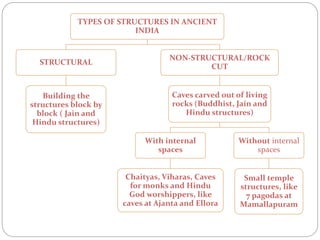
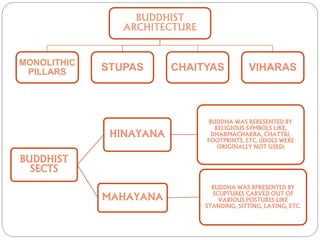
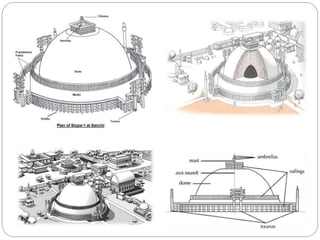
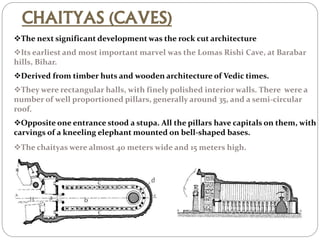
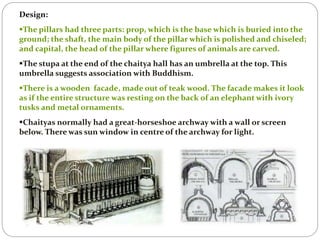
Buddhist architecture in ancient India included structures like stupas, chaityas, viharas, and stambhas. Stupas housed sacred Buddhist relics and had a rounded dome-like shape. Chaityas were prayer halls with a stupa at one end and were made in rock-cut caves. Viharas were monasteries that provided living quarters for monks. Stambhas were tall, polished stone pillars sometimes topped with sculptures. These structures developed under emperors like Ashoka who built many early Buddhist monuments to spread the religion across India.