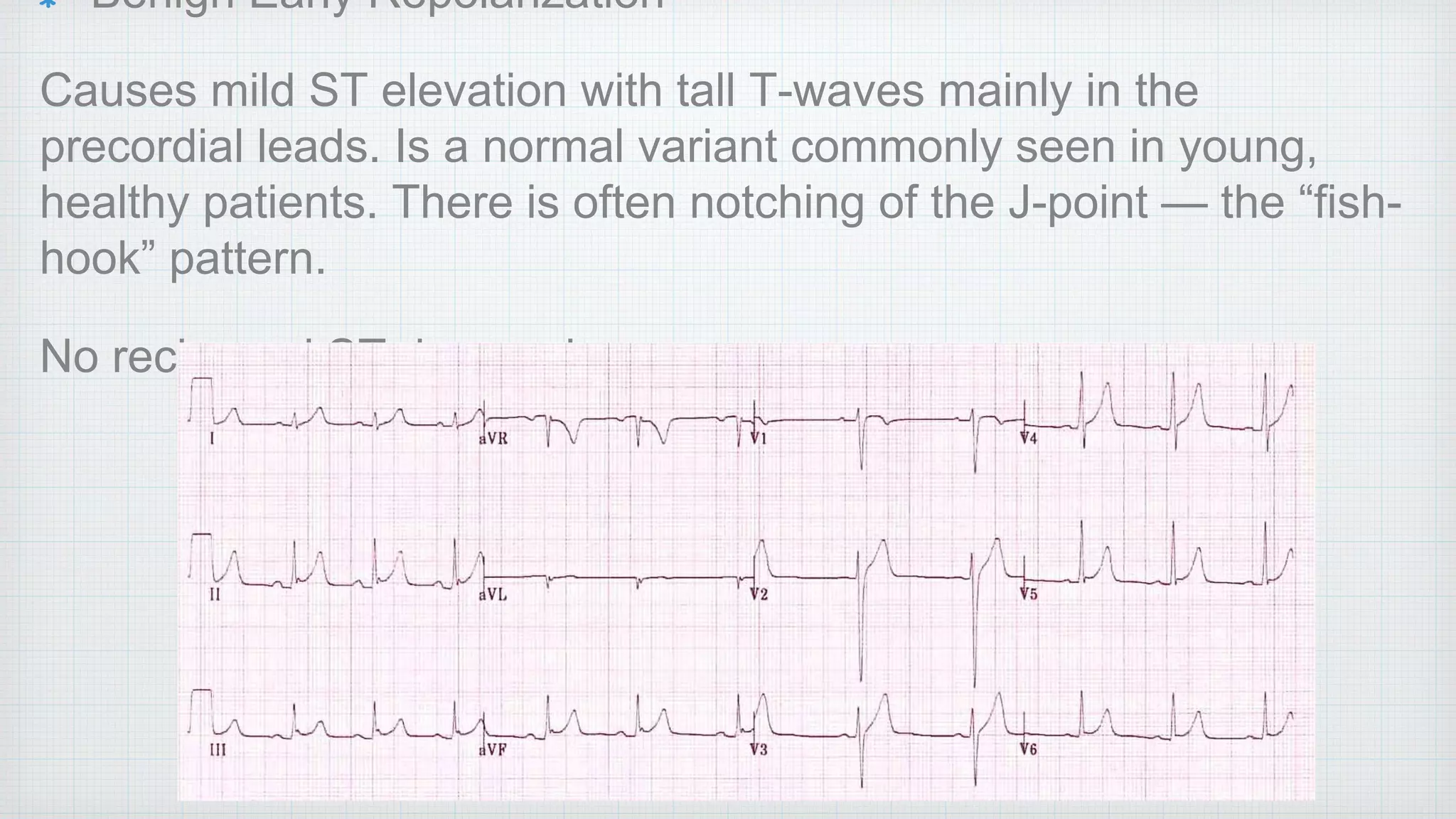
The document discusses various ECG abnormalities relevant to pulmonary medicine, including normal values for key ECG components and pathological changes associated with conditions like right atrial enlargement and hyperkalemia. It outlines specific characteristics of ECG waves, intervals, and segments that indicate conditions such as myocardial infarction and arrhythmias, as well as the implications of electrolyte imbalances like hypokalemia and hyperkalemia. The effects of these abnormalities on the heart's electrical activity, as well as diagnostic criteria for conditions like right bundle branch block and left bundle branch block, are also highlighted.