Embed presentation
Downloaded 78 times






![ Maintainability. Effort required to locate and fix an error
in a program.
Flexibility. Effort required to modify an operational
program.
Testability. Effort required to test a program to ensure
that it performs its intended function.
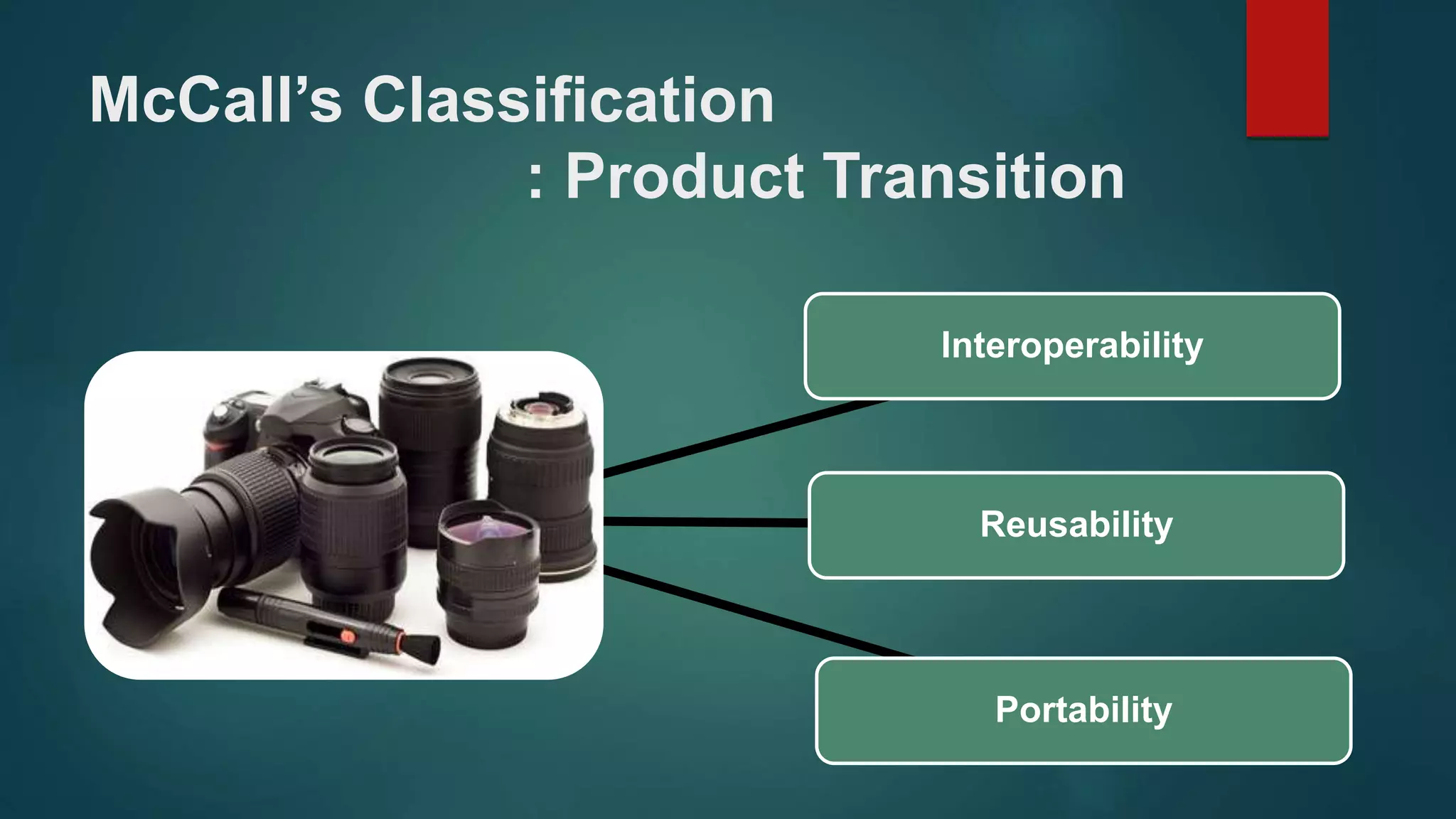
Portability. Effort required to transfer the program from
one hardware and/or software system environment to
another.
Reusability. Extent to which a program [or parts of a
program] can be reused in other applications—related to
the packaging and scope of the functions that the
program performs.
Interoperability. Effort required to couple one system to
another.
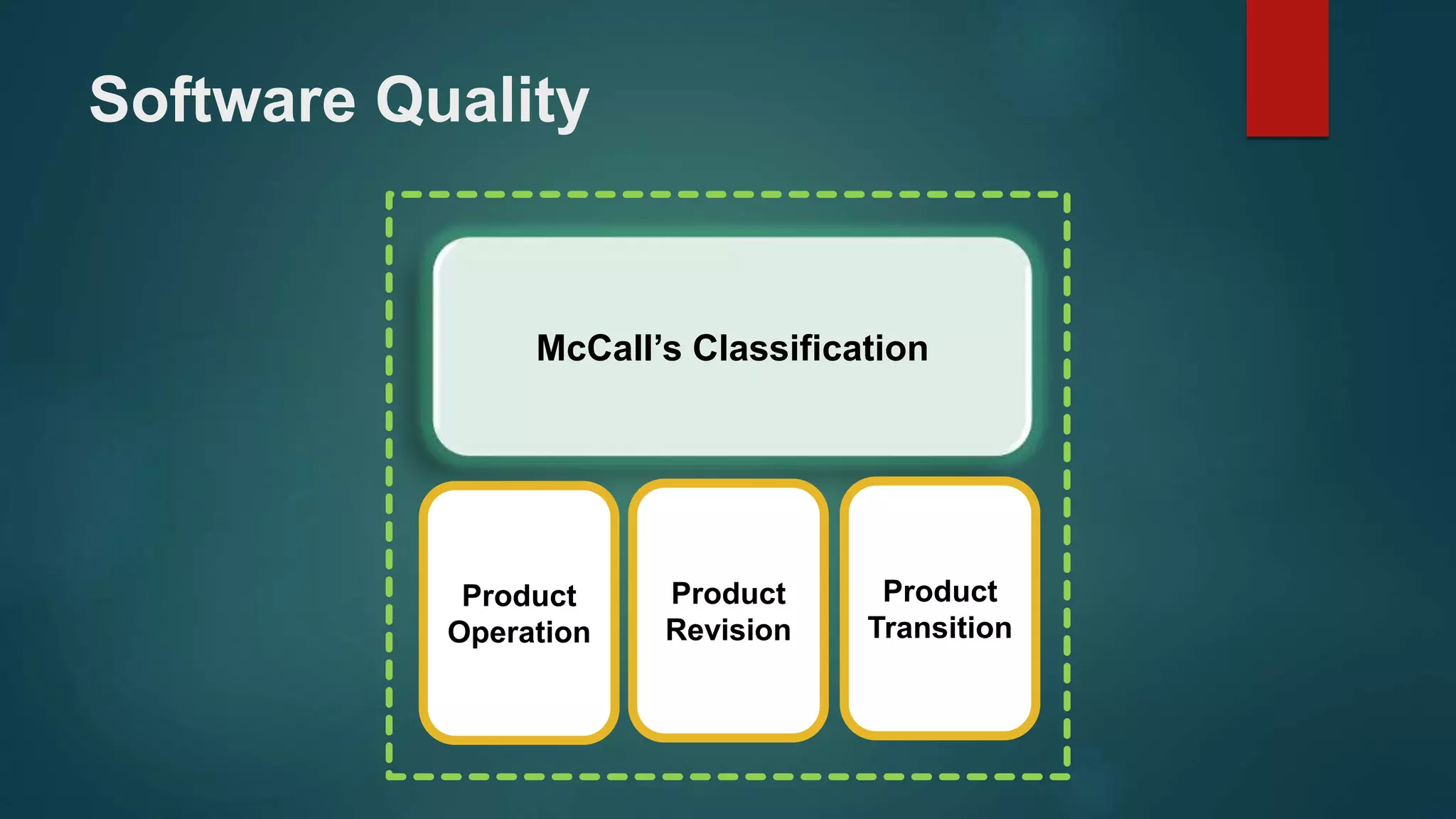
Product
Revision
Product
Transition](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/se-2-161226080901/75/Characteristics-of-Software-10-2048.jpg)


The document outlines various characteristics of software engineering, including cost considerations and failure rates for both software and hardware. It details McCall’s classification of software quality attributes such as correctness, reliability, efficiency, and usability, along with maintainability, flexibility, testability, portability, reusability, and interoperability. The document emphasizes the importance of these characteristics in ensuring that software meets user requirements and performs reliably.
Introduction to software engineering characteristics by Upekha Vandebona.
Comparison of software cost versus hardware cost and the implications of time and cost.
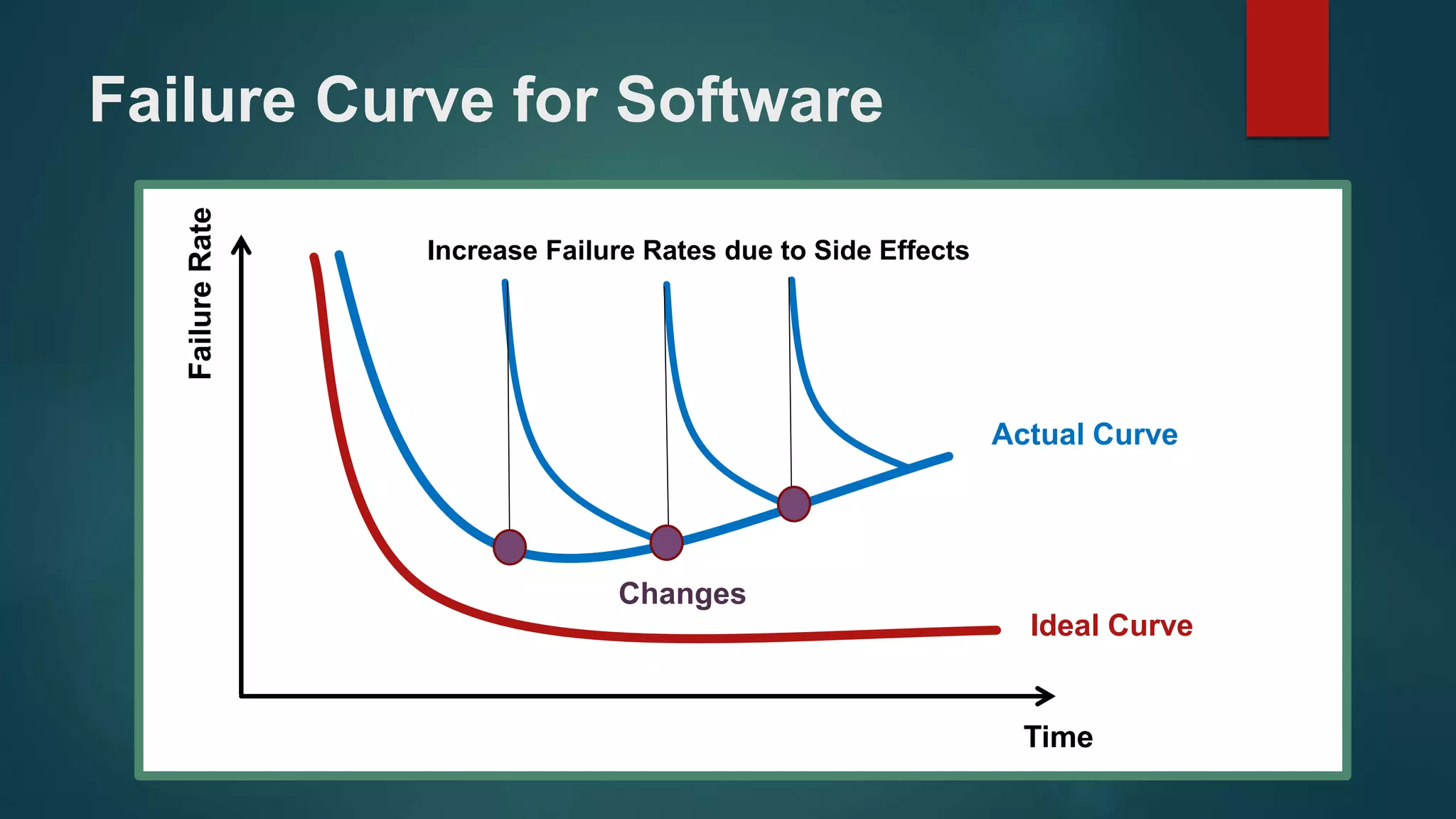
Examines the failure curve in hardware, focusing on stages like infant mortality and wear-out.
Analyzes software failure rates and the impacts of changes on failure rates in the ideal vs actual curves.
Introduces McCall's classification related to software quality involving product, operation, revision, and transition.
Discusses key quality attributes including correctness, reliability, usability, integrity, and efficiency.
Focuses on maintainability, flexibility, and testability as important qualities in software revision.
Highlights interoperability, reusability, and portability as critical elements in product transitions.
Defines correctness, reliability, efficiency, integrity, and usability in software products.
Describes maintainability, flexibility, testability, portability, reusability, and interoperability in software.









![ Maintainability. Effort required to locate and fix an error
in a program.
Flexibility. Effort required to modify an operational
program.
Testability. Effort required to test a program to ensure
that it performs its intended function.
Portability. Effort required to transfer the program from
one hardware and/or software system environment to
another.
Reusability. Extent to which a program [or parts of a
program] can be reused in other applications—related to
the packaging and scope of the functions that the
program performs.
Interoperability. Effort required to couple one system to
another.
Product
Revision
Product
Transition](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/se-2-161226080901/75/Characteristics-of-Software-10-2048.jpg)
