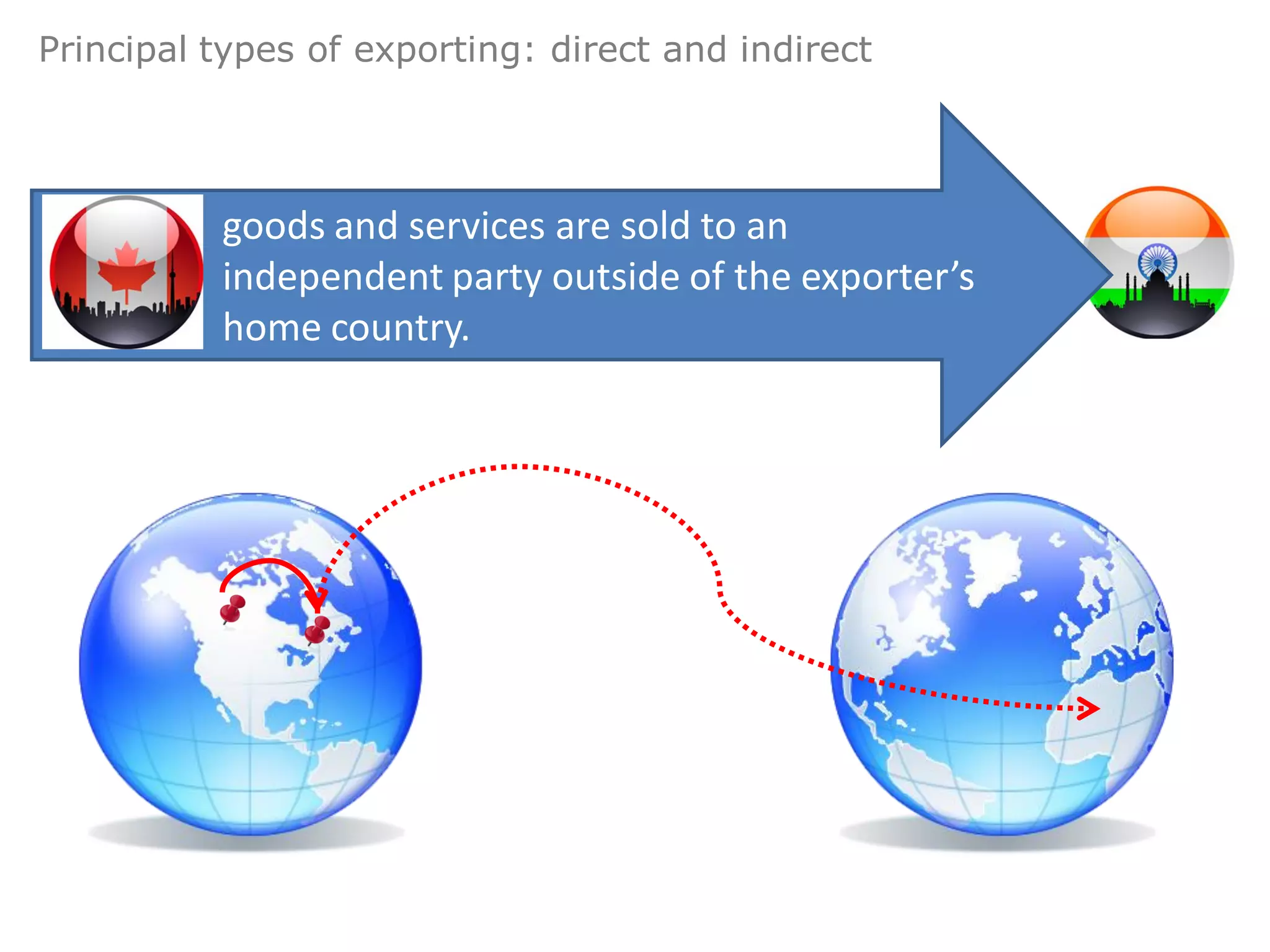
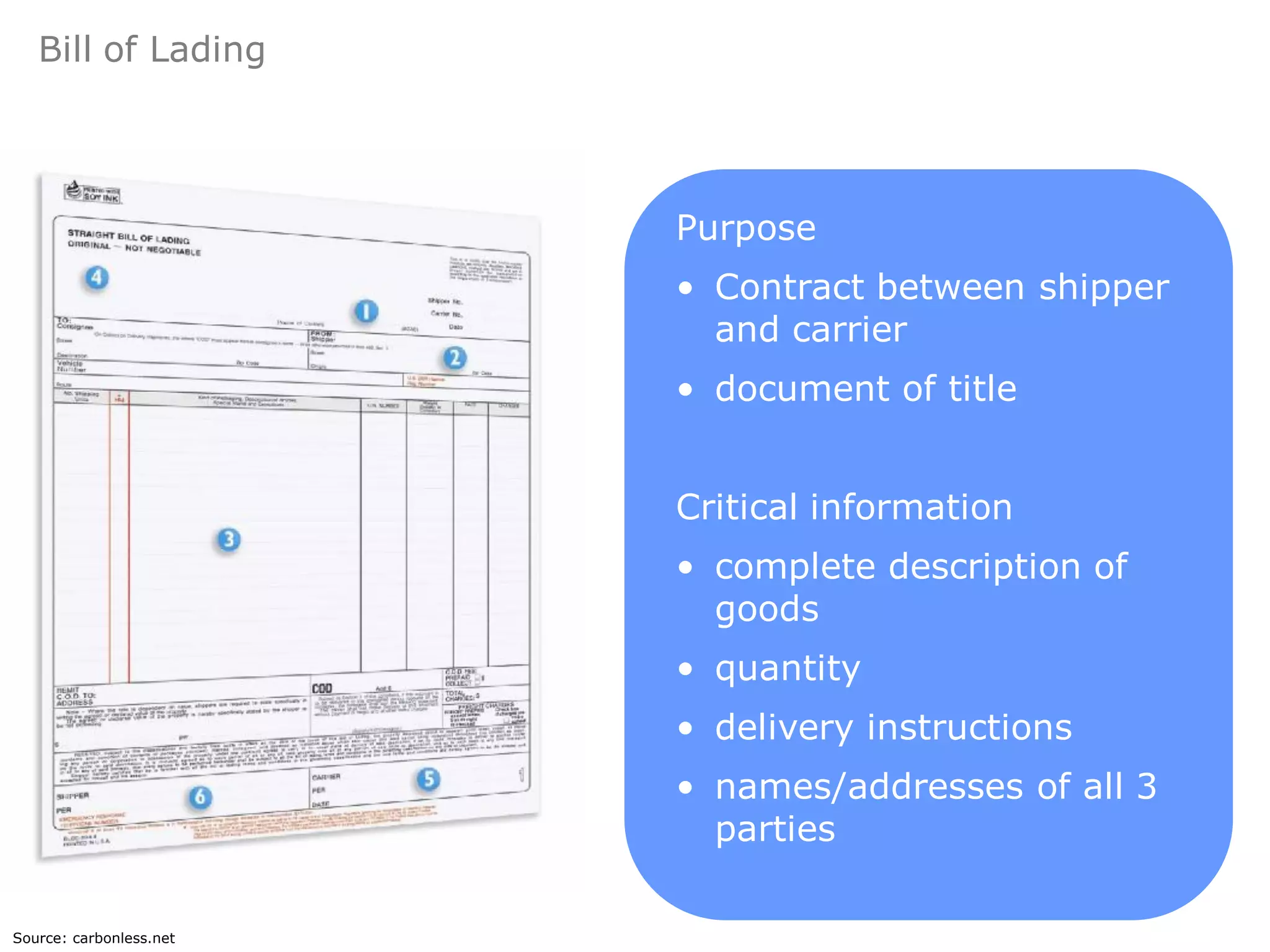
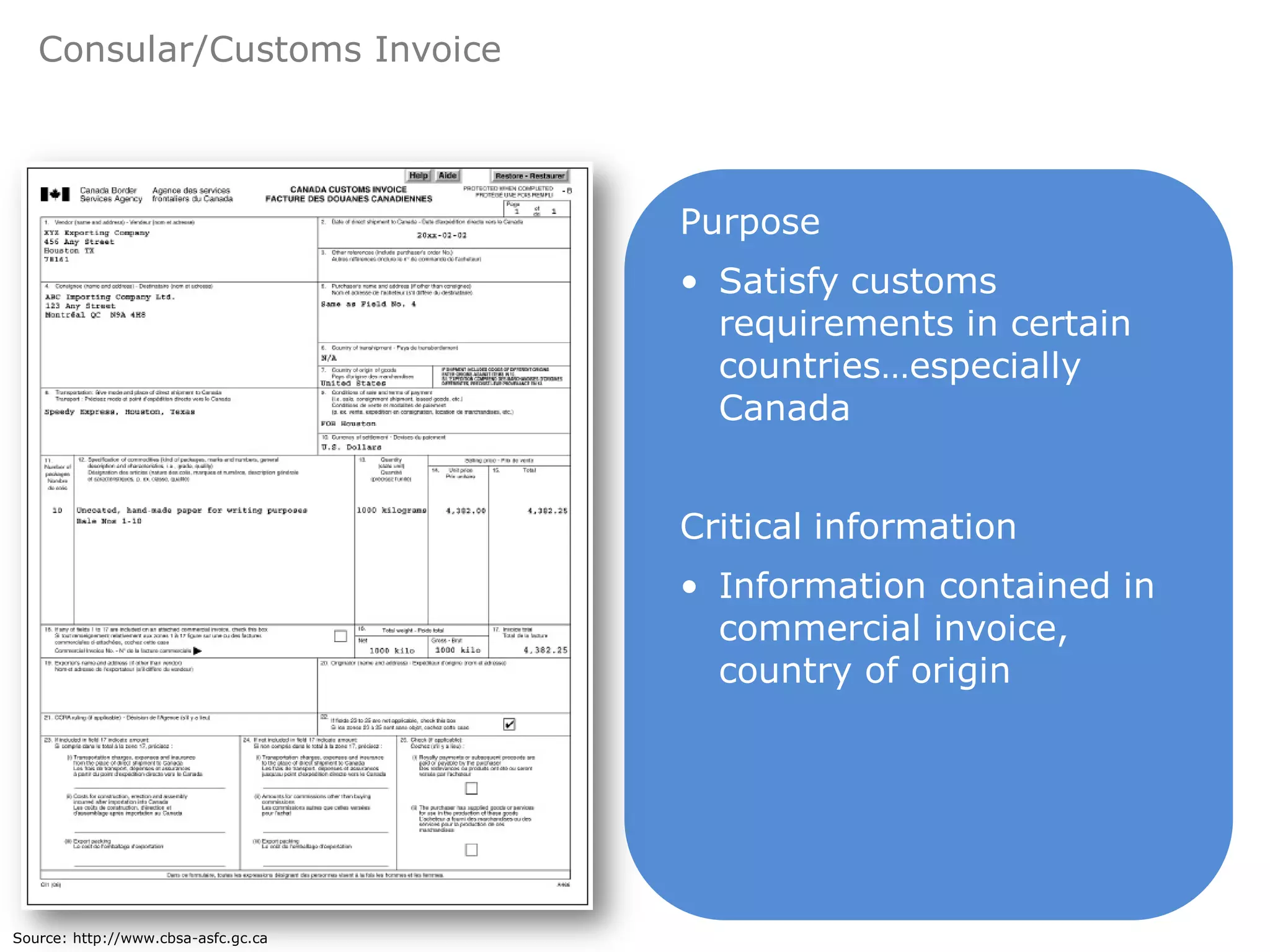
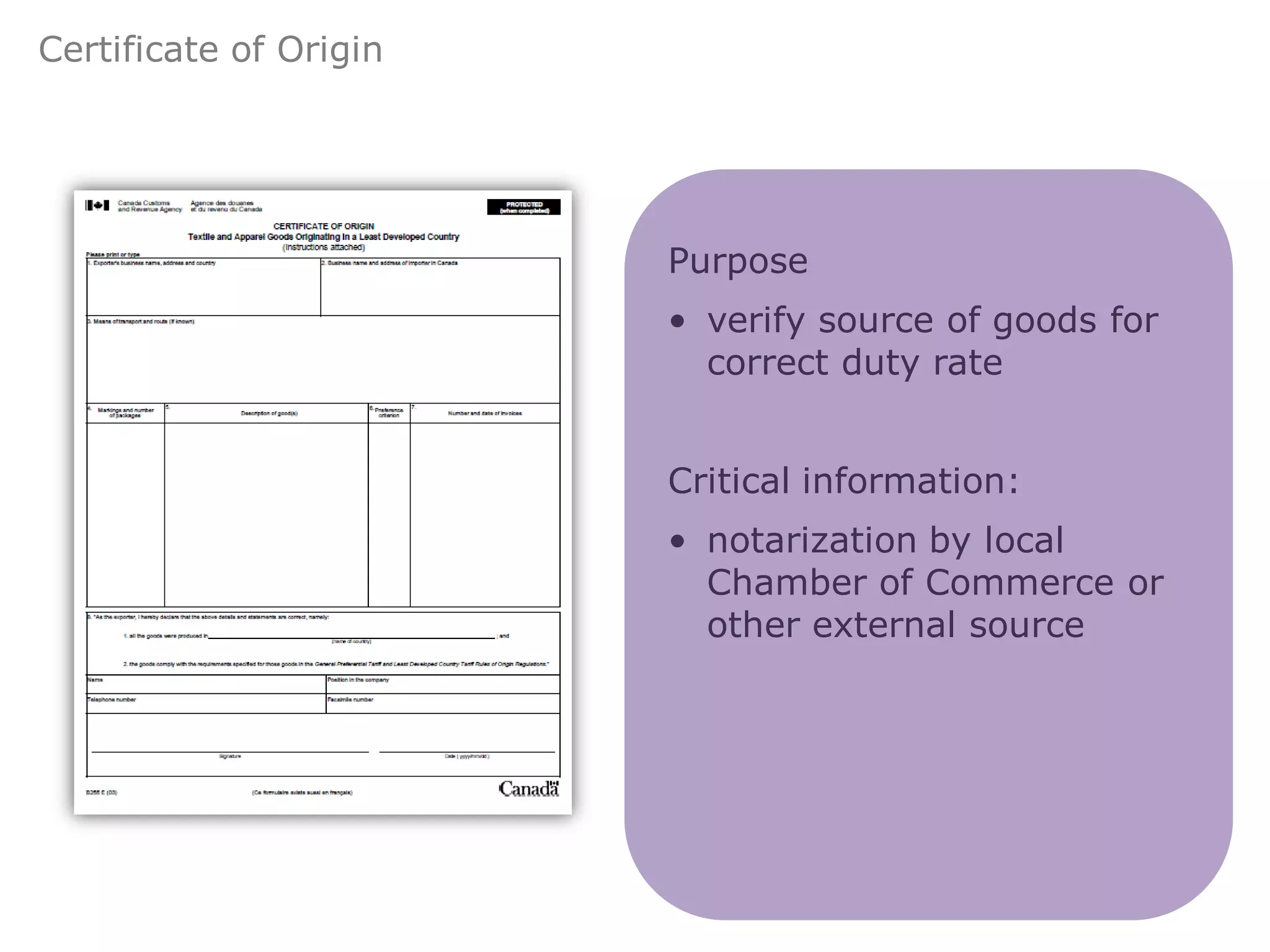
This document provides an overview of export and import strategies discussed in Chapter 13. It defines exporting and importing, outlines the strategic advantages of both, and identifies elements to consider when designing an export or import strategy. It also discusses direct and indirect selling approaches, key documentation requirements, and the use of countertrade arrangements. The document concludes with a reminder of homework assignments.