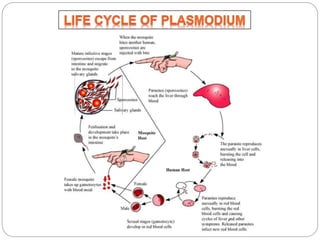
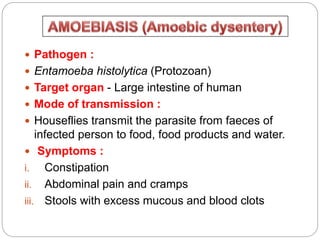
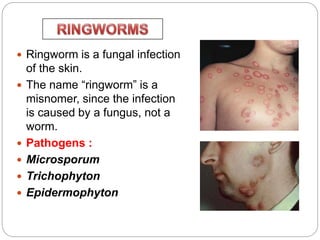
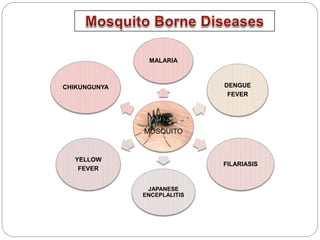
This document discusses various diseases caused by pathogens like bacteria, viruses, protozoa, and fungi. It provides details on the causative agents, target organs, modes of transmission, symptoms, and prevention for diseases like typhoid, pneumonia, common cold, malaria, amoebiasis, ascariasis, elephantiasis, and ringworm. It emphasizes the importance of personal and public hygiene for prevention of diseases through measures like proper disposal of waste, use of clean water and food, cleaning of water sources, and mosquito control.