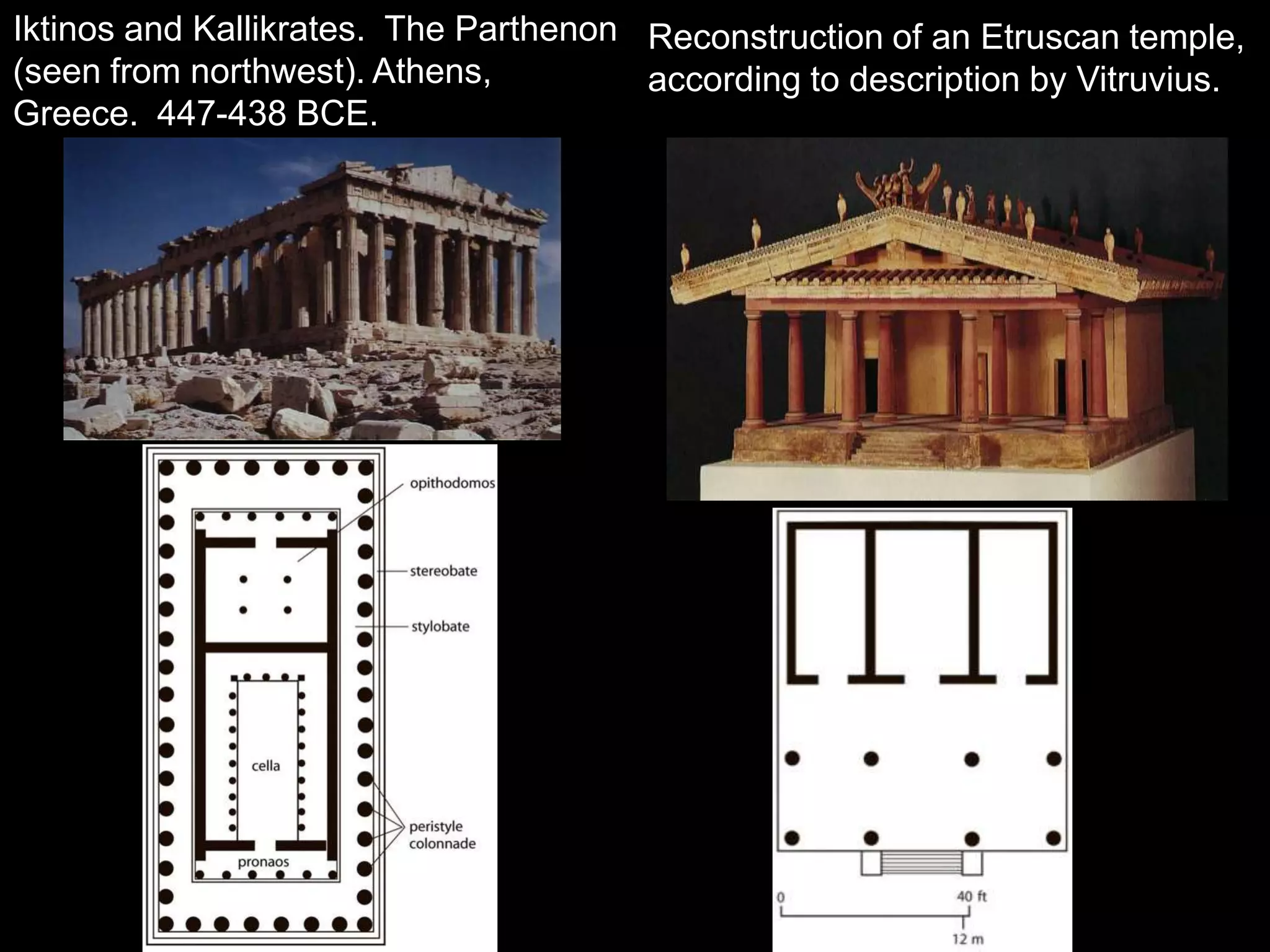
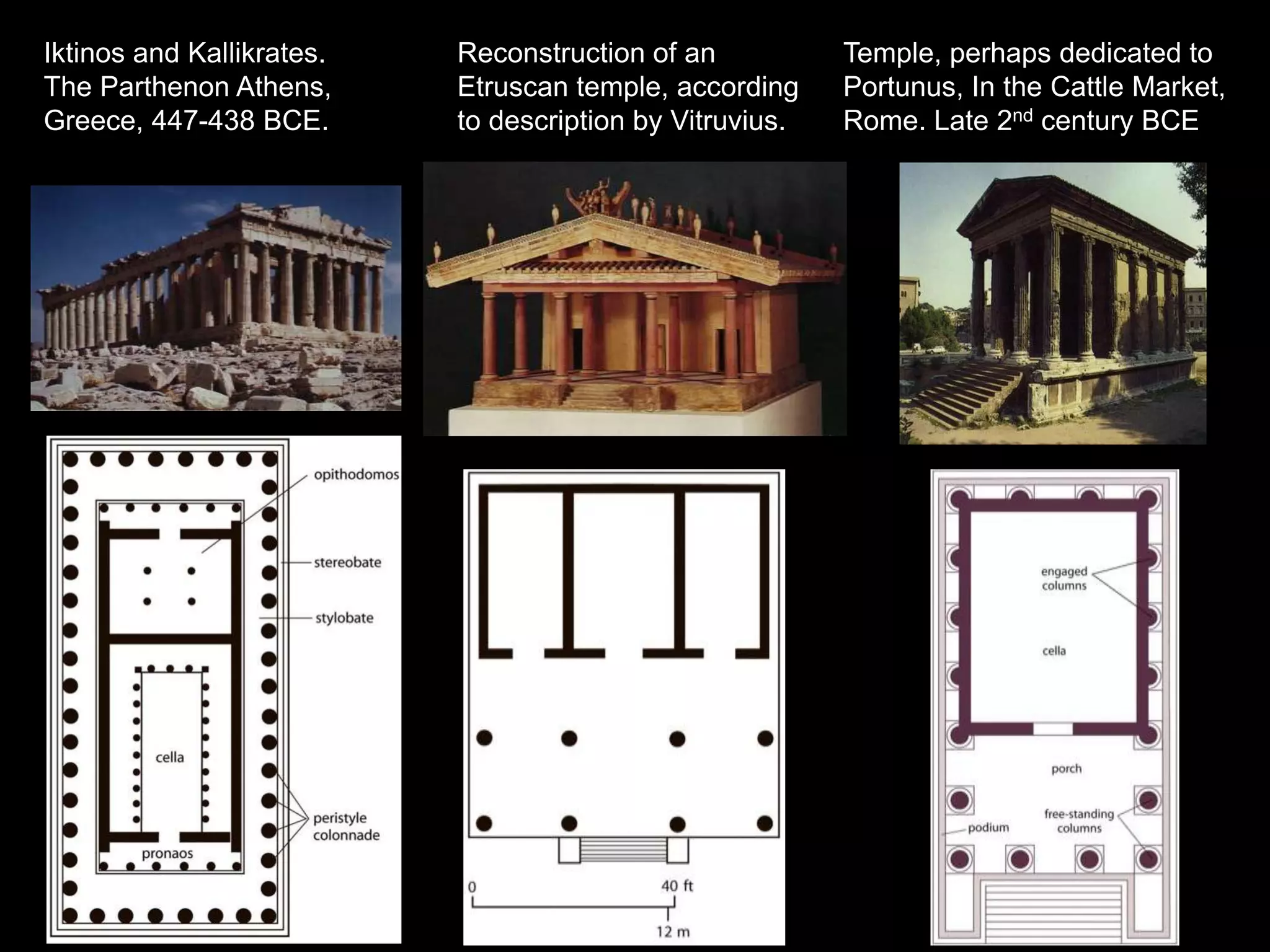
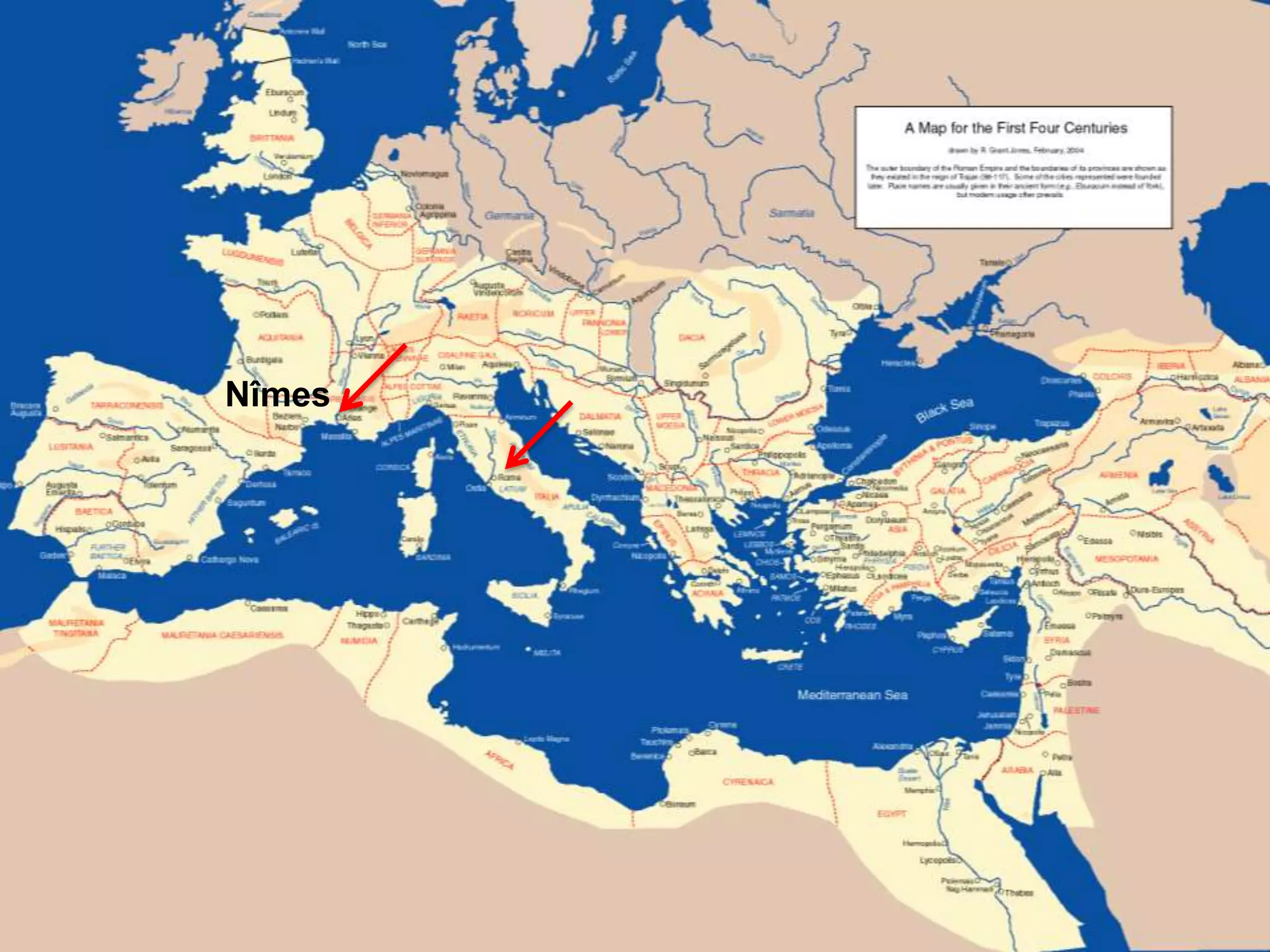
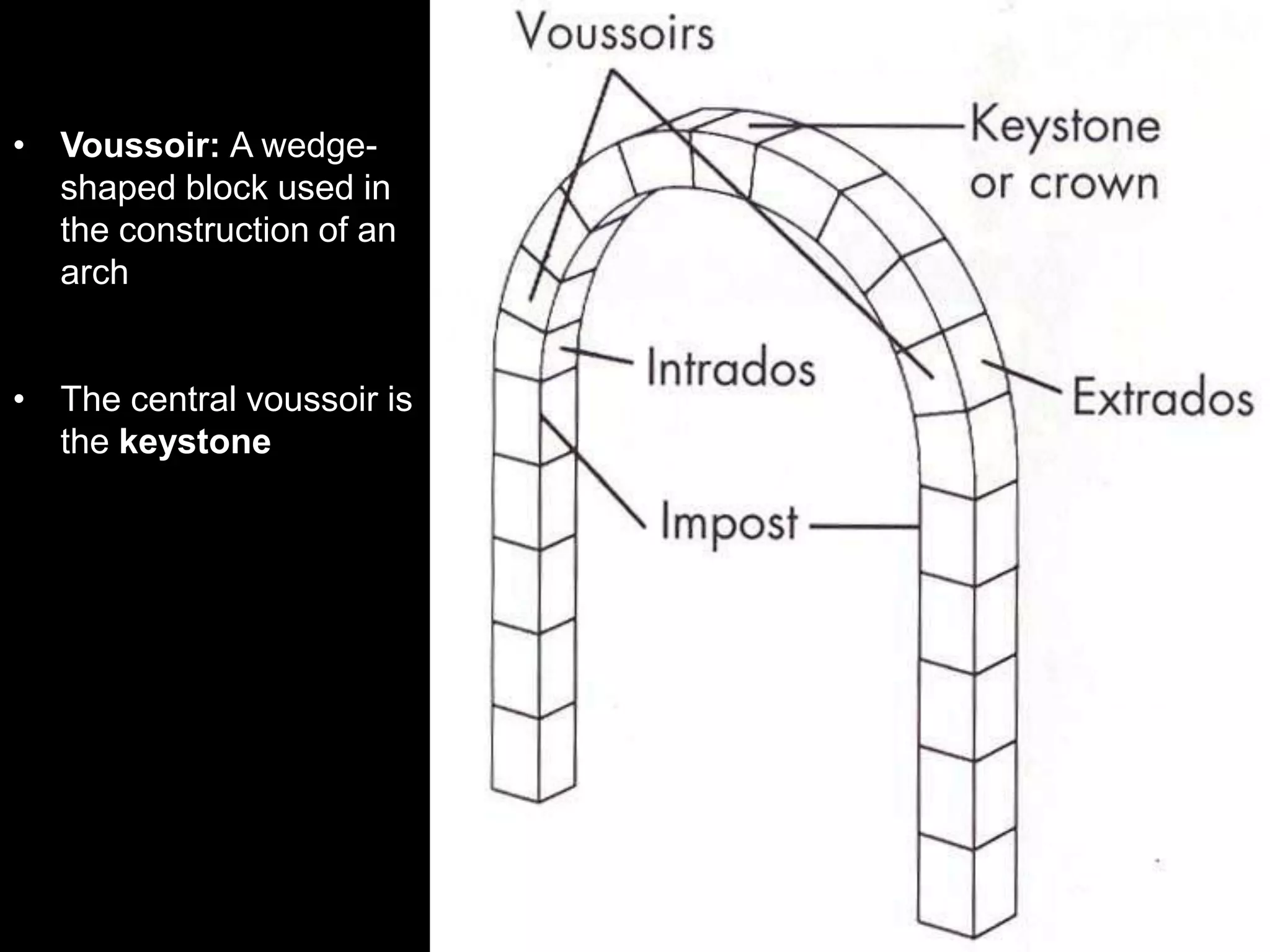
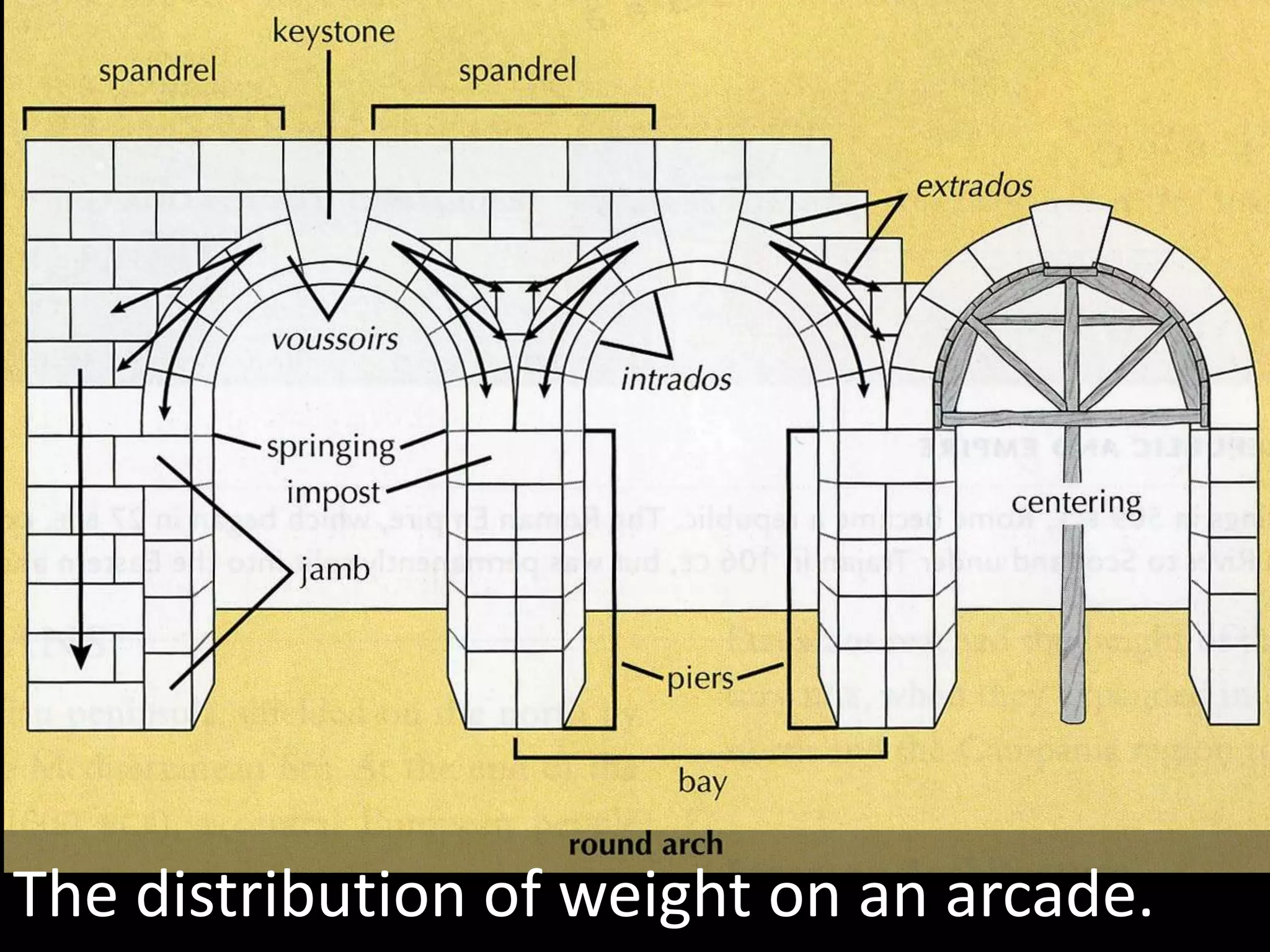
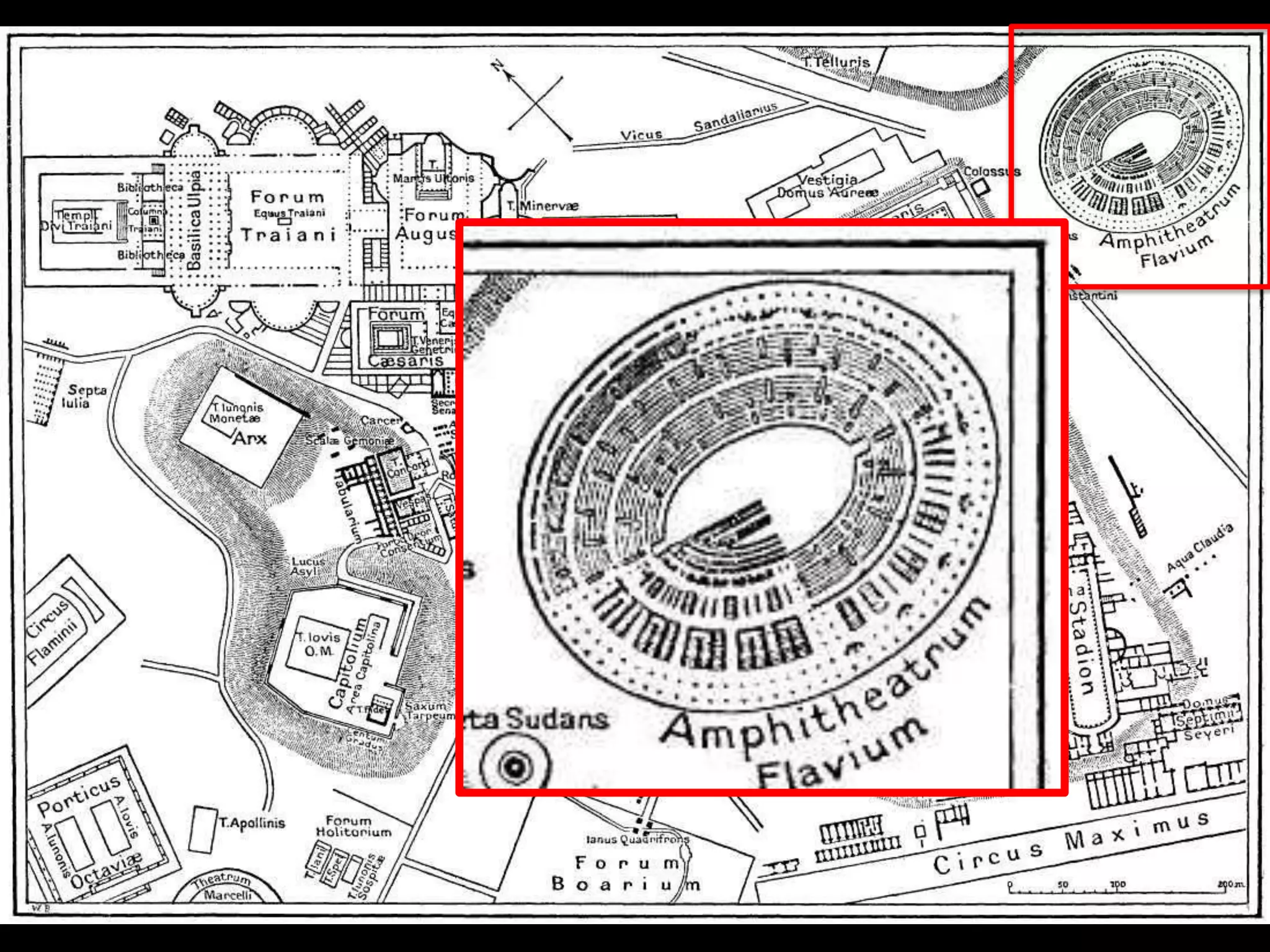
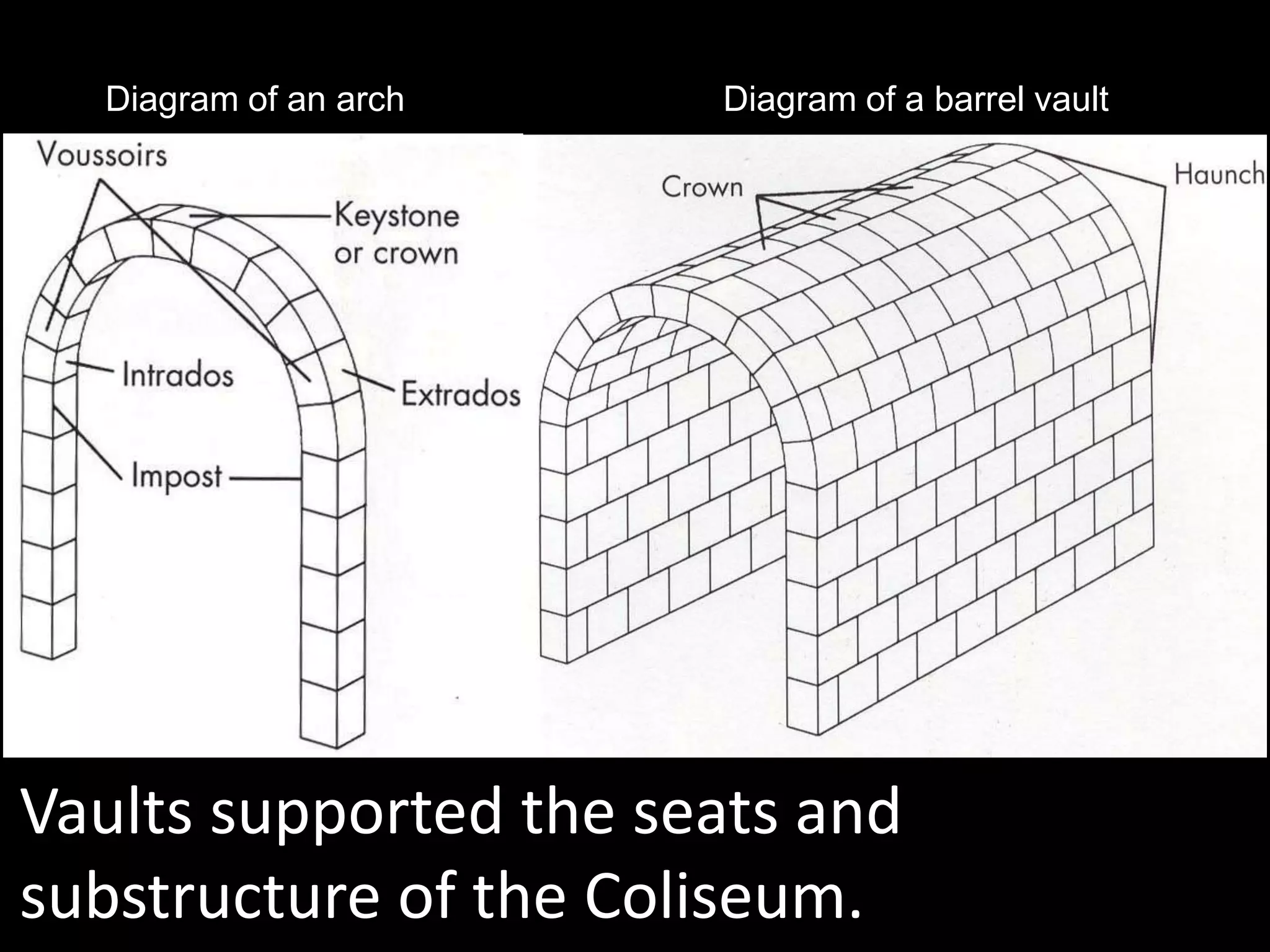
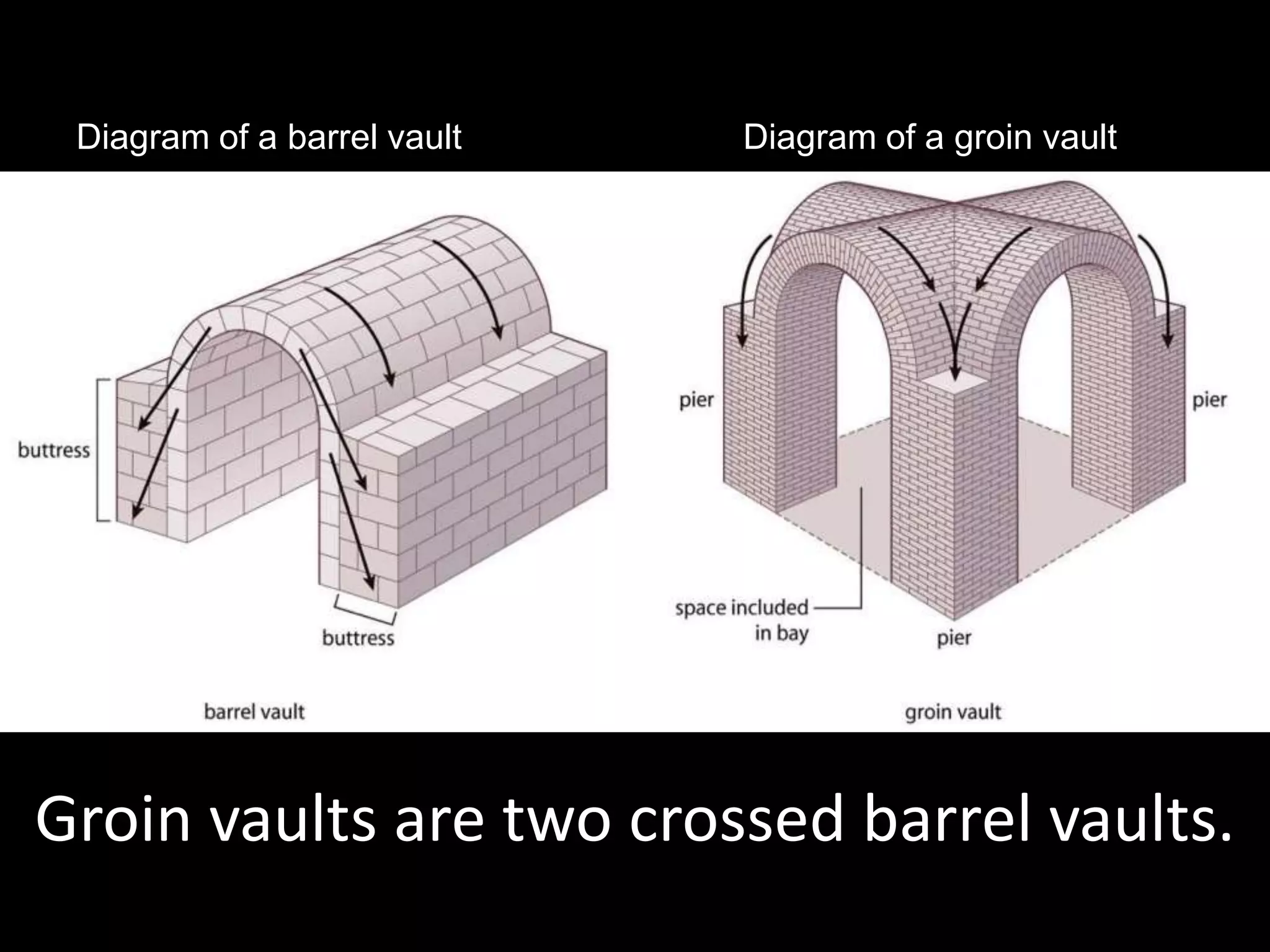
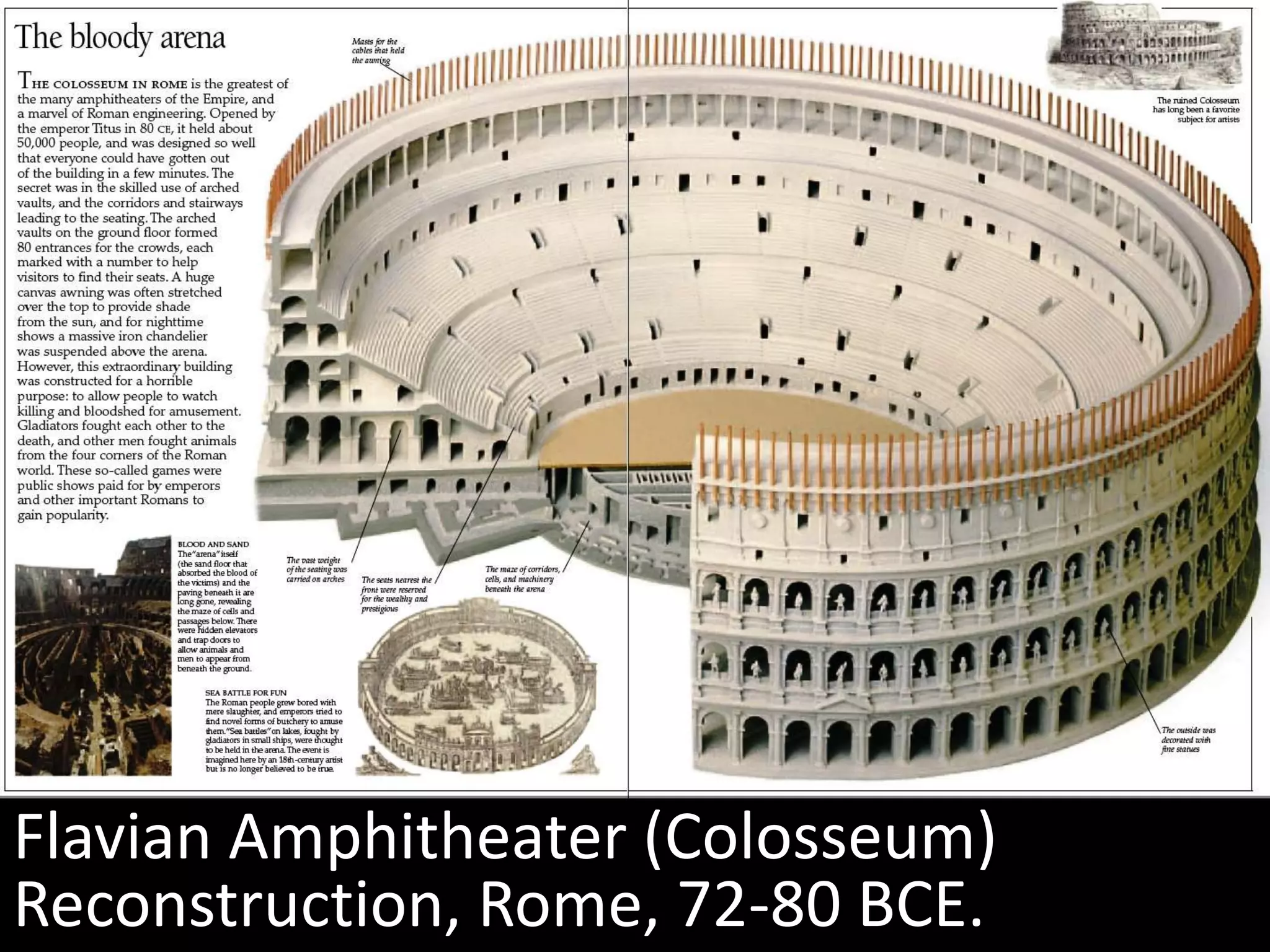
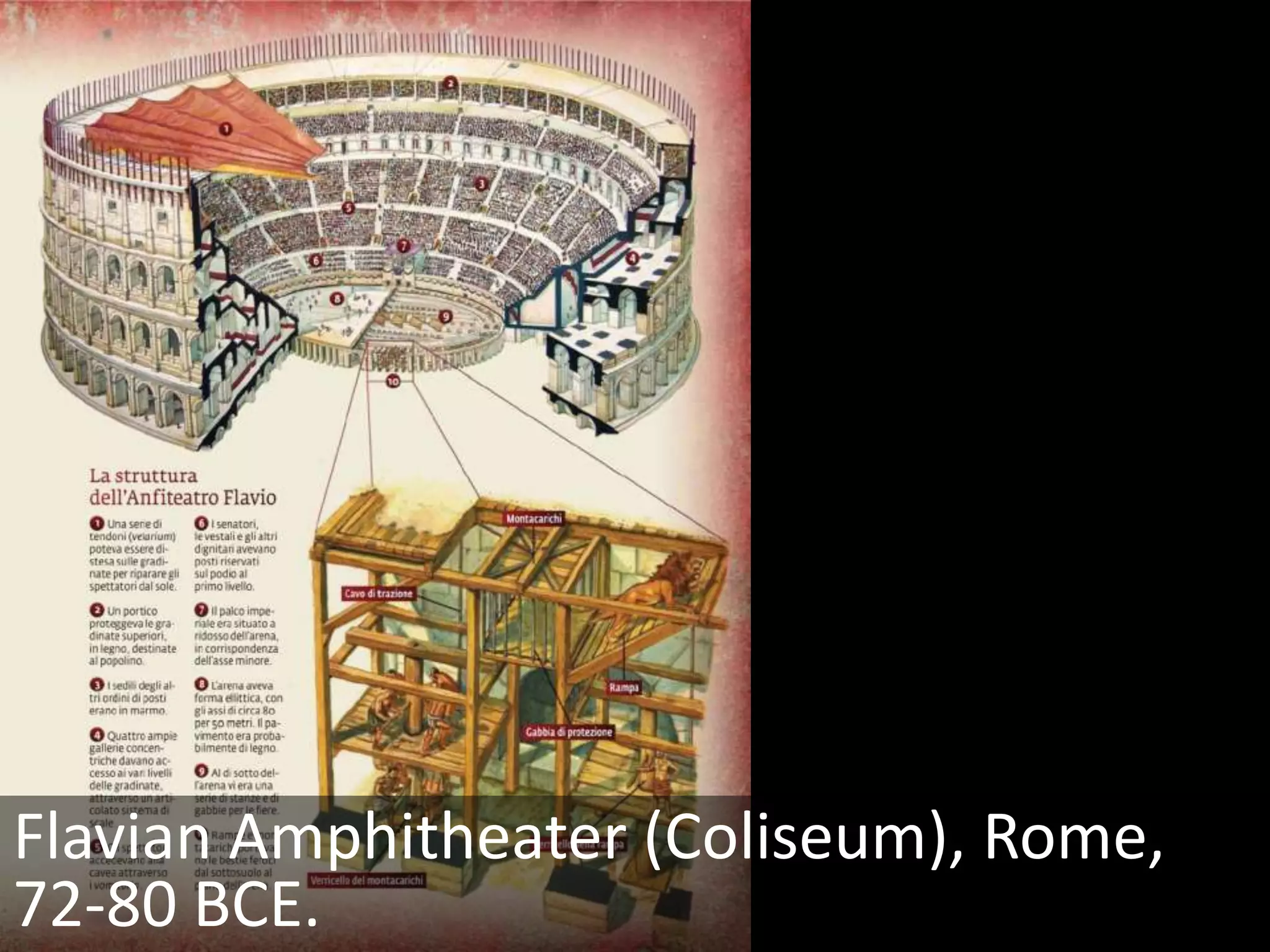
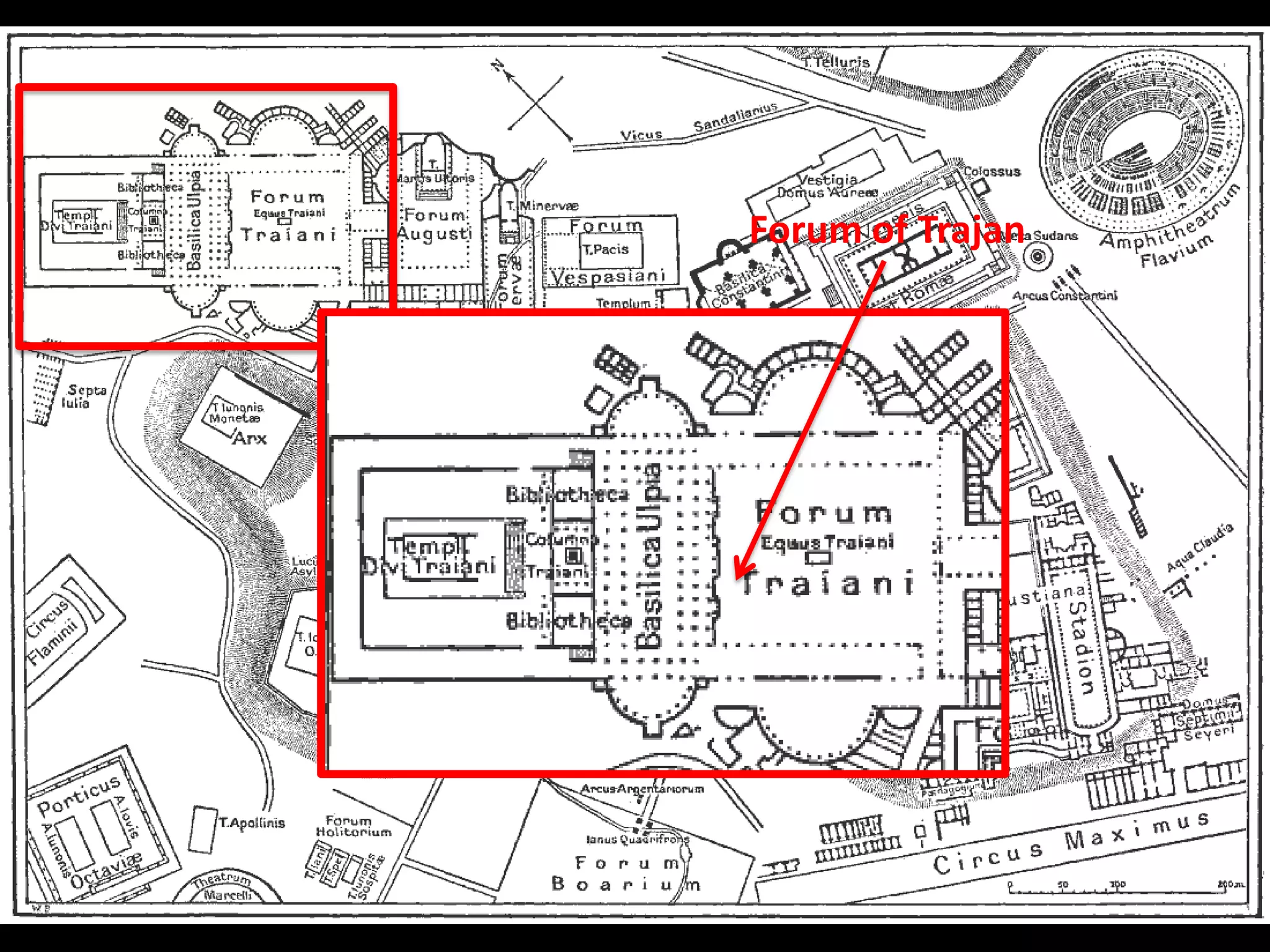
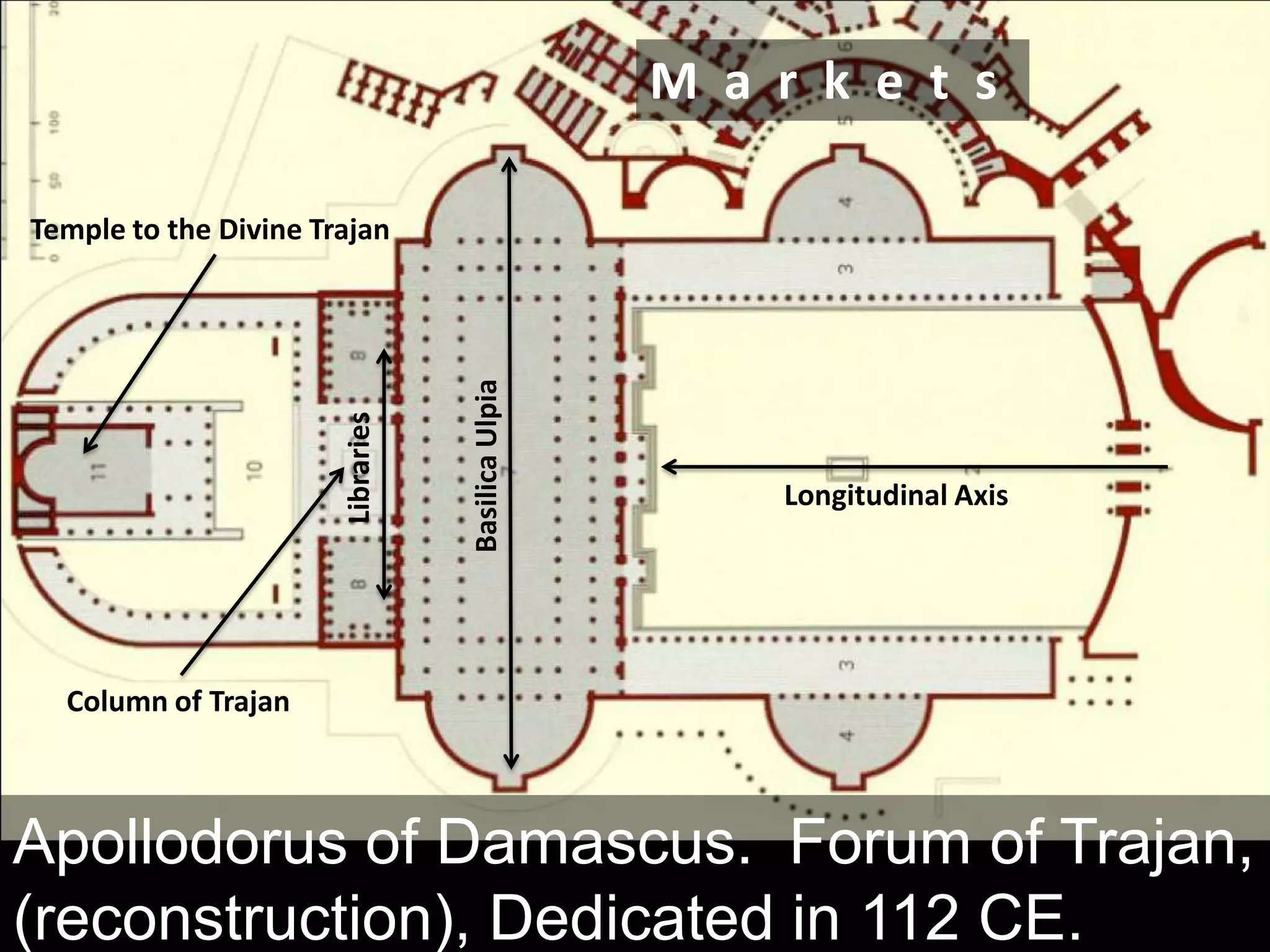
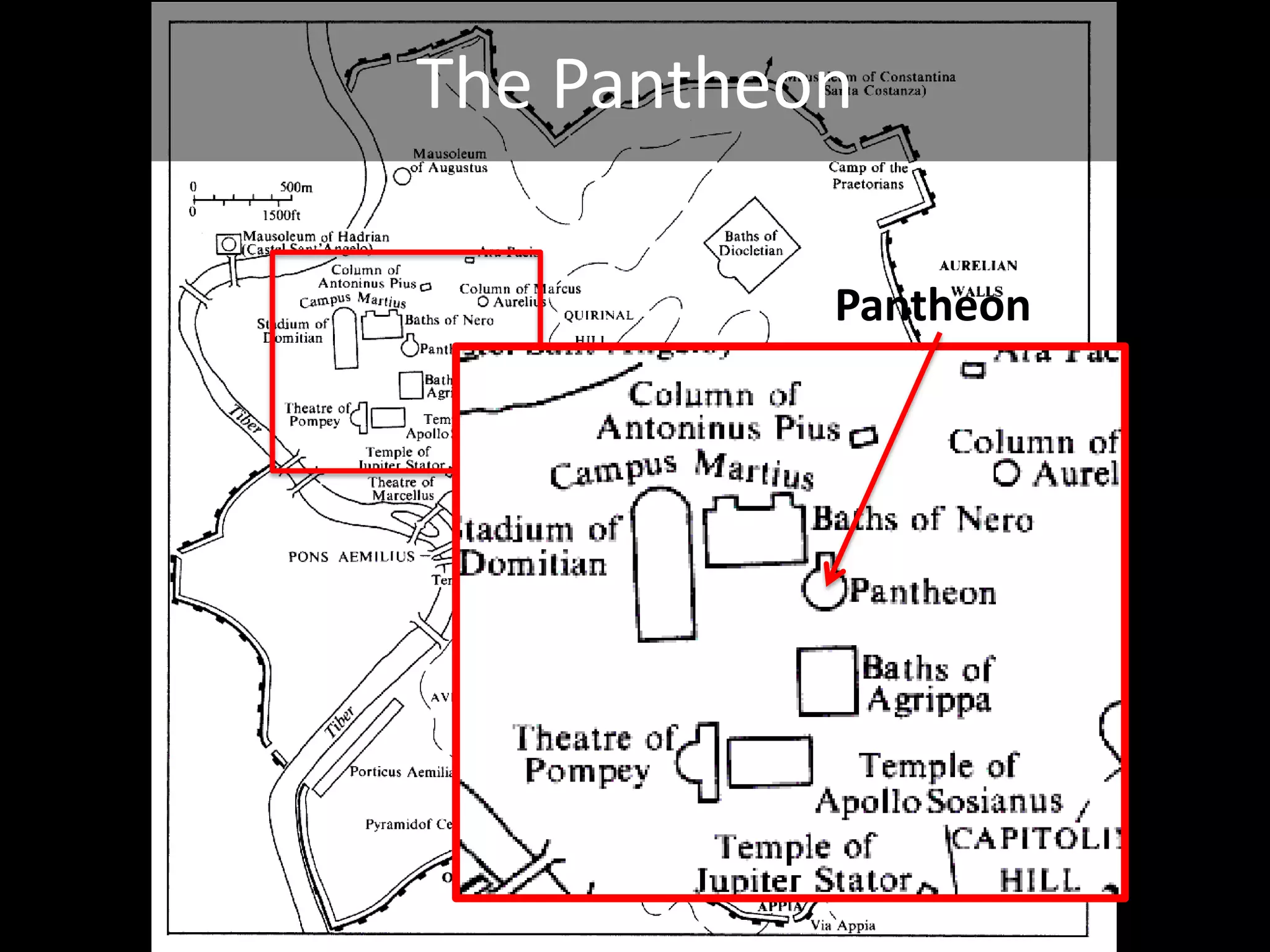
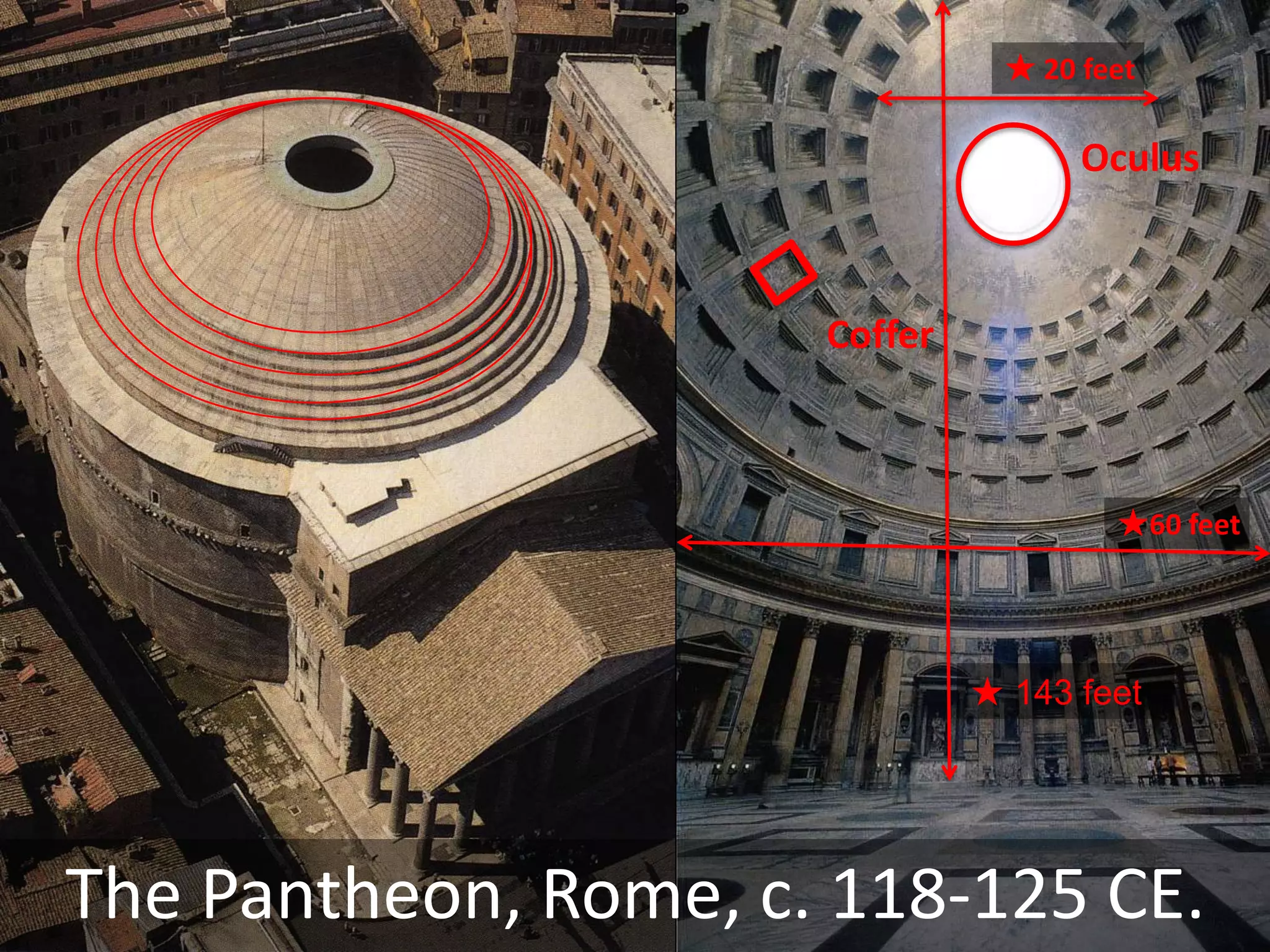
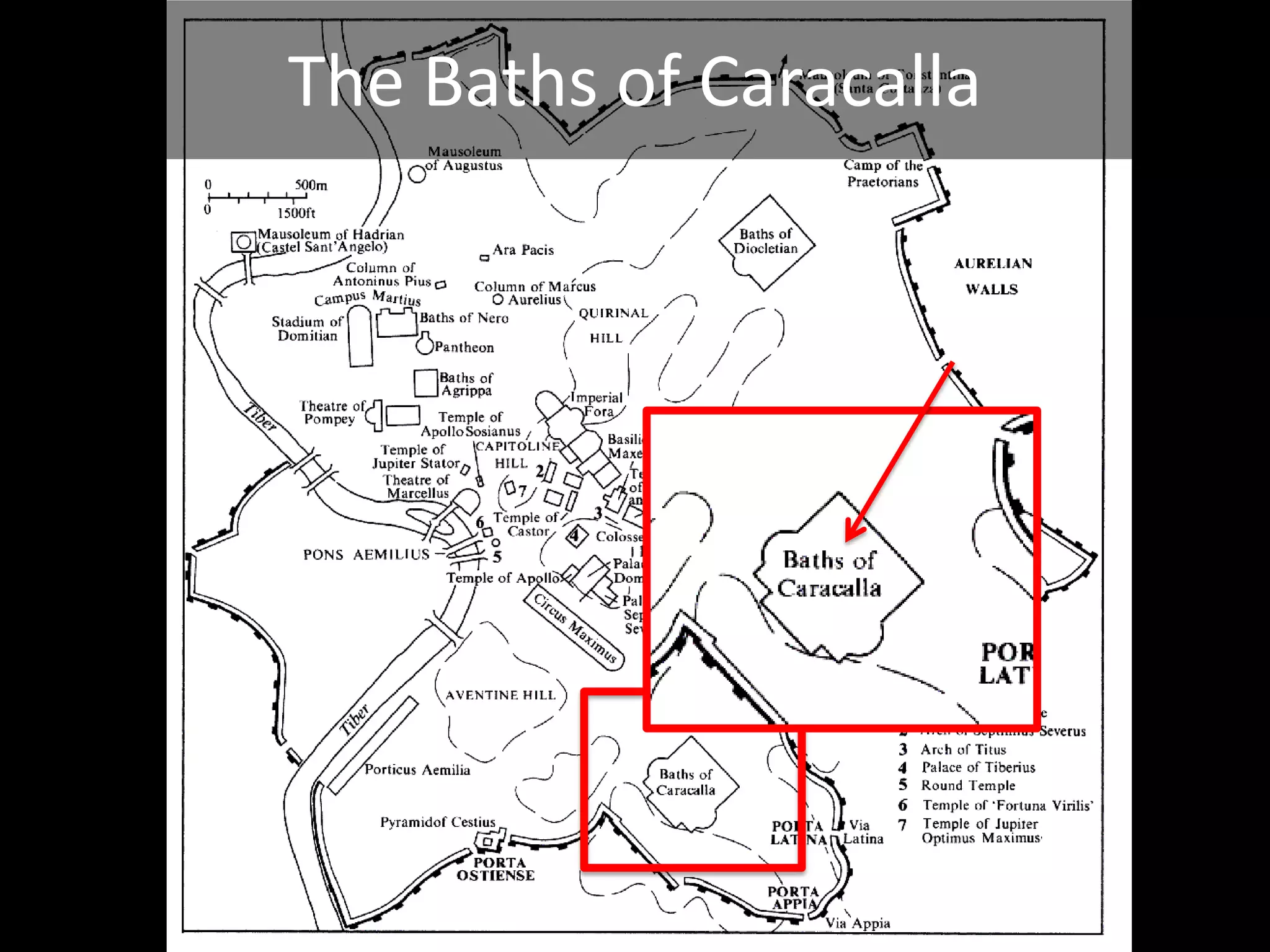
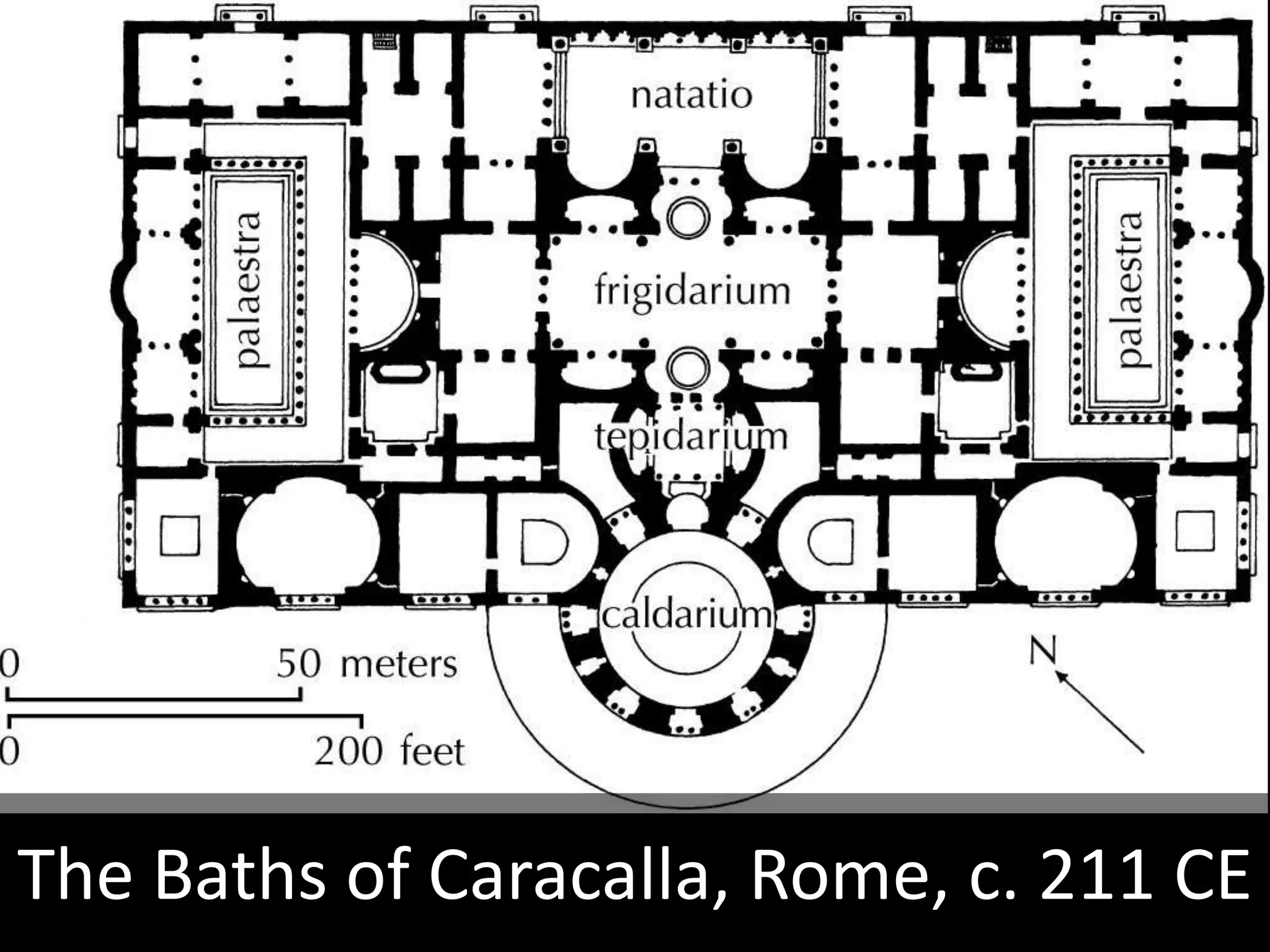
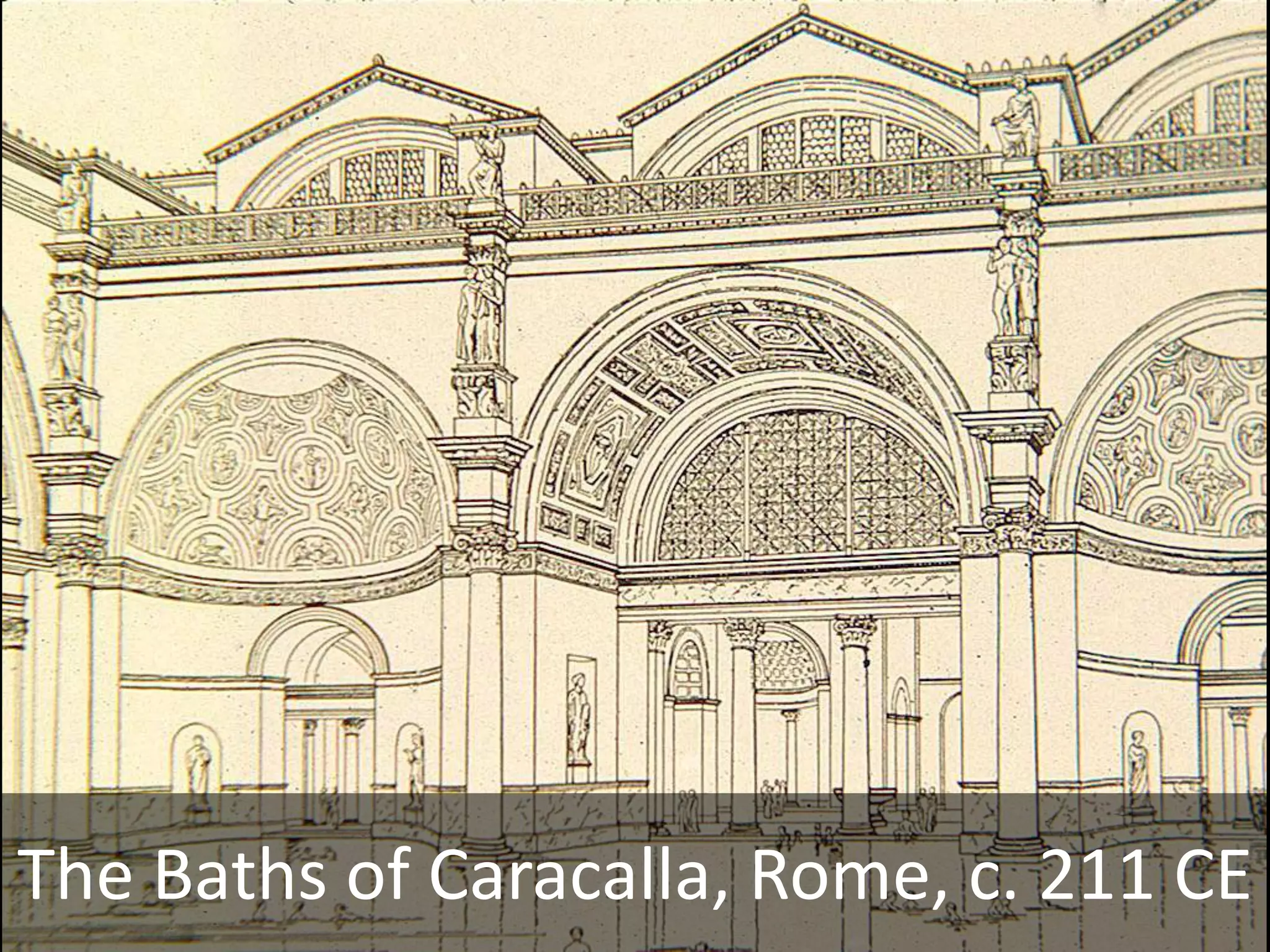
Roman architecture evolved from Etruscan and Greek influences, developing new techniques like the arch, vault and concrete that allowed for larger structures. Some key examples include the Pont du Gard aqueduct, the Colosseum which could seat 50,000, and the Pantheon's monumental dome. Public architecture and facilities like baths and forums reinforced imperial power and provided entertainment for citizens.