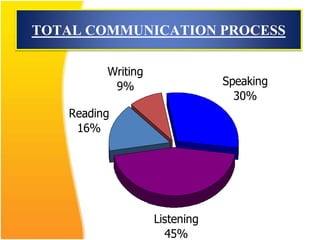
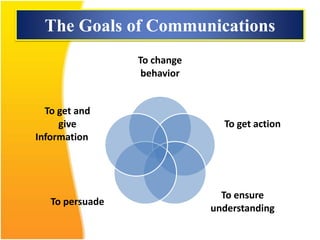
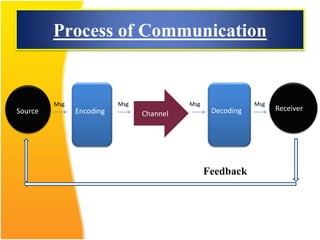
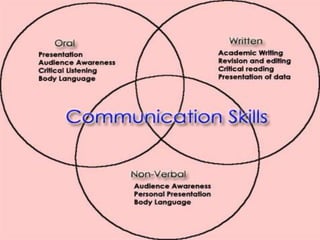
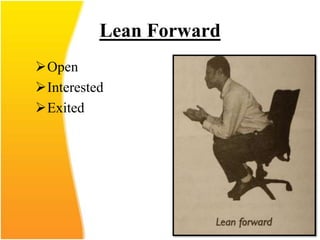
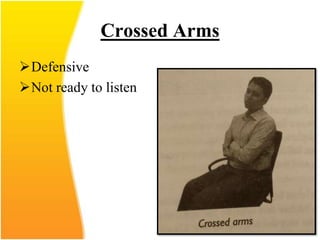
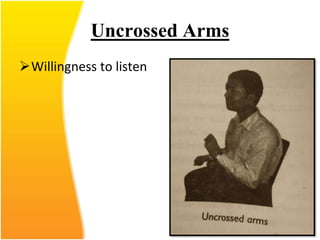
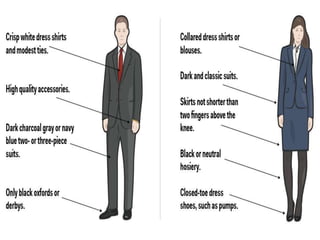
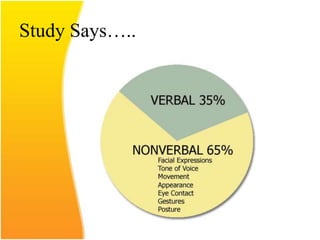
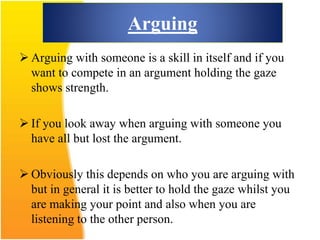
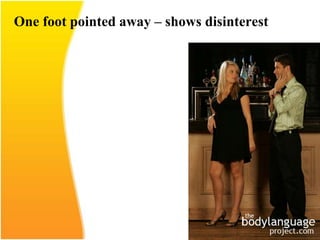
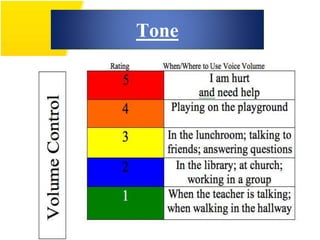
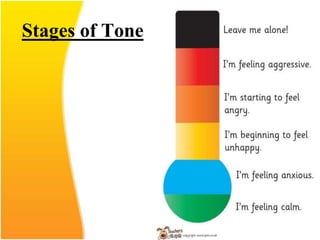
This document discusses the importance of effective communication skills, emphasizing the significant role of listening, body language, and non-verbal cues. It outlines various techniques to improve communication, including active listening, maintaining appropriate eye contact, and understanding different handshakes. Additionally, it highlights how posture, gestures, and proximity affect the perception and outcomes of interactions.