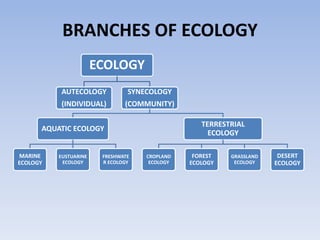
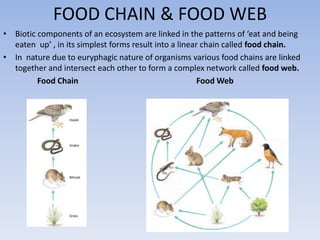
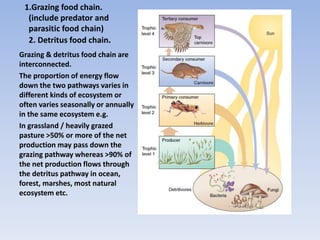
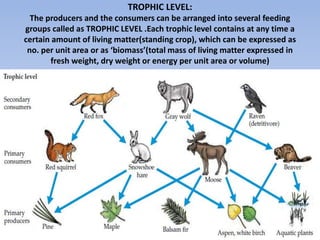
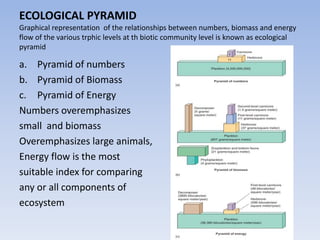
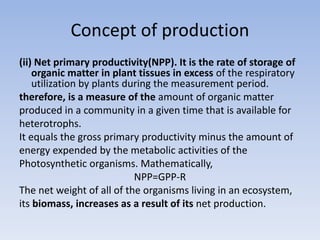
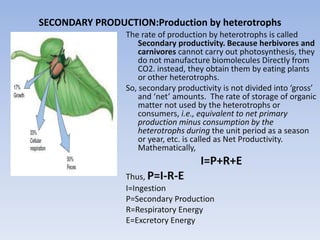
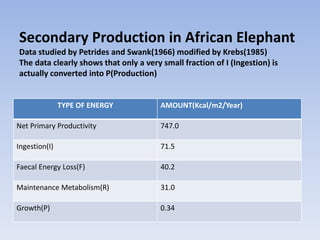
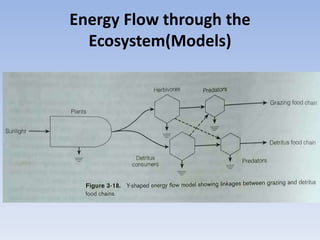
This document provides an overview of ecosystems and ecology. It begins with definitions of ecology and ecosystem from various scholars. An ecosystem is defined as all the organisms in a given area interacting with the physical environment. Key components of ecosystems discussed include biotic and abiotic factors, producers and consumers, trophic levels, food chains and webs. Ecological concepts like pyramids of numbers, biomass and energy, primary and secondary productivity, and energy flow through ecosystems are also summarized. Diagrams illustrate these concepts and energy flows at the global, community and individual organism levels.