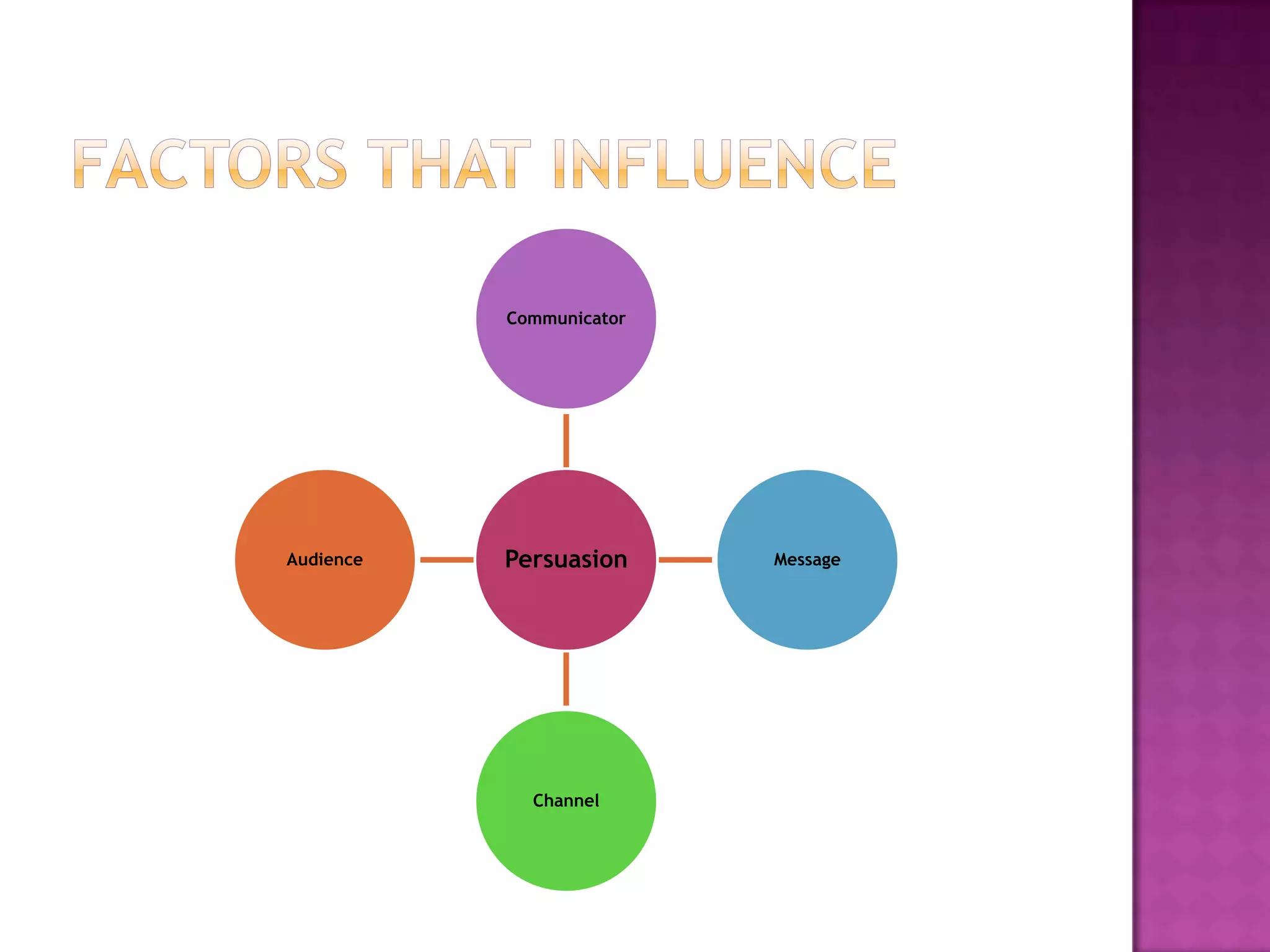
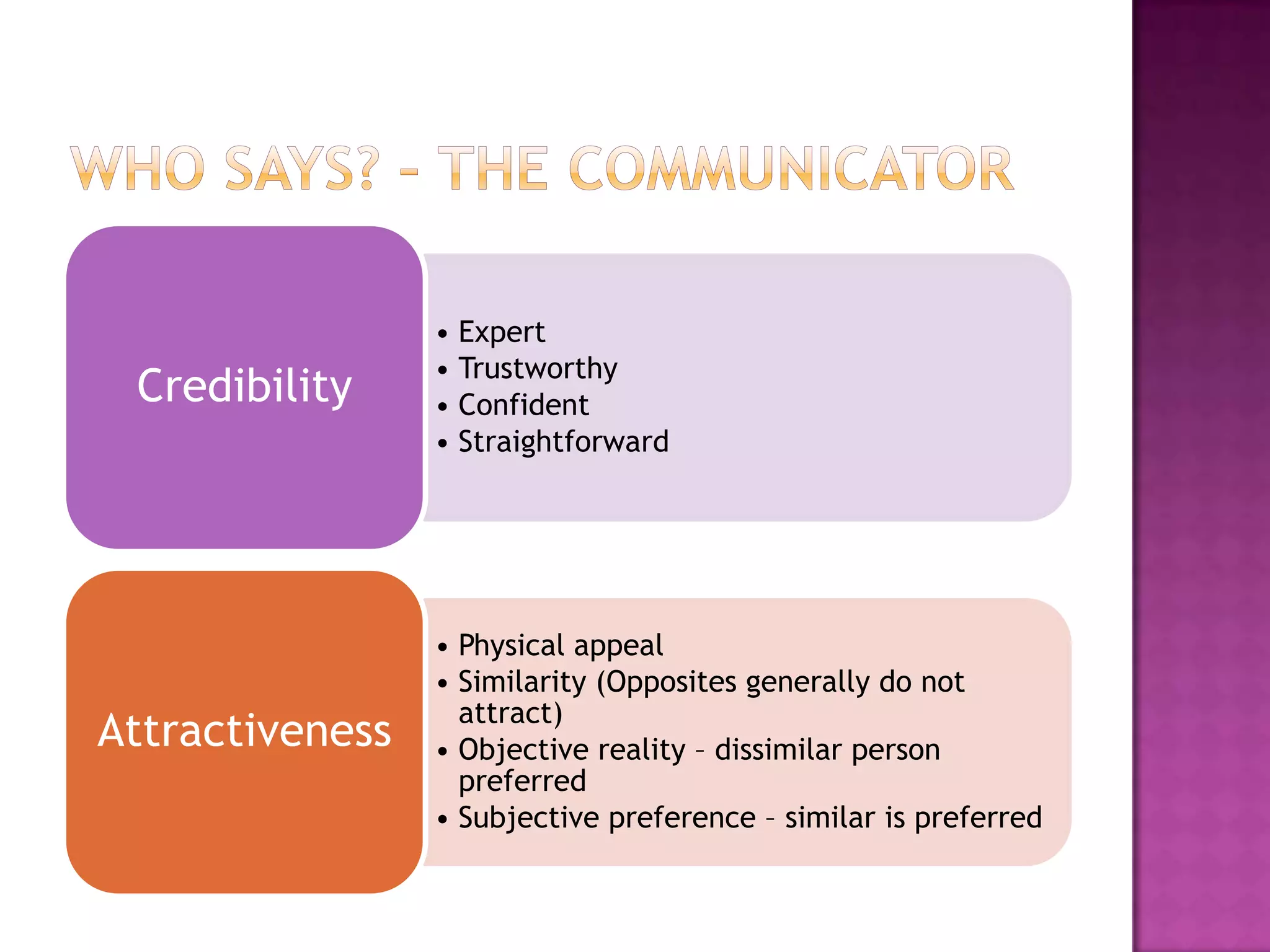
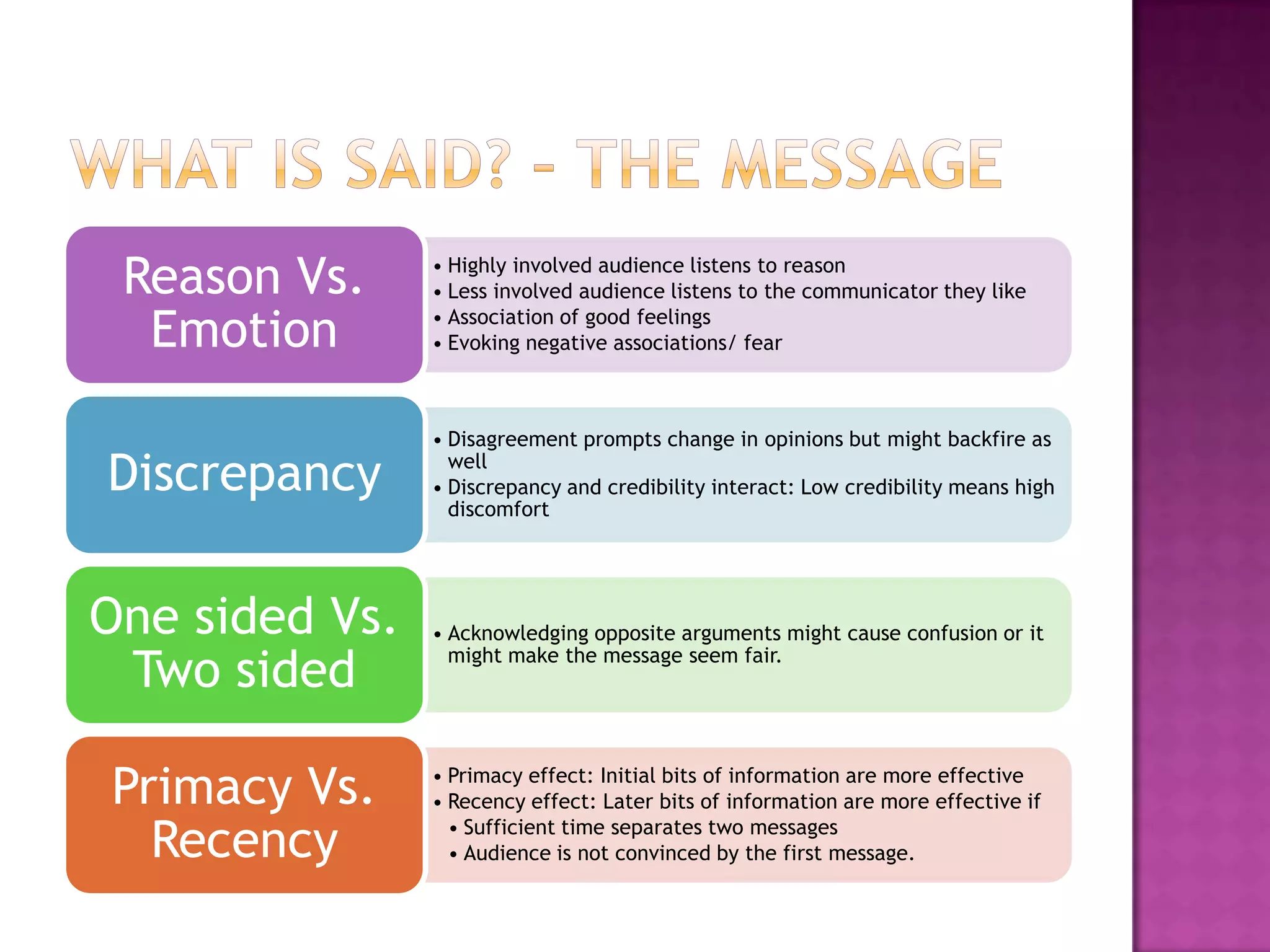
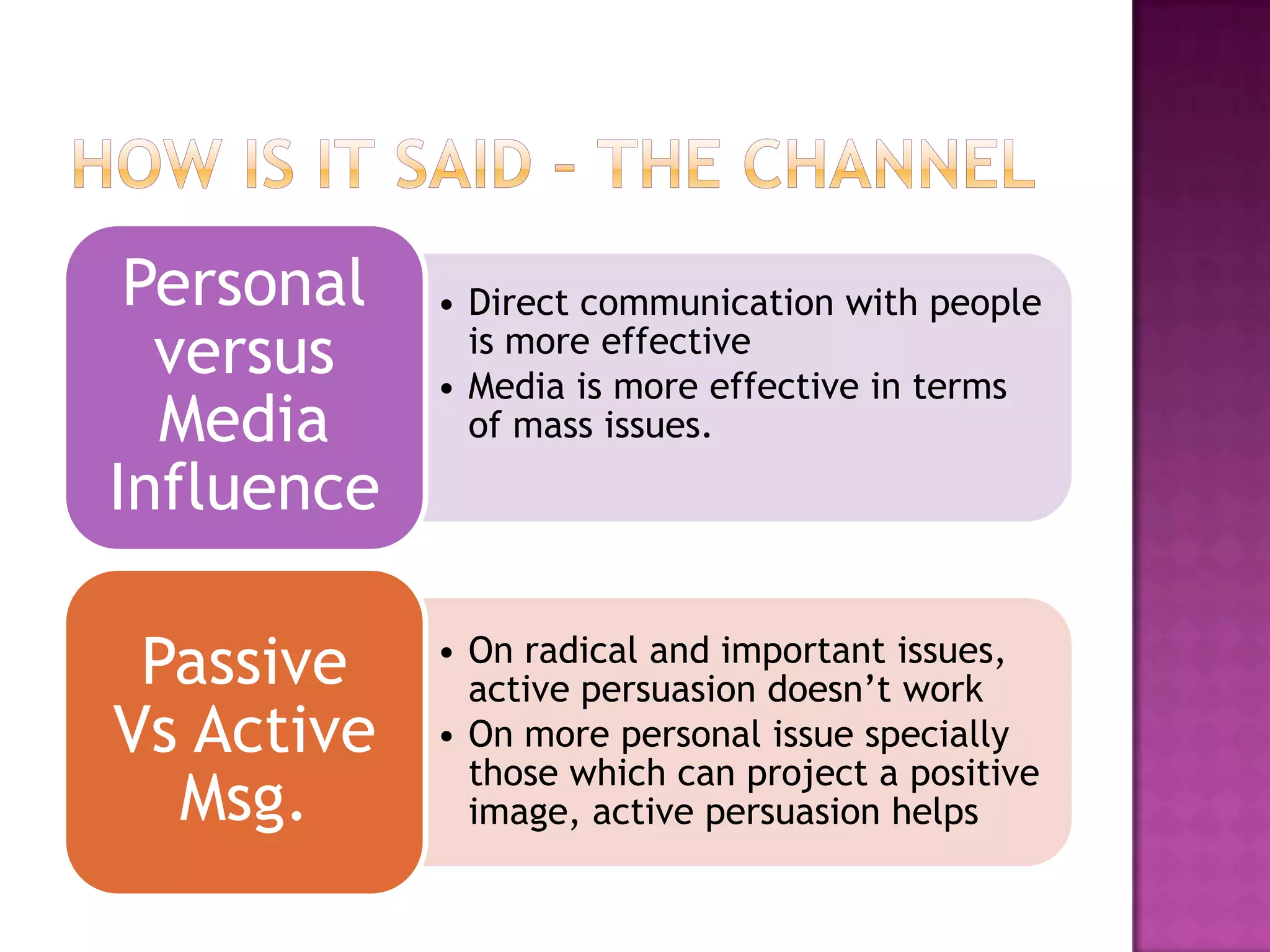
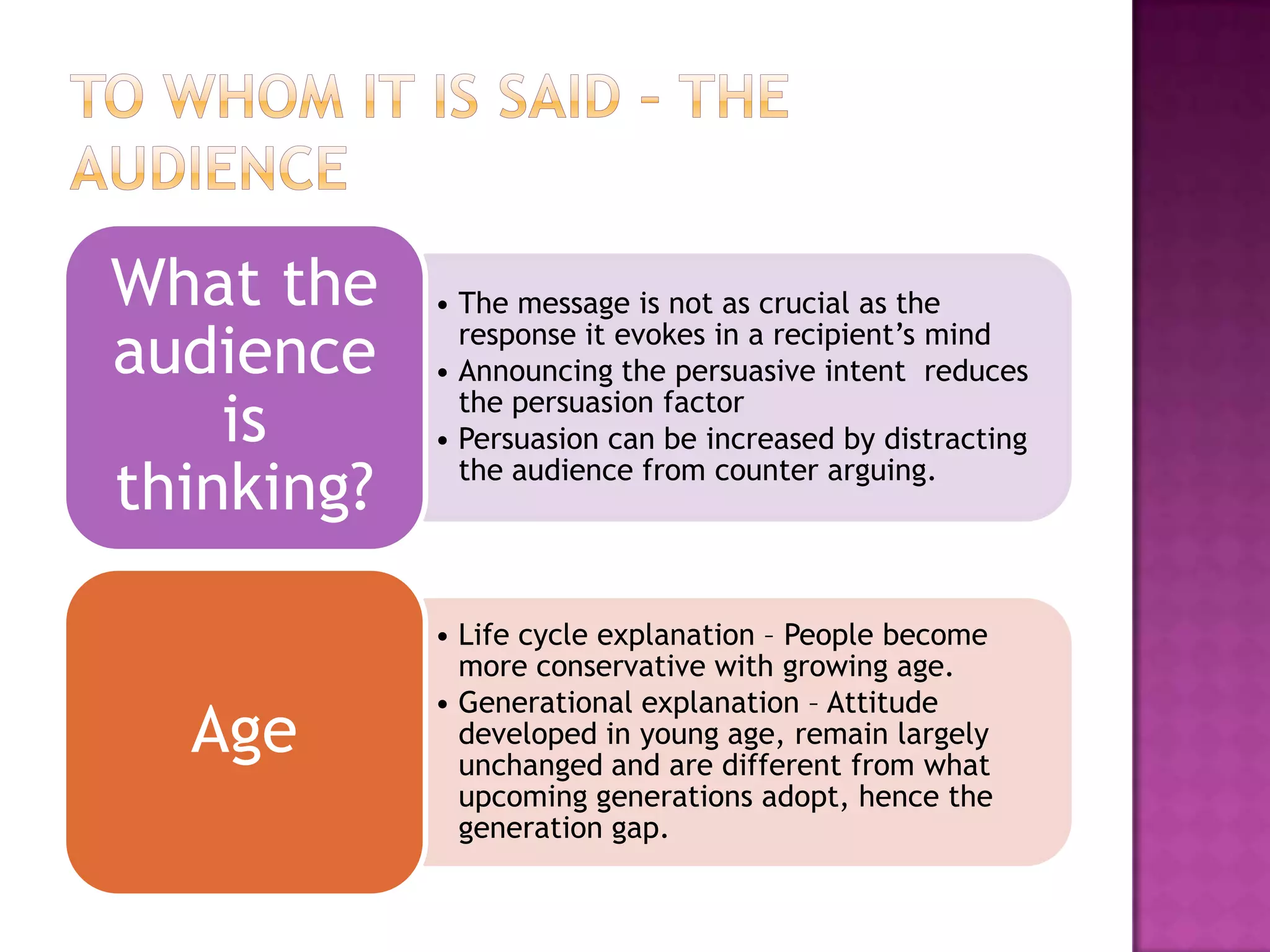
Effective persuasion requires establishing credibility with the audience, making the message attractive, and addressing the audience's reasoning and emotions. Different techniques work better depending on factors like the audience's level of involvement, their existing views, and whether the message is presented actively or passively. The most important aspect of persuasion may be what thoughts and feelings the message evokes in the recipient's mind rather than just the content of the message itself.