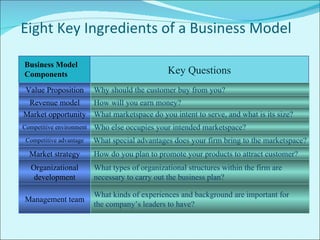
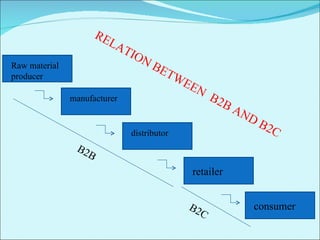
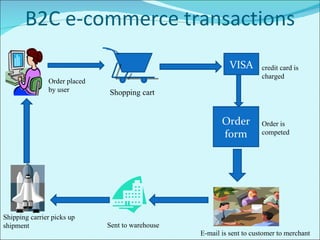
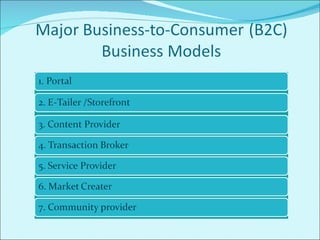
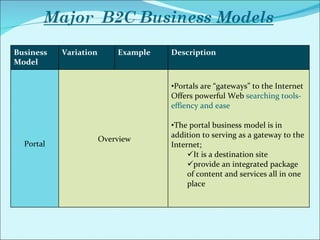
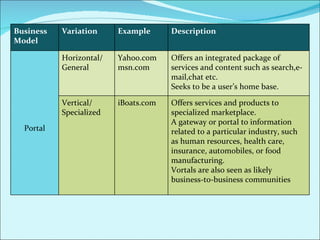
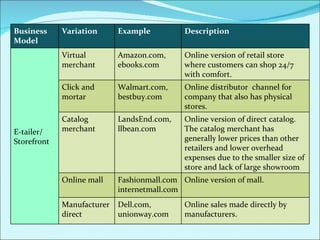
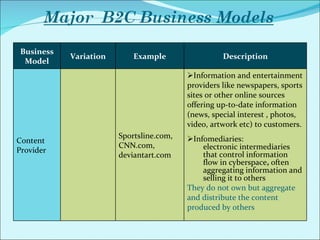
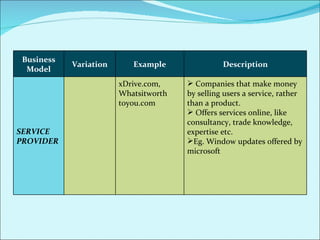
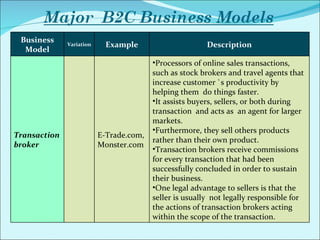
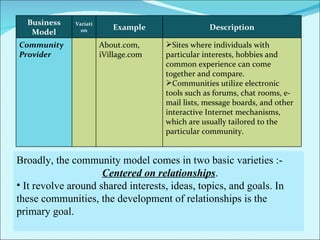
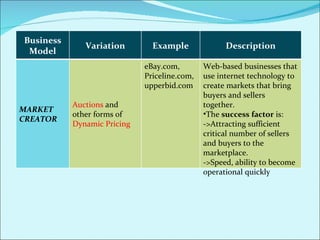
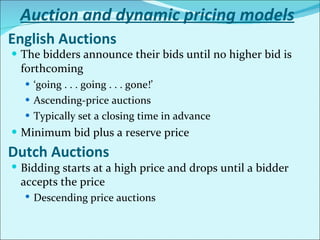
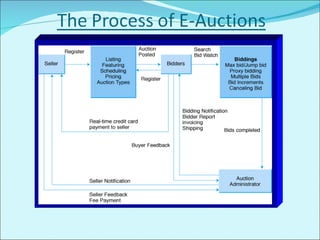
The document discusses various business models used in B2C e-commerce. It defines key terms like business model and e-commerce business model. It also describes different types of business models like portals, e-tailers, content providers, service providers, transaction brokers, community providers, and market creators. Each model is explained with examples. The document also discusses capabilities of B2C models like instant communication, global reach, reduced costs, and increased efficiency.