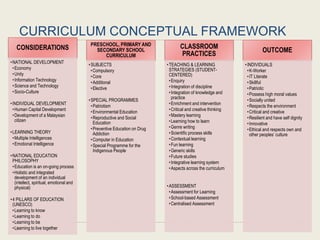
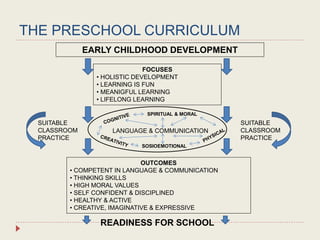
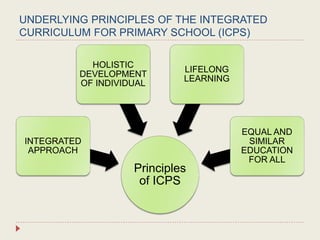
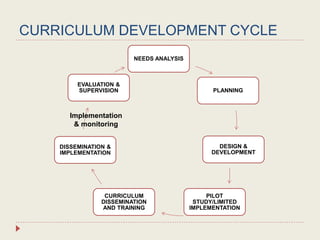
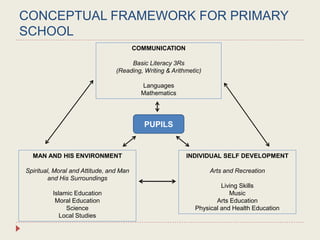
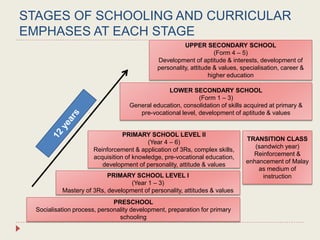
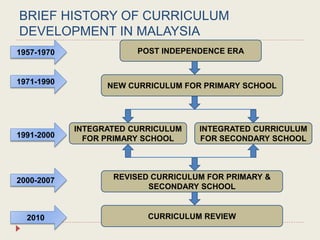
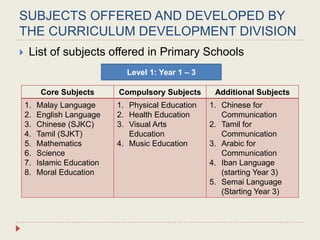
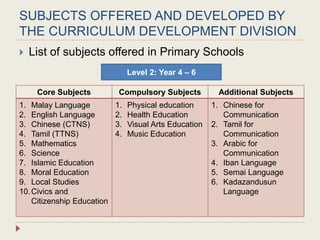
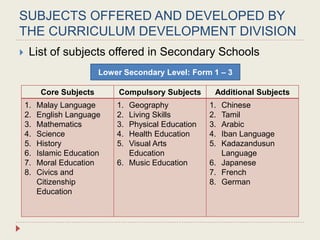
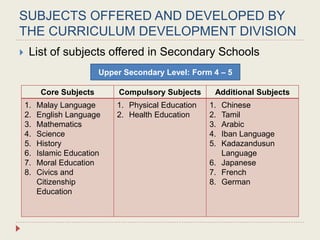
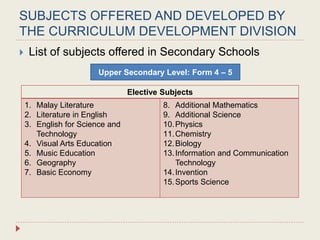
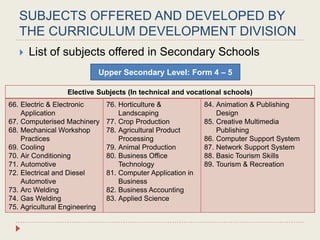
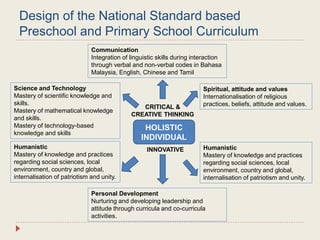
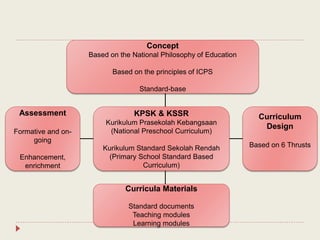
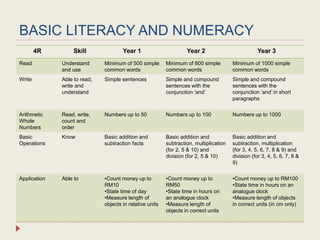
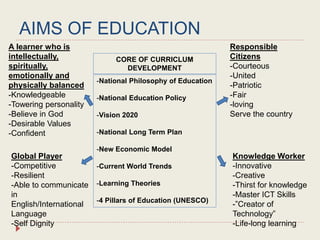
The Curriculum Development Division (CDD) develops curriculum for Malaysian schools from preschool through secondary level. It oversees curriculum design, implementation, support materials, and research. The CDD aims to develop students holistically based on Malaysia's National Education Philosophy through subjects like Malay, English, Math, Science, and moral education. It follows a curriculum cycle of needs analysis, planning, design, pilot testing, dissemination, implementation and evaluation. The CDD has revised the curriculum over time and now offers a range of core, elective and additional subjects at each school level.







![THE NATIONAL CURICULUM IN THE 1996
EDUCATION ACT
“... an educational programme that includes
curriculum and co-curricular activities which
encompasses all the knowledge, skills, norms,
values, cultural elements and beliefs to help
develop a pupil fully with respect to the physical,
spiritual, mental and emotional desirable moral
values and to transmit knowledge”
Educational Act 1996
[Education (national Curriculum) Regulation 1997]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/curriculumdevelopmentdivisionmoe-150629093715-lva1-app6892/85/Curriculum-development-division-moe-pdf-5-9-320.jpg)