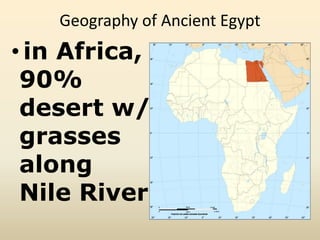
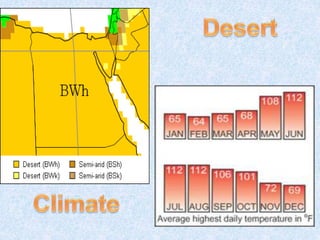
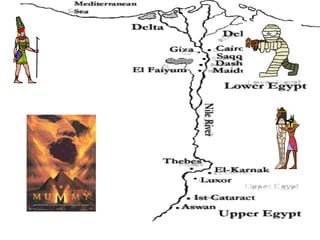
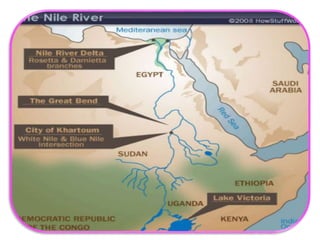
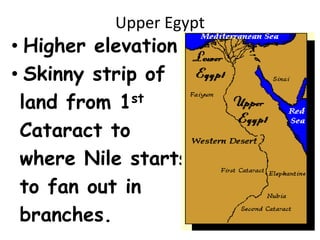
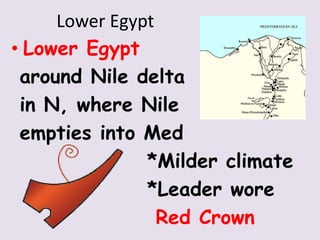
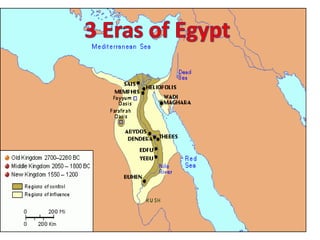
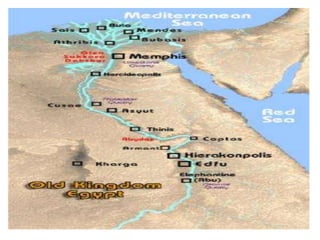
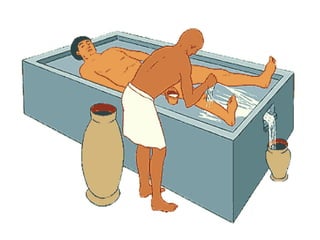
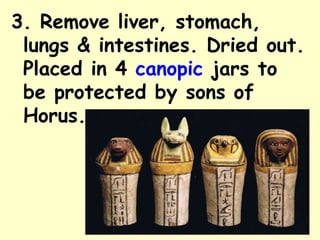
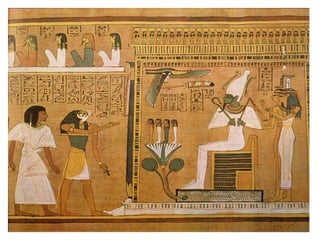
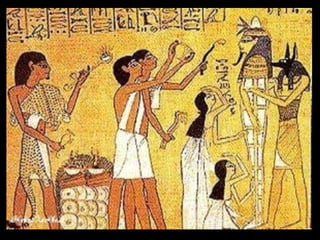
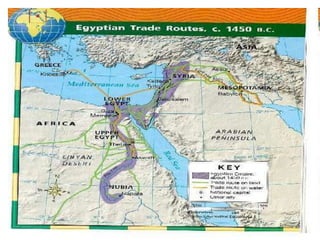
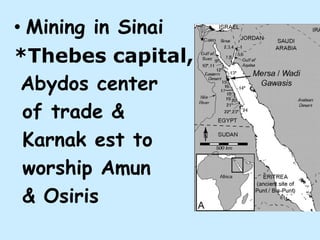
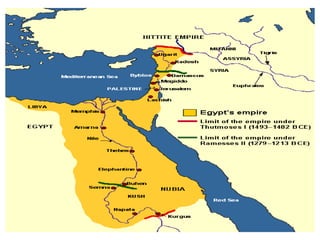
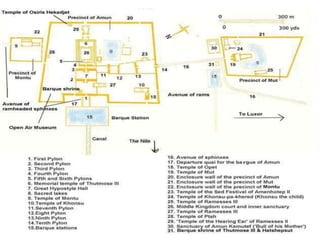
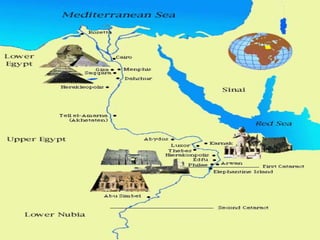
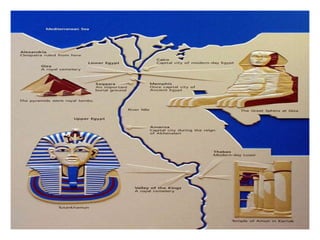
1. Ancient Egypt was centered along the fertile banks of the Nile River, which flooded annually and deposited rich soil. The river was crucial for agriculture, trade, transportation and water.
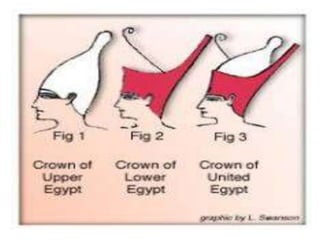
2. Egyptian society was divided into upper and lower kingdoms that were eventually united under King Narmer. Power was centered on the pharaoh, who was seen as both the political and spiritual leader.
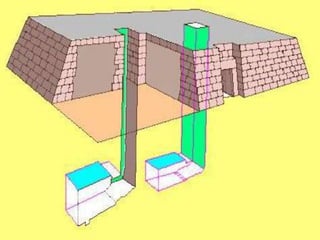
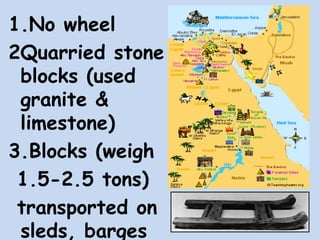
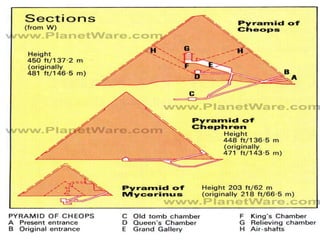
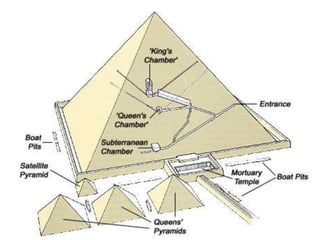
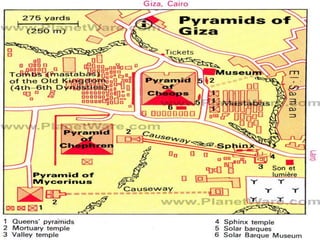
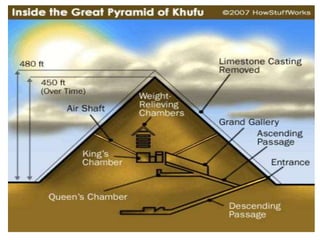
3. The pyramids, such as the massive structures at Giza, were elaborate tombs built to protect the pharaohs and allow their souls to transition to the afterlife. Other important structures included temples and mastabas.