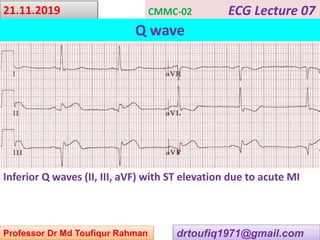
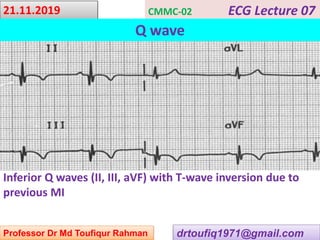
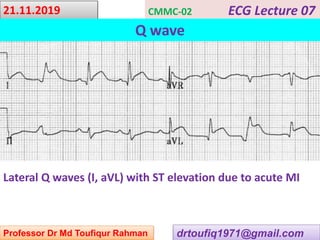
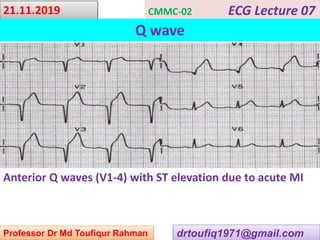
This document contains a series of lectures from Professor Dr. Md Toufiqur Rahman on the topic of Q waves on electrocardiograms (ECGs). The professor defines a Q wave as any negative deflection preceding an R wave, representing normal left-to-right depolarization of the interventricular septum. Small, normal Q waves can be seen in specific left-sided leads. Larger or abnormal Q waves may indicate myocardial infarction or other conditions like cardiomyopathy. Examples of pathological Q waves and their associations with ST segments and T waves are shown from different leads.