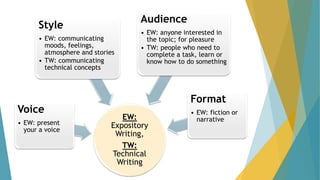
This document discusses professional communications within IT, focusing on the preparation of various forms of written and oral presentations suitable for different audiences. It highlights the significance of user documentation, contrasting technical writing with expository writing, and emphasizes clarity, readability, and precision in technical documents. Additionally, it outlines components essential for creating effective user manuals and provides guidance on structuring information to assist users effectively.
![Chapter 1 - Professional
Communications
IT 5105 – Professional Issues in IT
Upekha Vandebona
upe.vand@gmail.com
[Writing]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch1-professionalcommunicationwriting-160418054552/75/Professional-Communication-in-Computing-Writing-1-2048.jpg)