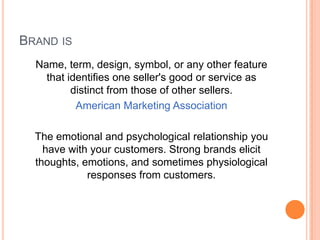
The document discusses various aspects of branding, including what a brand is, what brands do, and different types of brands. A brand represents the complete experience a customer has with a company, product, or service and is meant to create recognition, loyalty and differentiate a company from its competitors. The document also outlines different types of branding like corporate, employer, cause, co-branding, and community branding. Overall, the purpose of branding is to build emotional connections with customers and simplify their purchasing decisions.