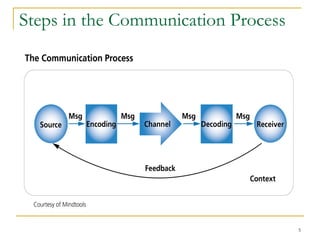
This document discusses effective communication skills for leadership. It outlines the communication process, including understanding communication, transmission of messages between a sender and receiver, and potential barriers. It also describes different types of formal and informal communication in organizations. Finally, it provides tips for improving communication, such as developing listening skills, encouraging two-way communication, and being aware of different perspectives.