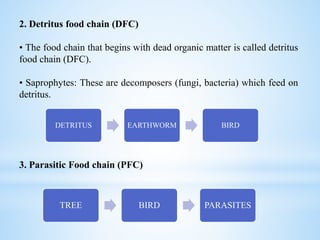
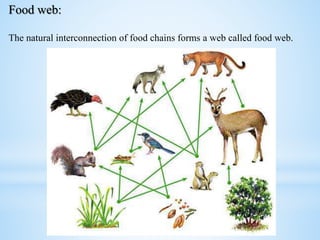
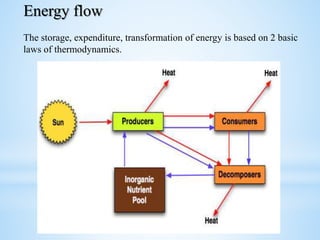
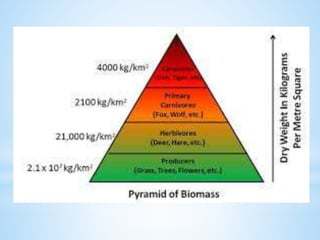
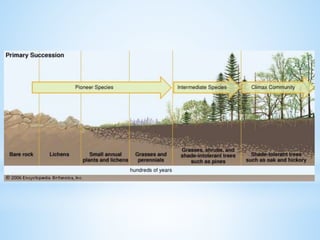
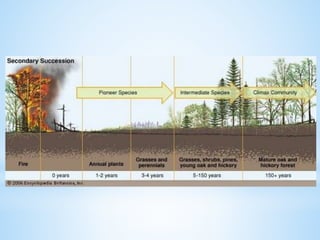
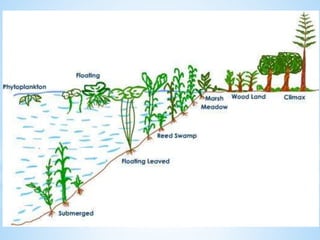
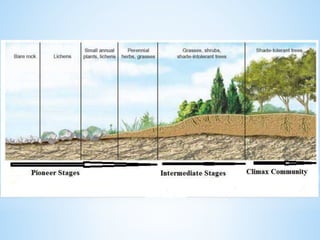
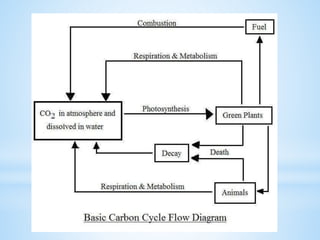
An ecosystem is a functional unit consisting of living organisms interacting with each other and their non-living environment. Key components include producers, consumers, and decomposers interacting within a web of food chains and nutrient cycles. Energy enters through producers via photosynthesis and is transferred between trophic levels, with only 10% typically being transferred between adjacent levels as depicted in ecological pyramids. Ecosystems also cycle nutrients and undergo successional changes over time as conditions change.