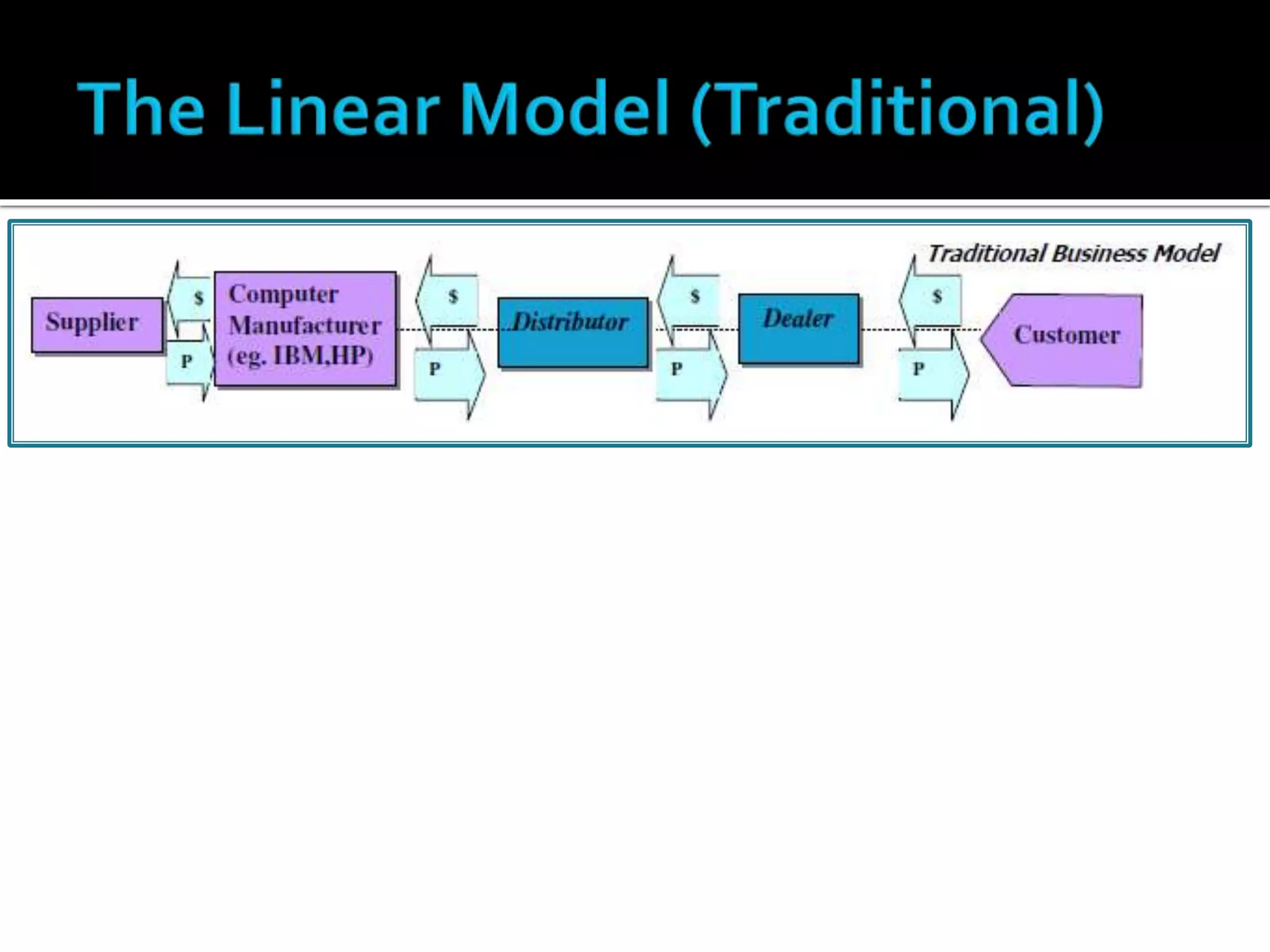
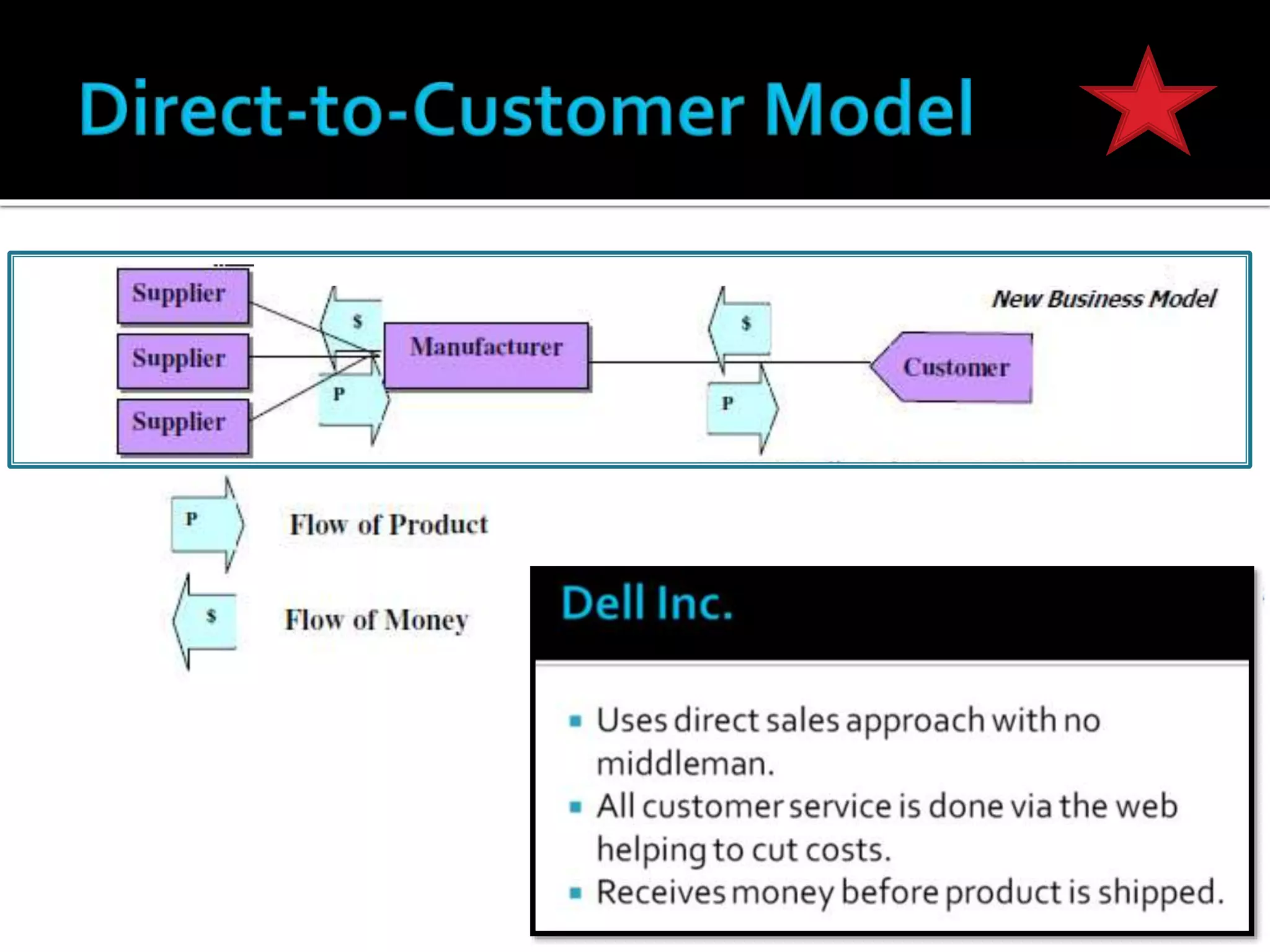
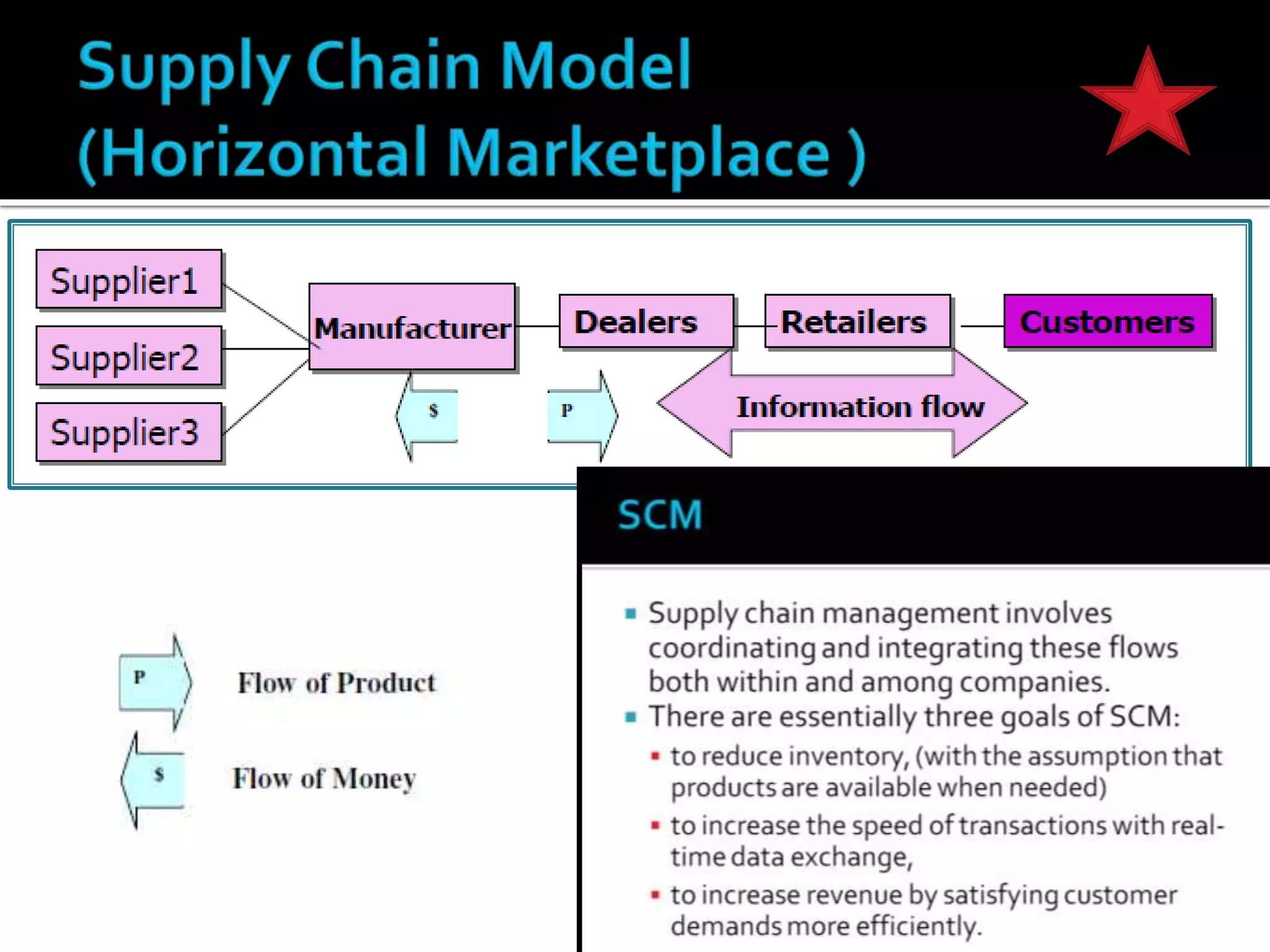
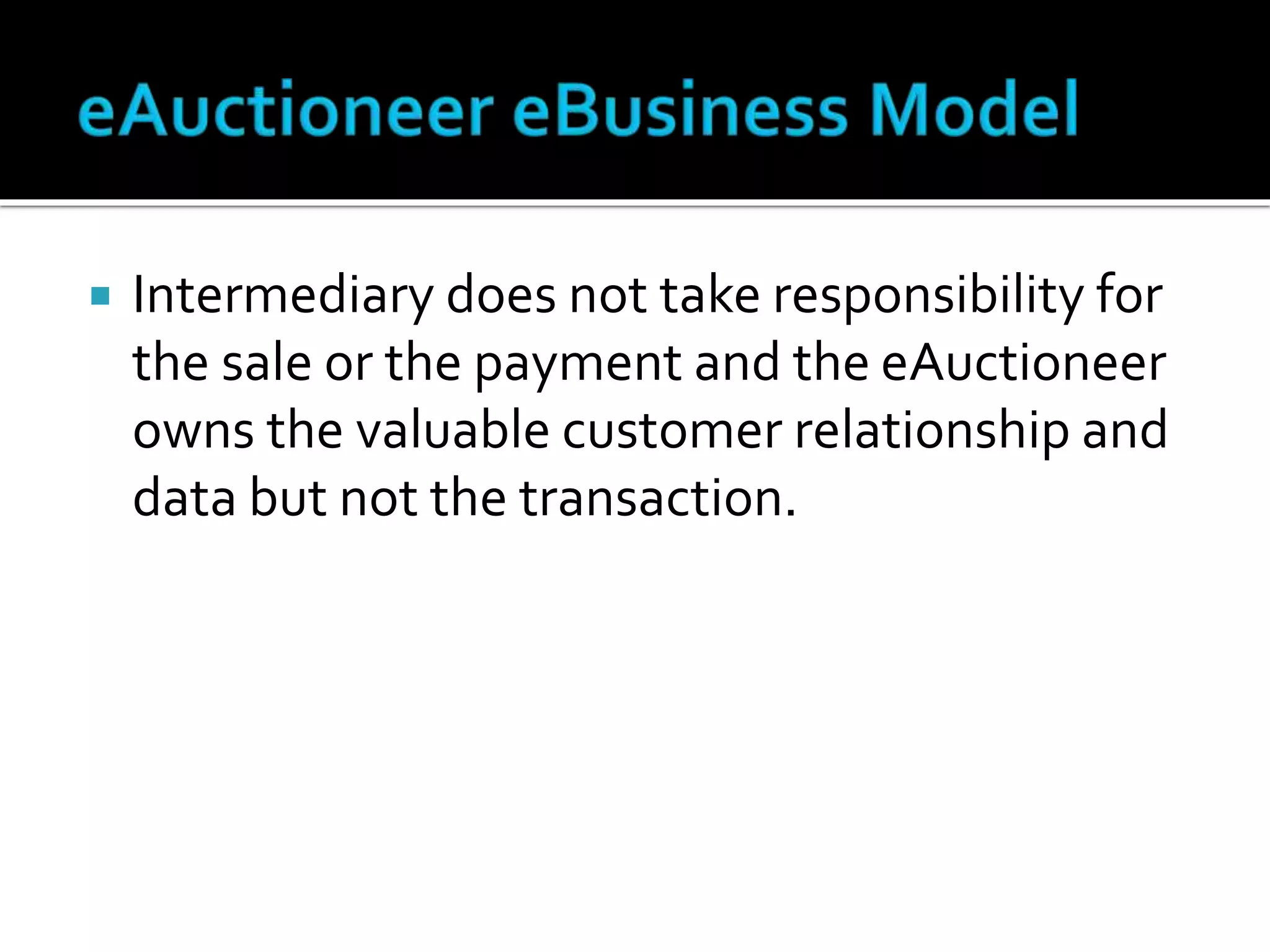
The document discusses several revenue models for e-business, including:
1) Selling directly to customers at lower prices, building custom orders, and receiving earlier payment. This allows faster delivery and product release.
2) Using customer data to provide customized services.
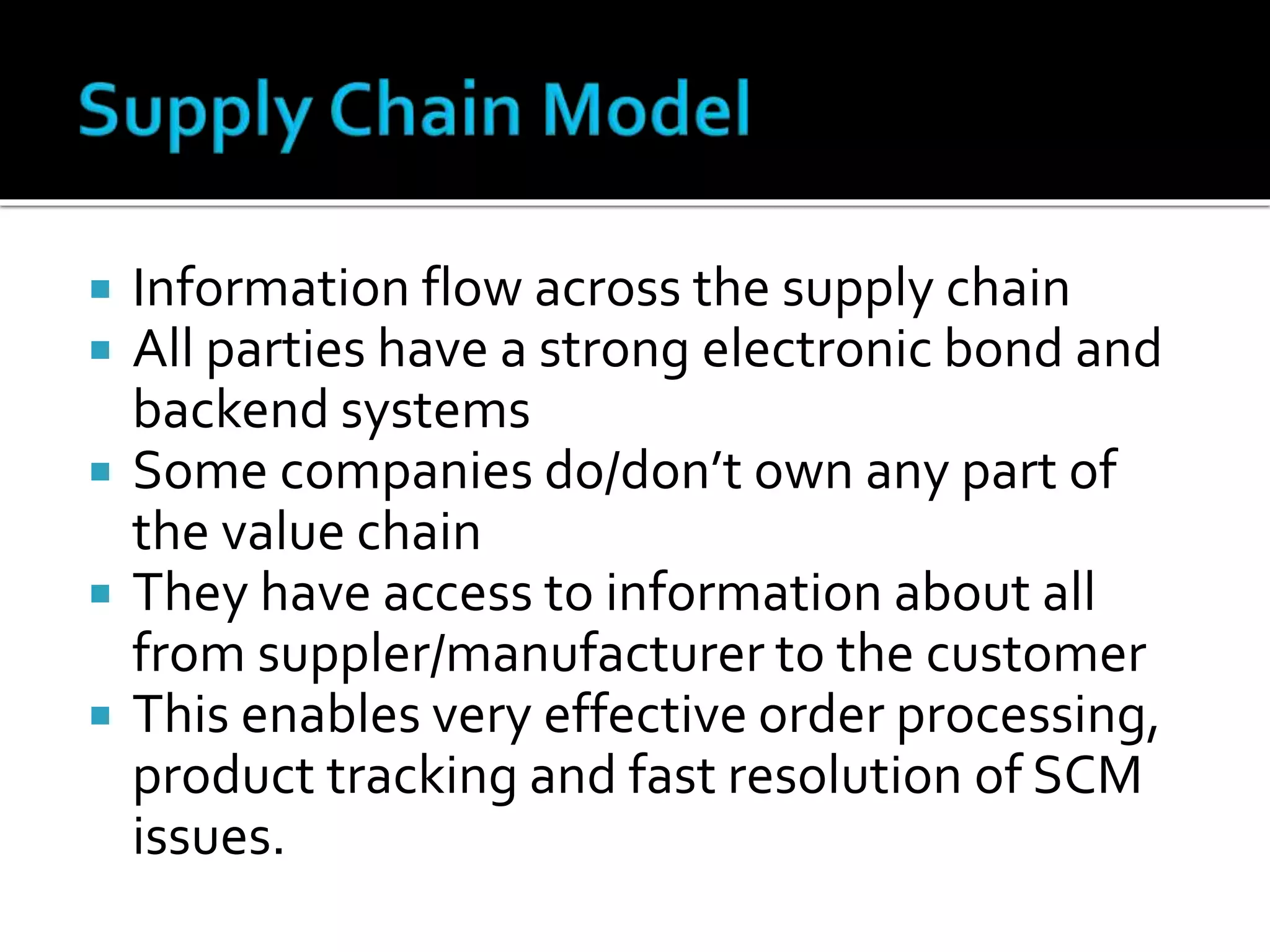
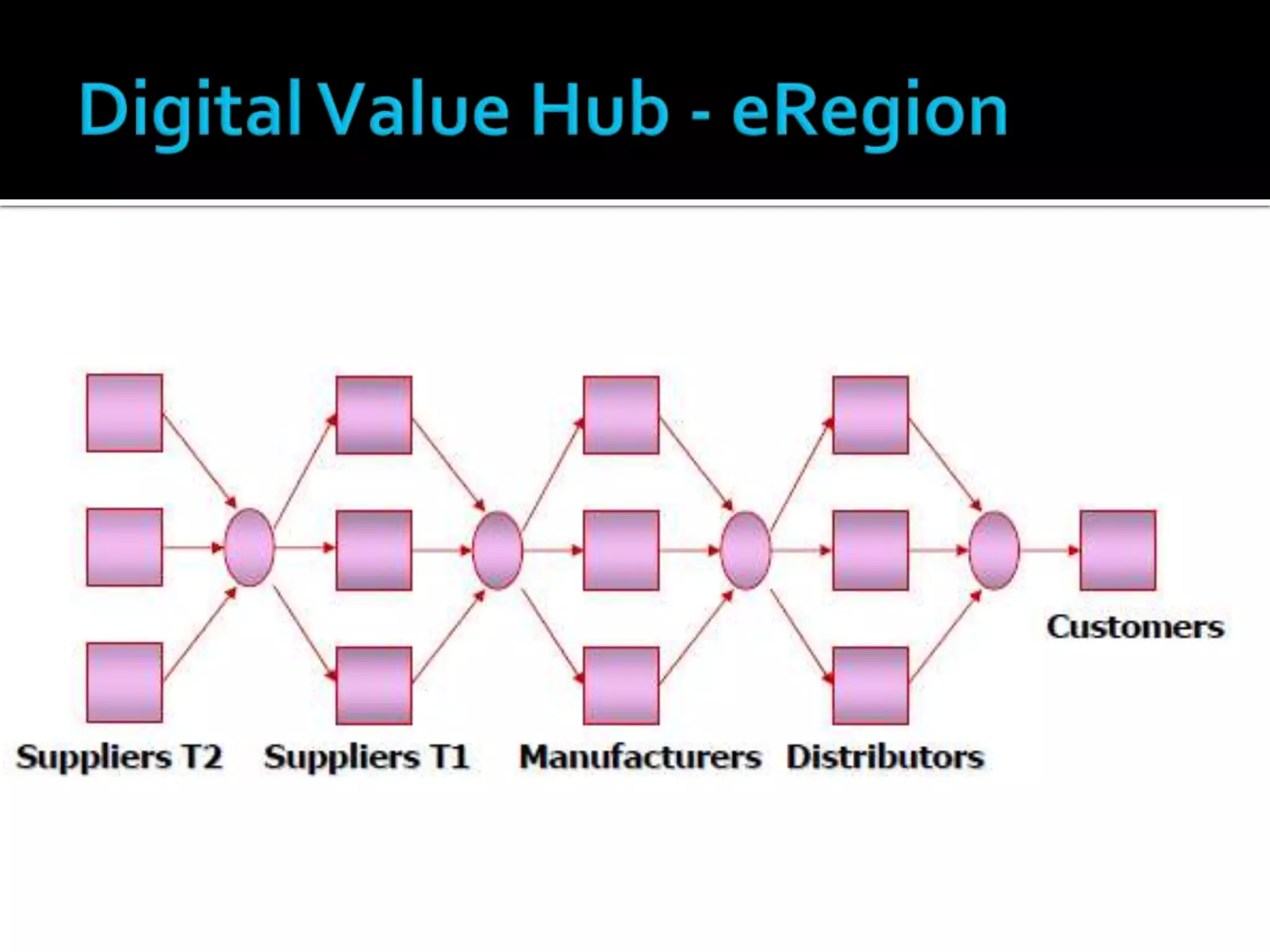
3) Leveraging information sharing across the supply chain for effective order processing, product tracking, and issue resolution.
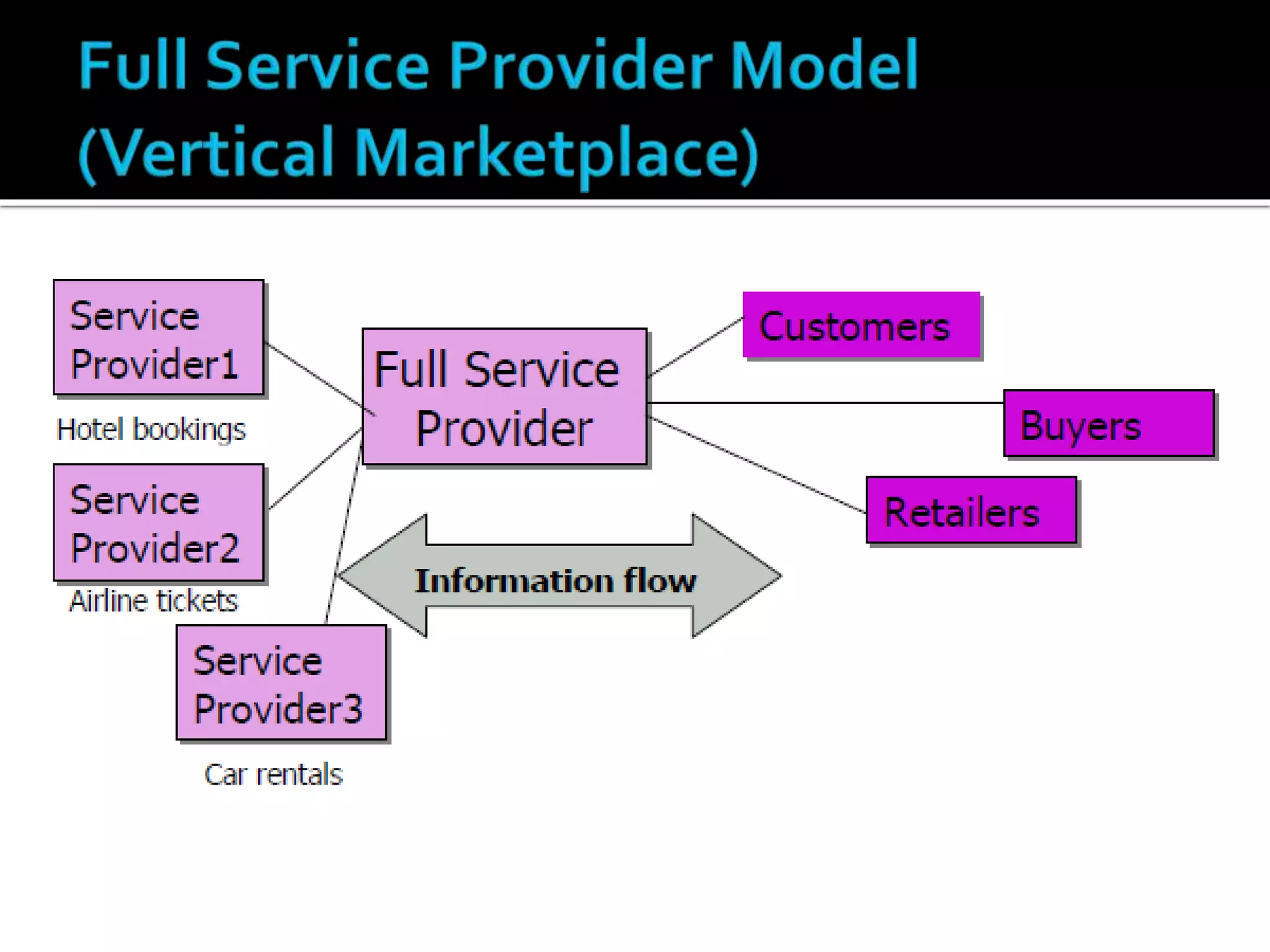
4) Bundling own and third-party products/services and offering multiple sales channels for economies of scale.
5) Industry collaboration and partnerships to gain competitive advantages over foreign competitors.
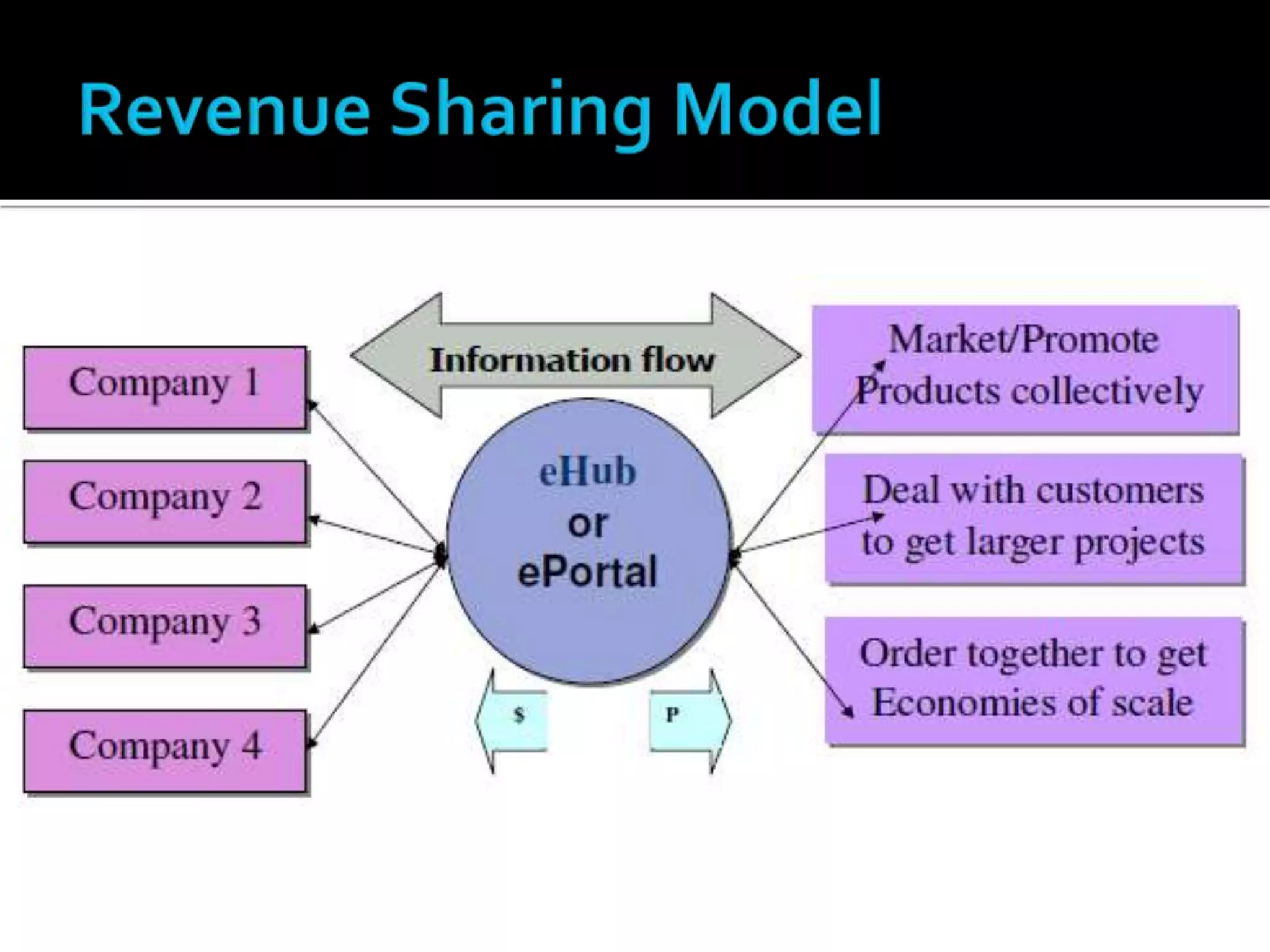
6) Collective marketing portals where small sellers work together on larger projects by pooling resources and profits.