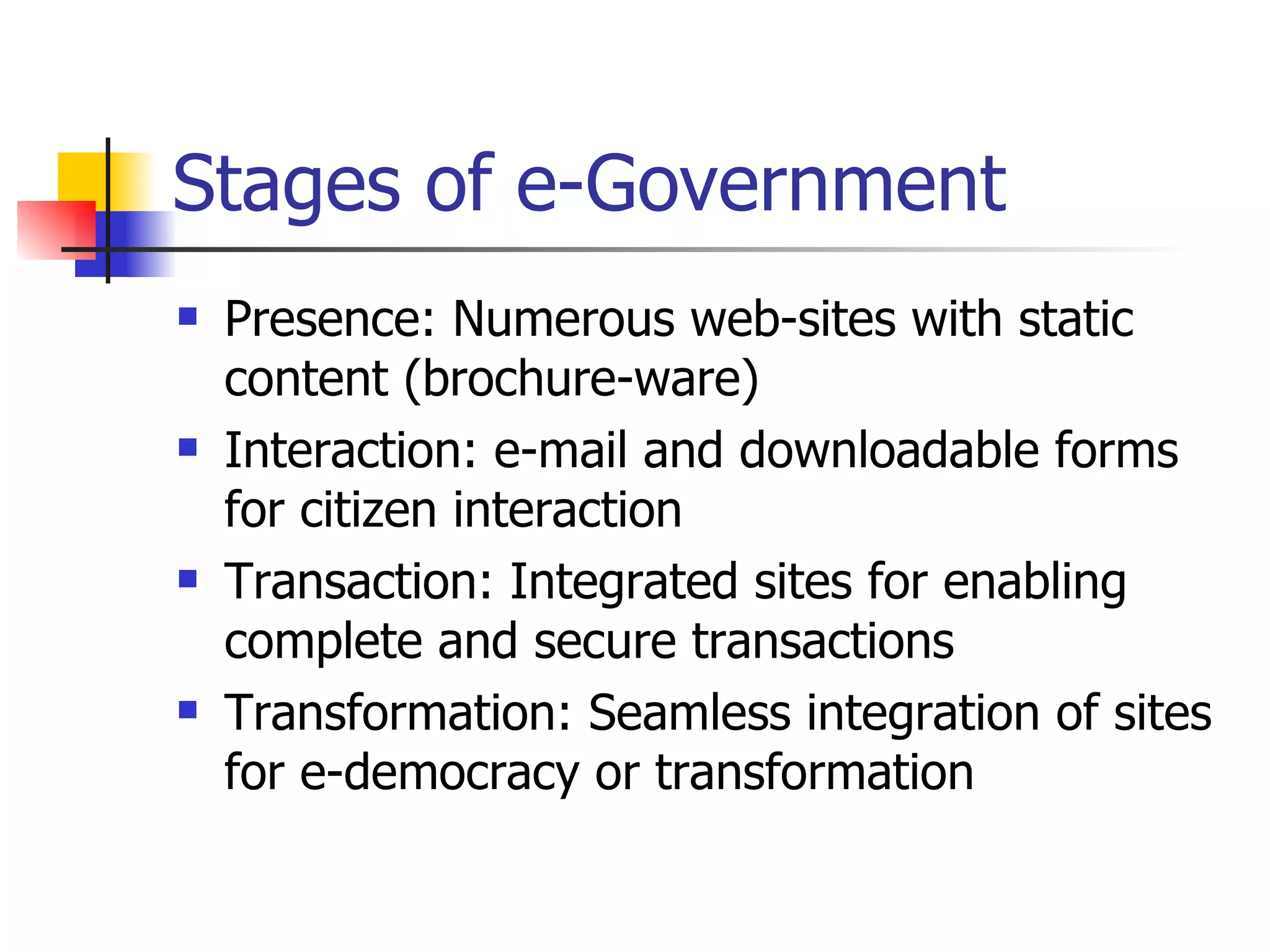
The document discusses e-governance in India with a focus on using it to improve the education sector. It outlines the goals of e-governance like improving transparency and services. When applied to education, e-governance can help increase accessibility, scalability, and quality of education while reducing costs. Key challenges include reaching remote areas, maintaining quality at scale, and making education relevant in the emerging knowledge economy.



































































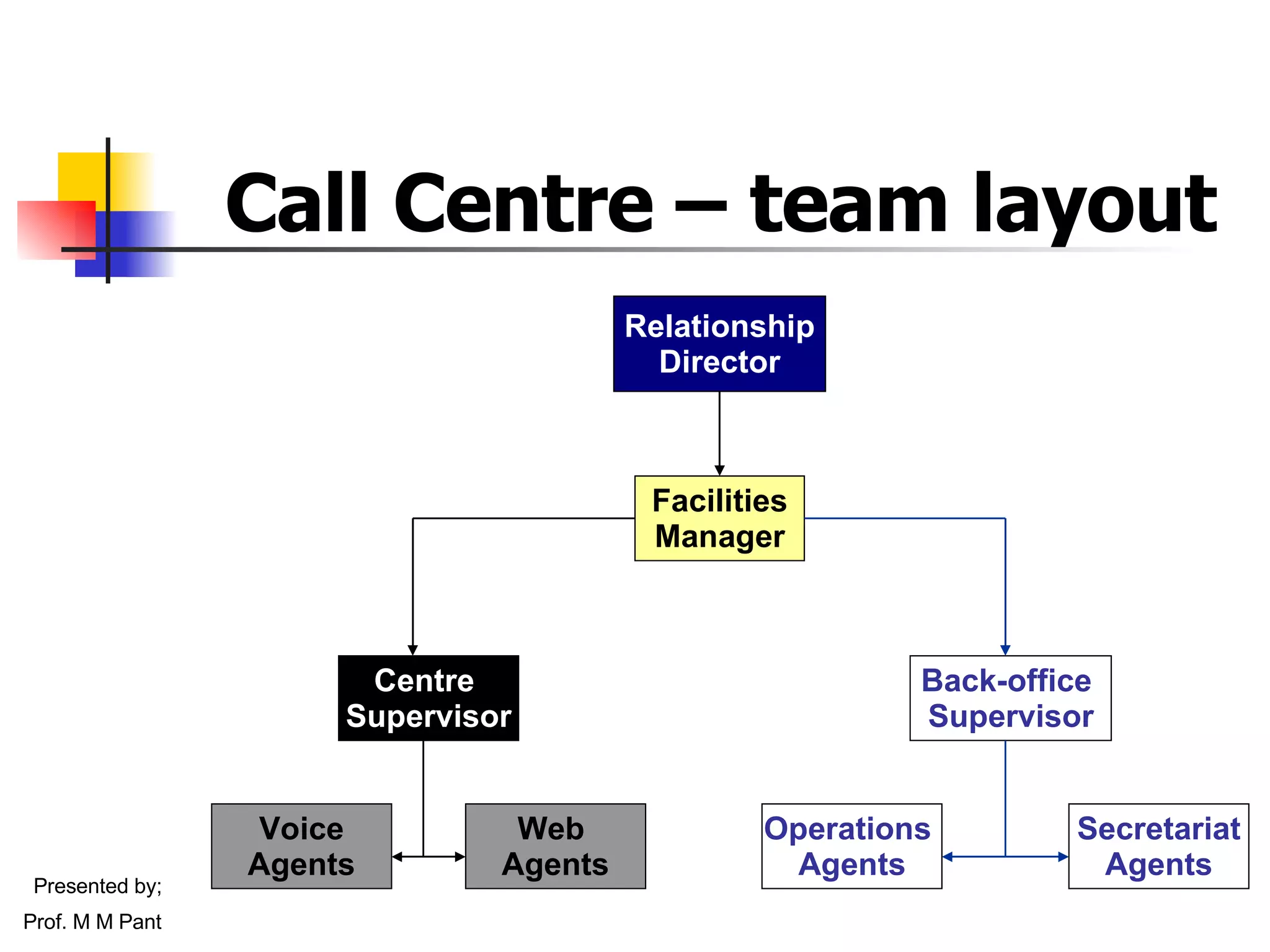



![The biggest brand …. ever This single point of confluence would have a huge brand recognition A single all-India number 16008648 A single web portal www.indianedu.ac.in Faculty e-mail id’s such as [email_address] Student life-long id’s (to continue as alumni) [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/egovernance-focus-on-education-1217791380283999-9/75/e-governance-in-context-of-education-73-2048.jpg)
![[email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/egovernance-focus-on-education-1217791380283999-9/75/e-governance-in-context-of-education-74-2048.jpg)