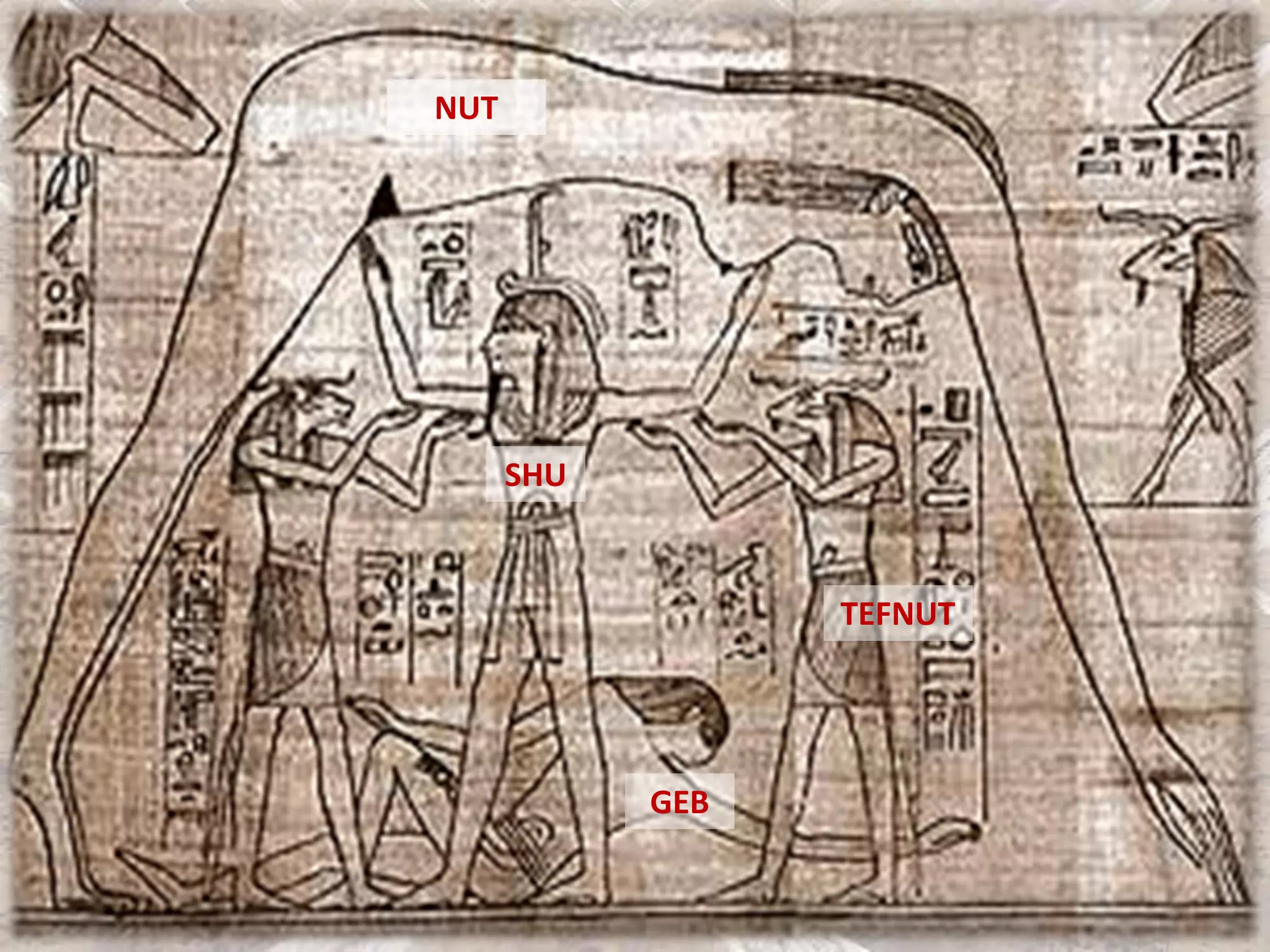
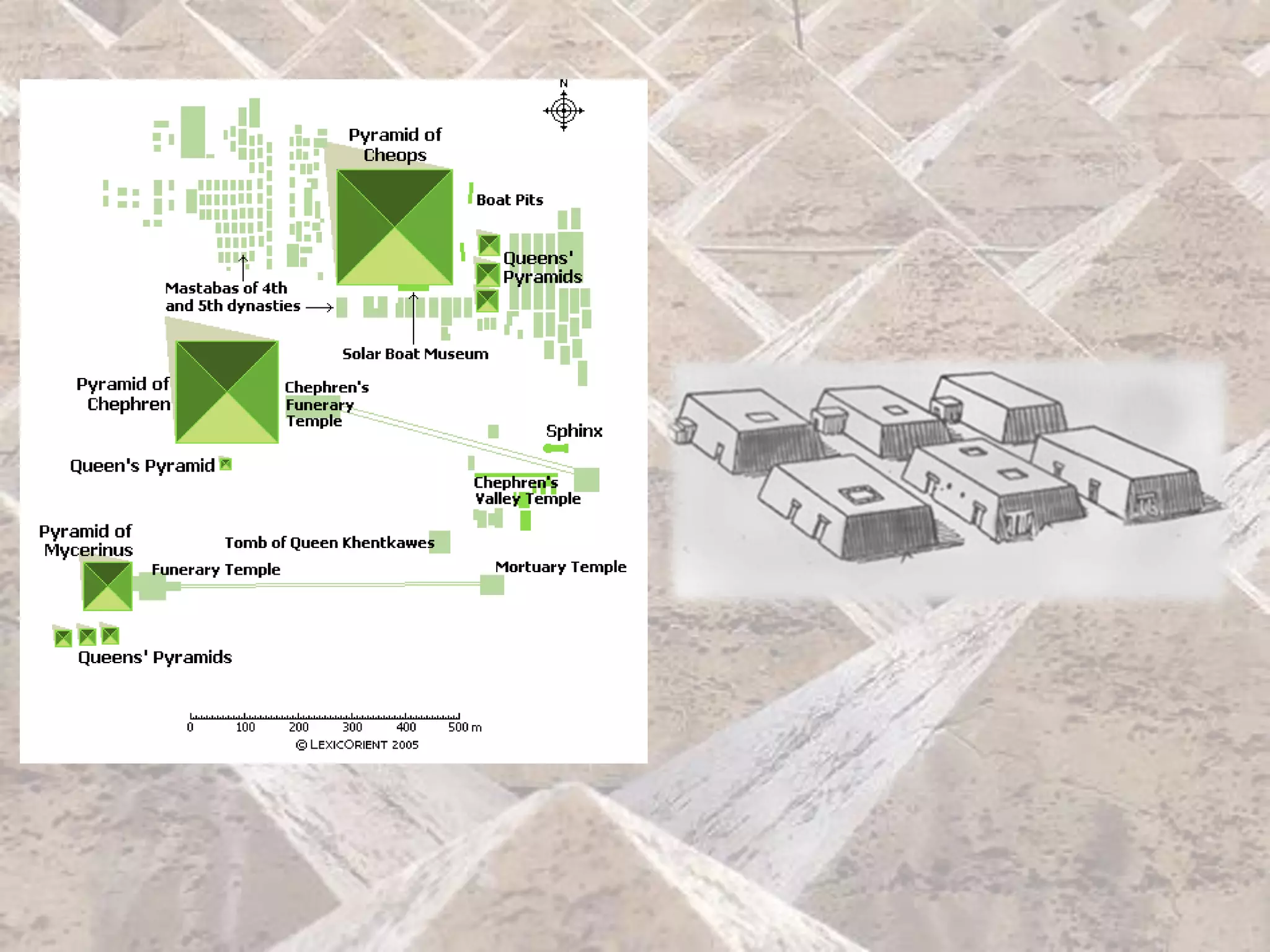
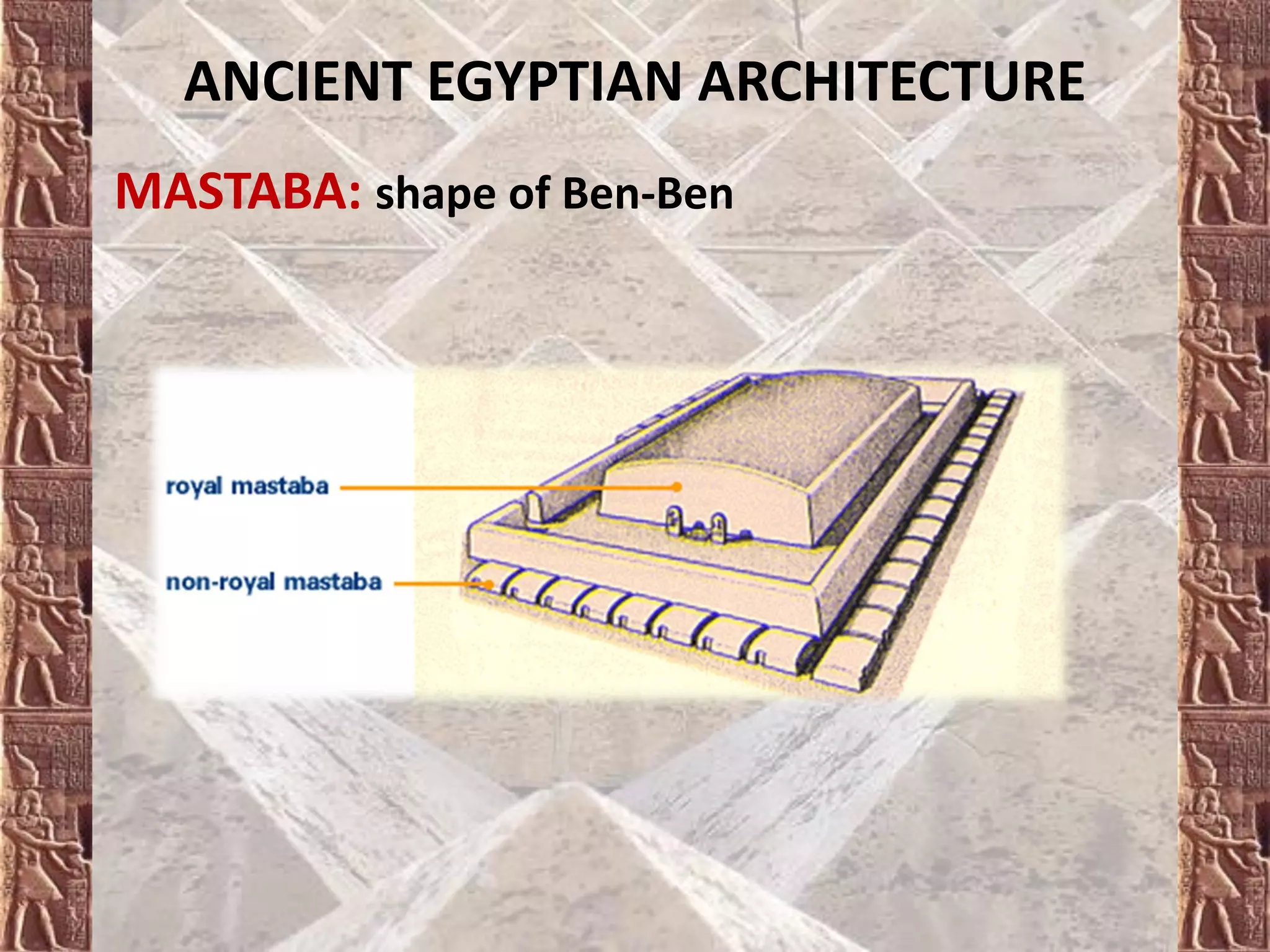
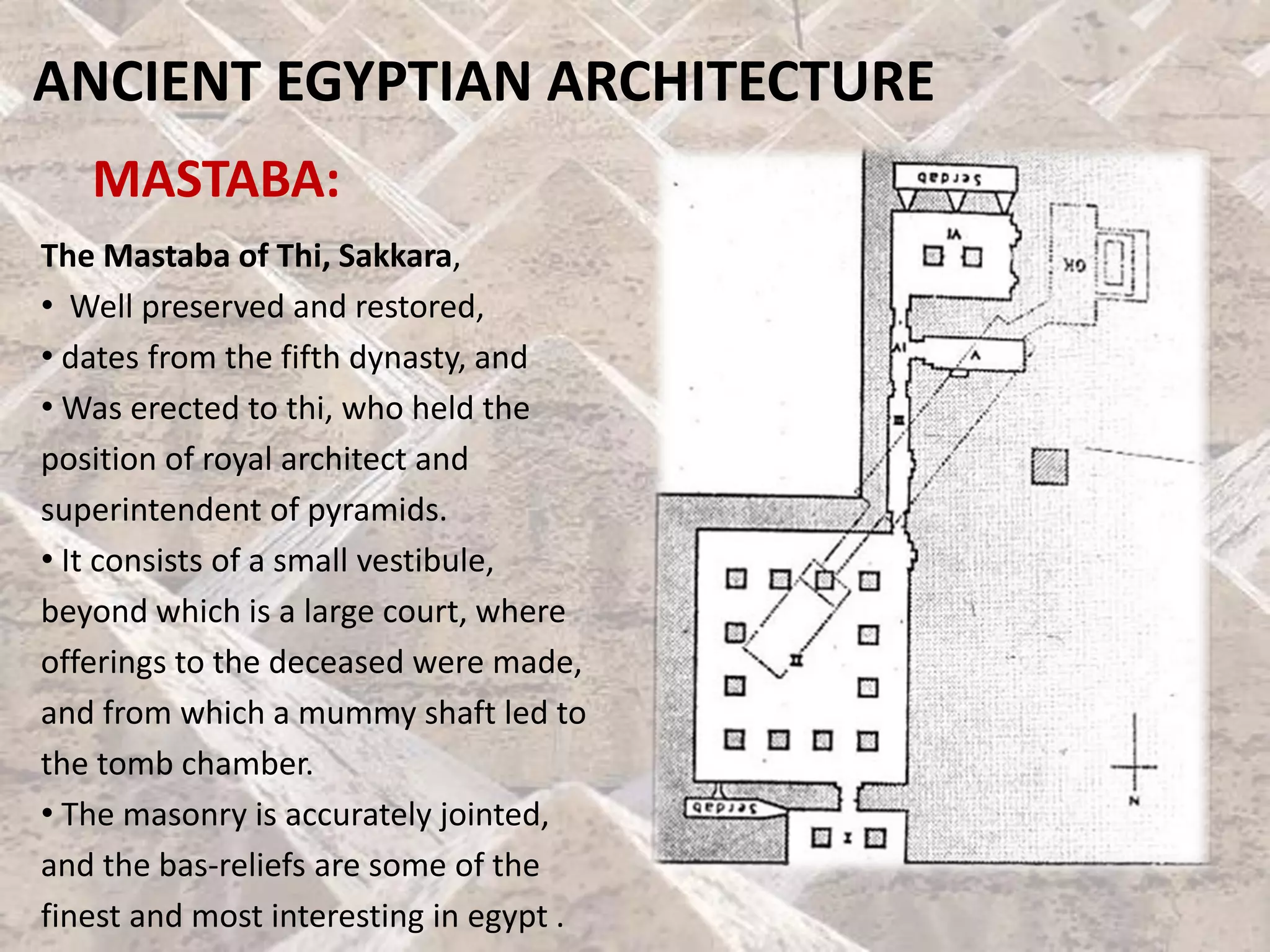
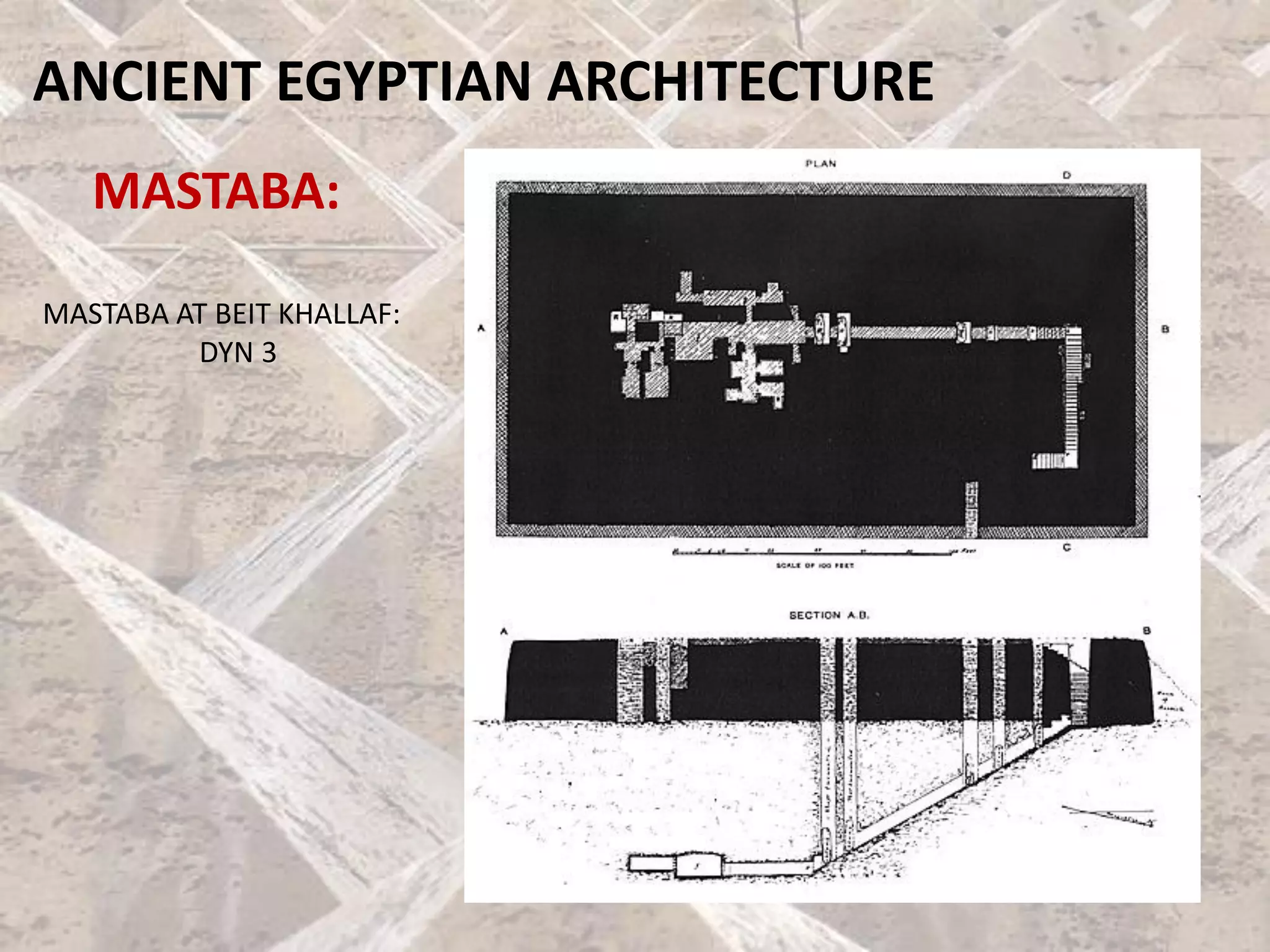
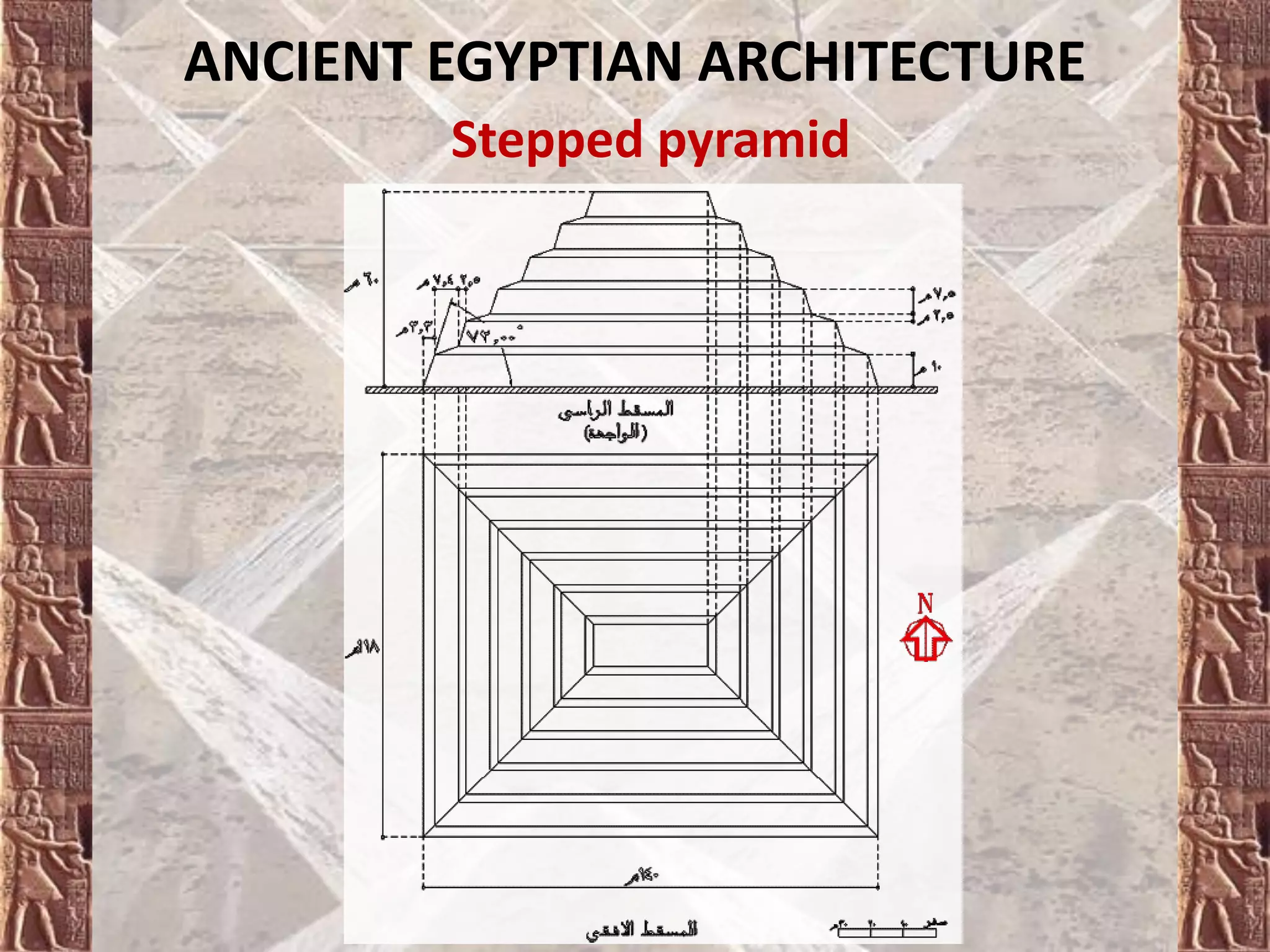
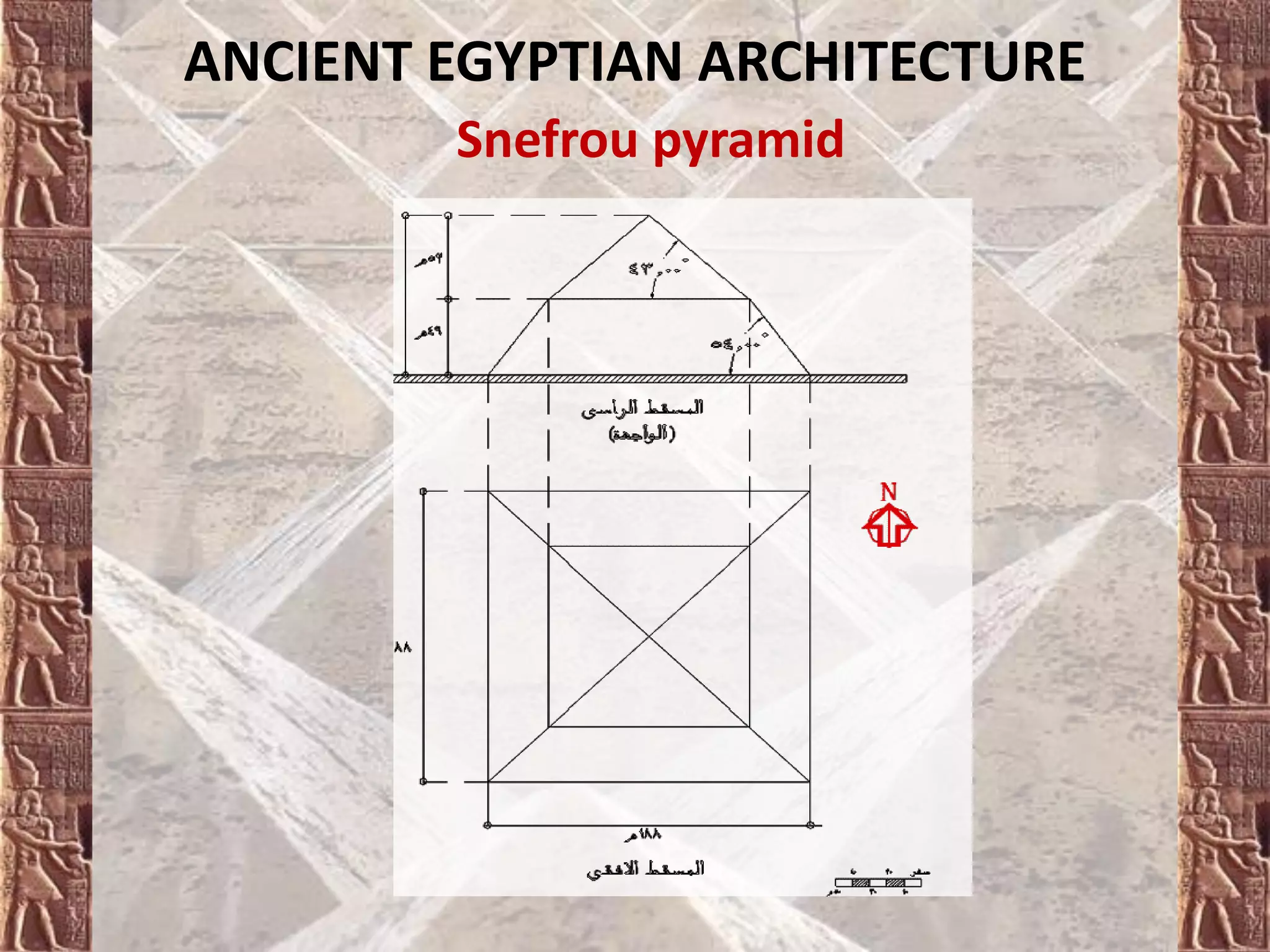
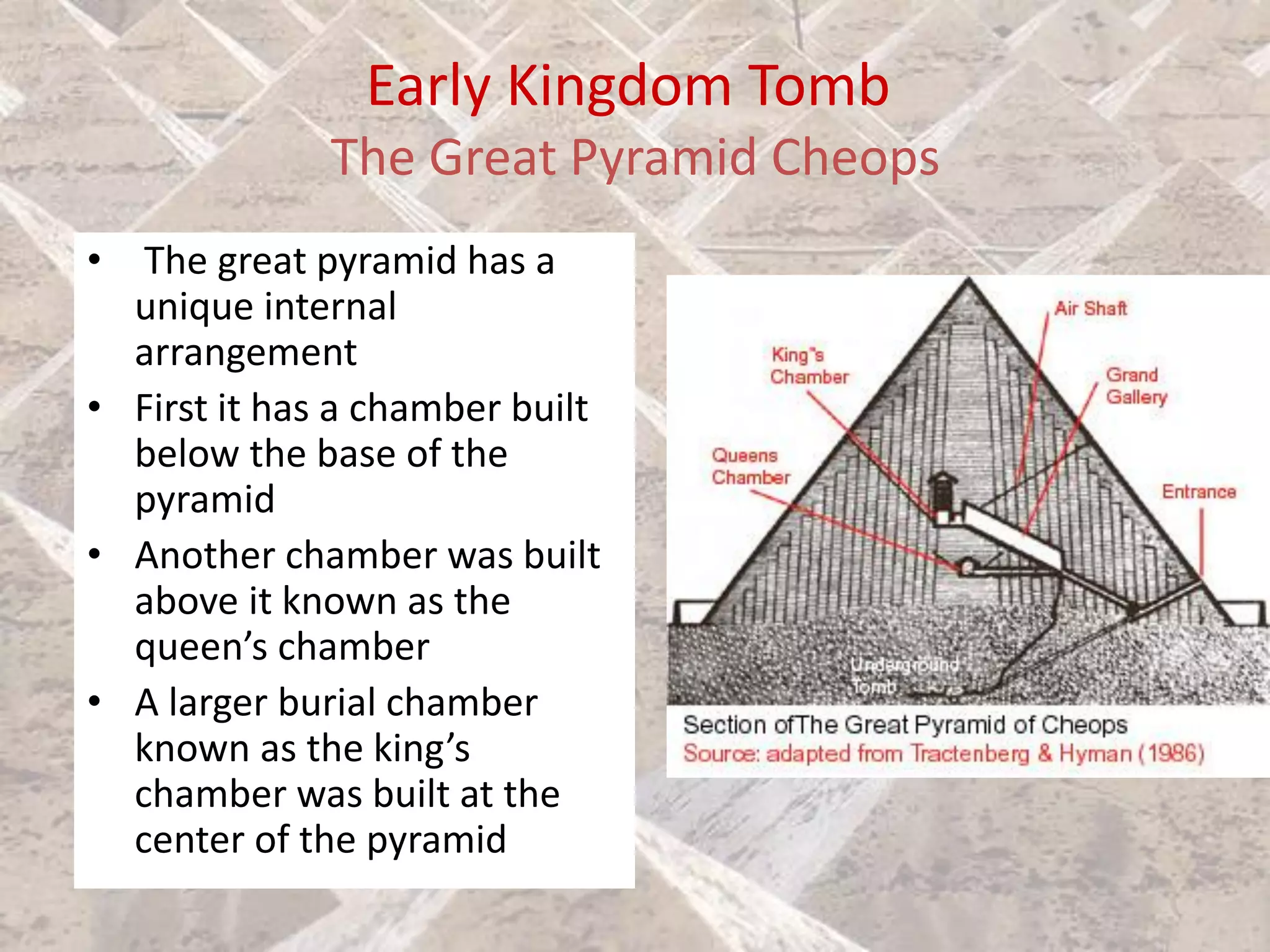
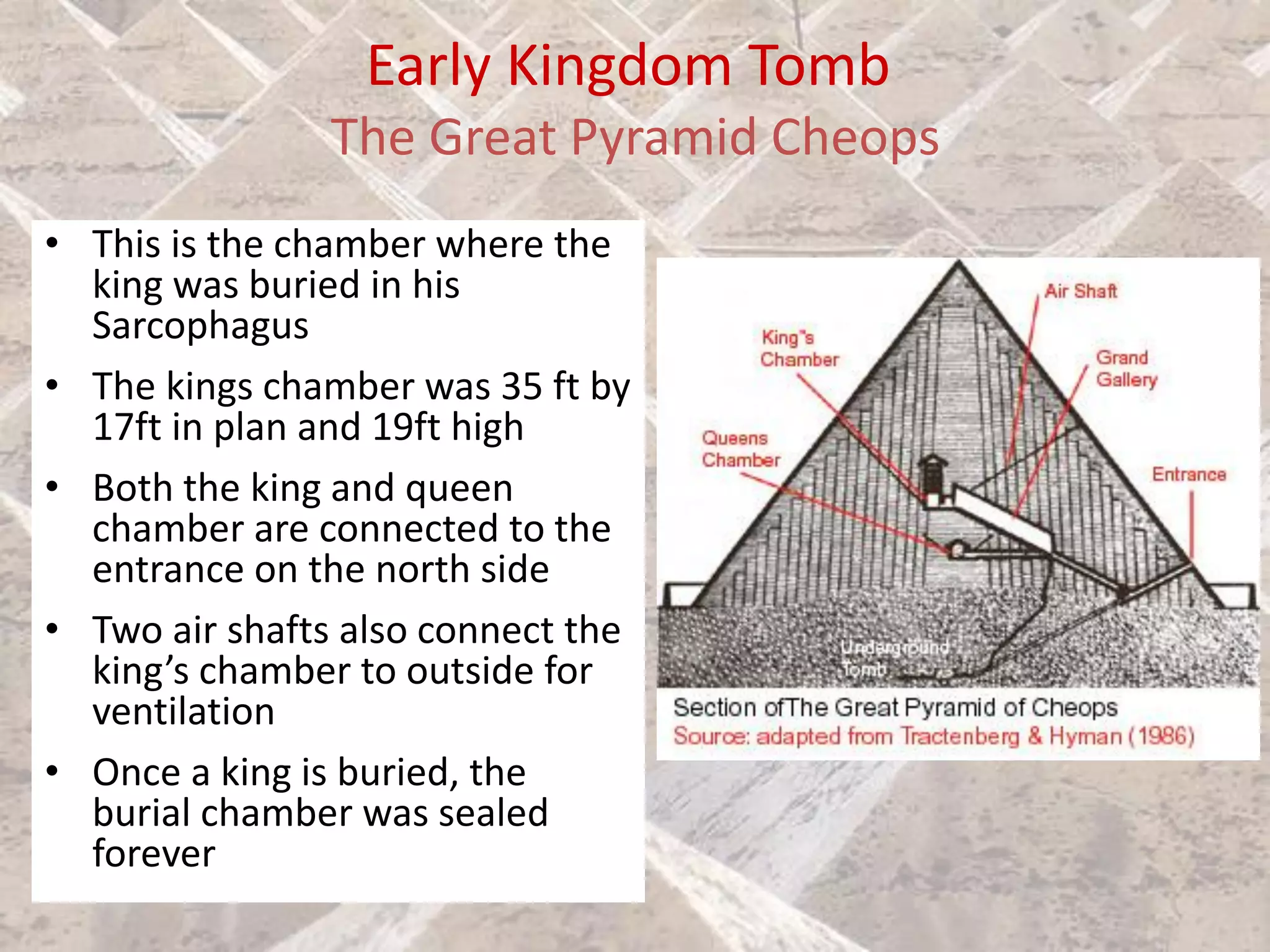
Ancient Egyptian architecture evolved over time from simple mastabas to stepped pyramids and finally true geometric pyramids. The mastaba was an early above-ground tomb in the shape of a bench with chambers inside. Stepped pyramids, like that built for King Zoser, stacked mastabas on top of each other. Later pharaohs' attempts at true pyramids resulted in structures like the Bent Pyramid. The peak of pyramid construction was reached at Giza with Khufu's Great Pyramid, the largest in size and most precisely constructed.