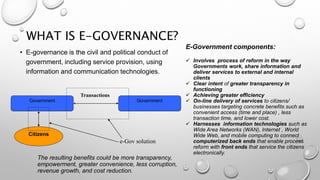
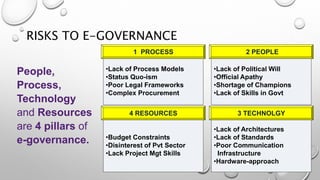
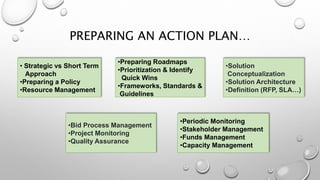
This document identifies risks and proposes an action plan for e-governance in India. It defines e-governance as using information technologies to improve government services and transactions between government, citizens, and businesses. The main risks are related to people, processes, technology, and resources. An action plan should include strategic approaches, policy preparation, roadmaps, prioritization, frameworks, resource management, and stakeholder engagement. The private sector and international organizations can help manage risks by providing advice, funding, and expertise to conceptualize solutions and implement e-governance projects successfully.