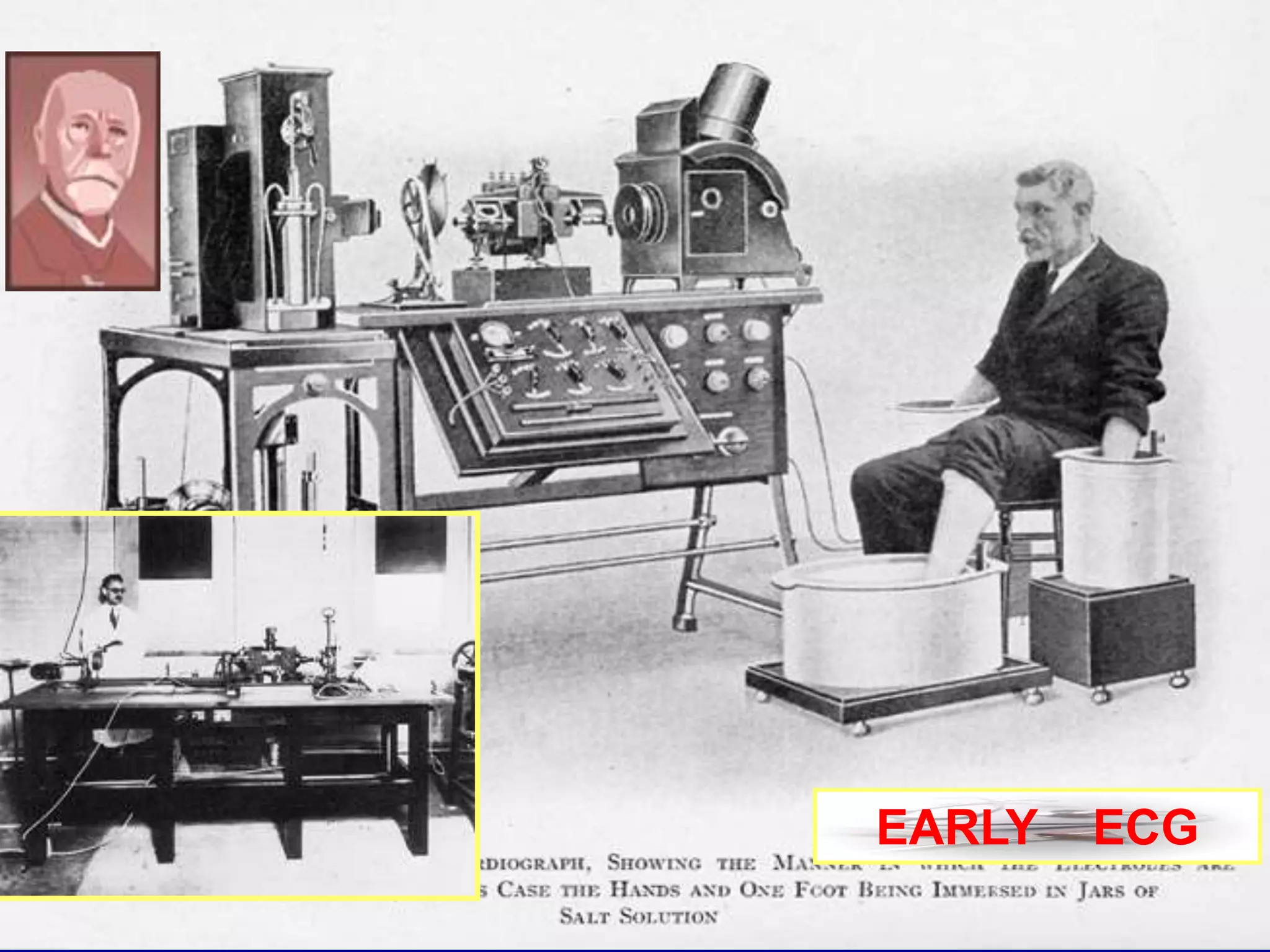
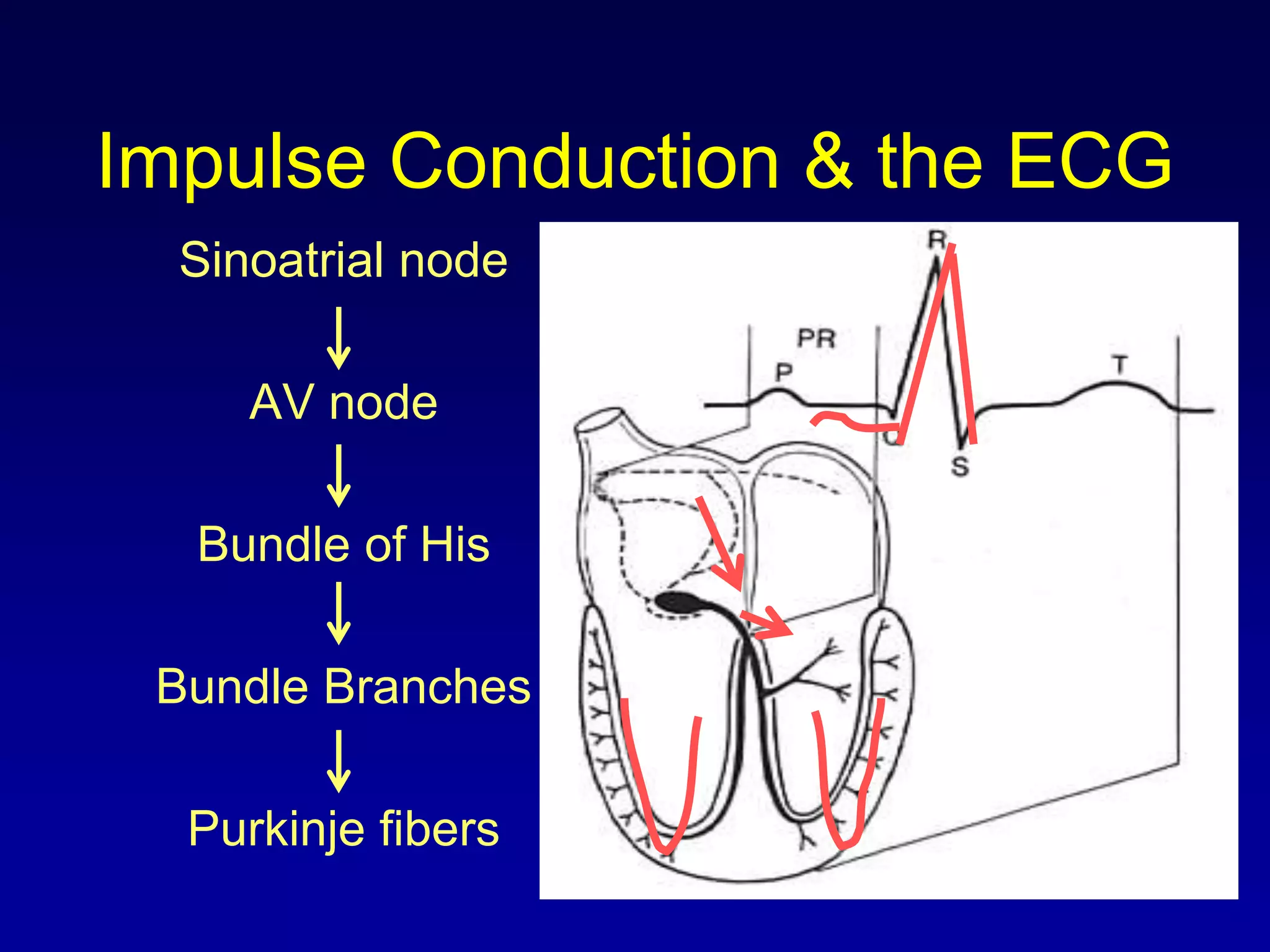
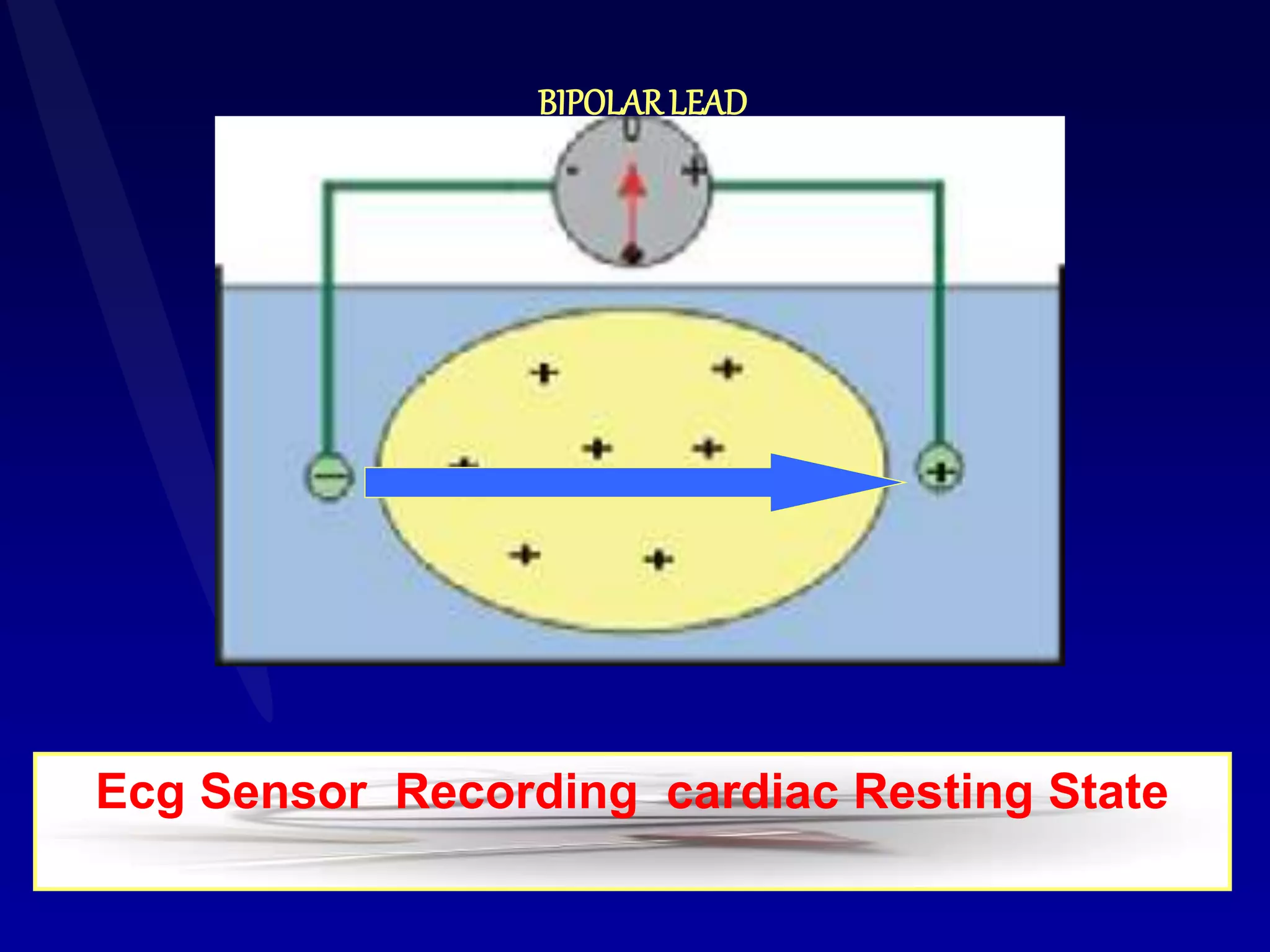
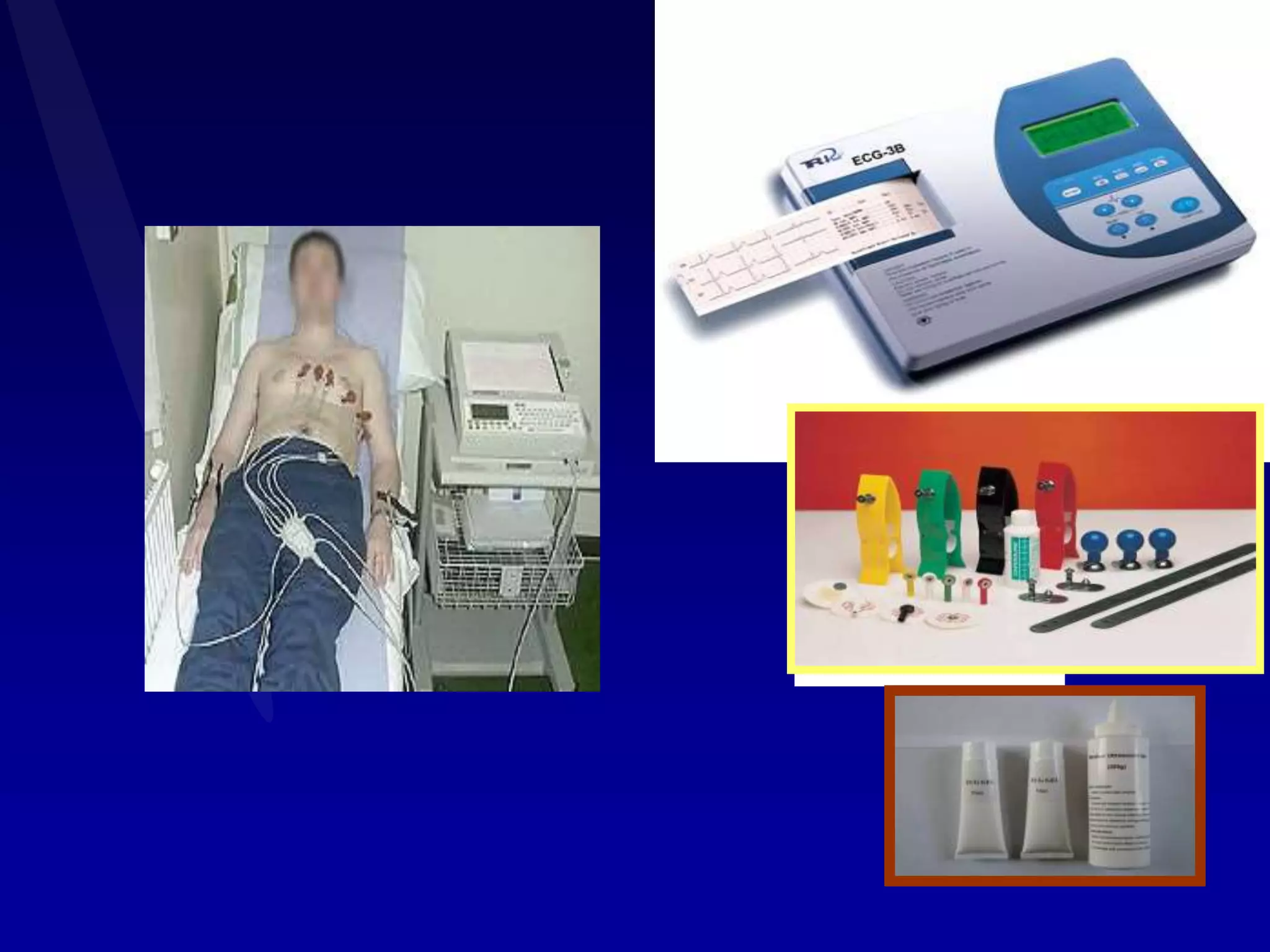
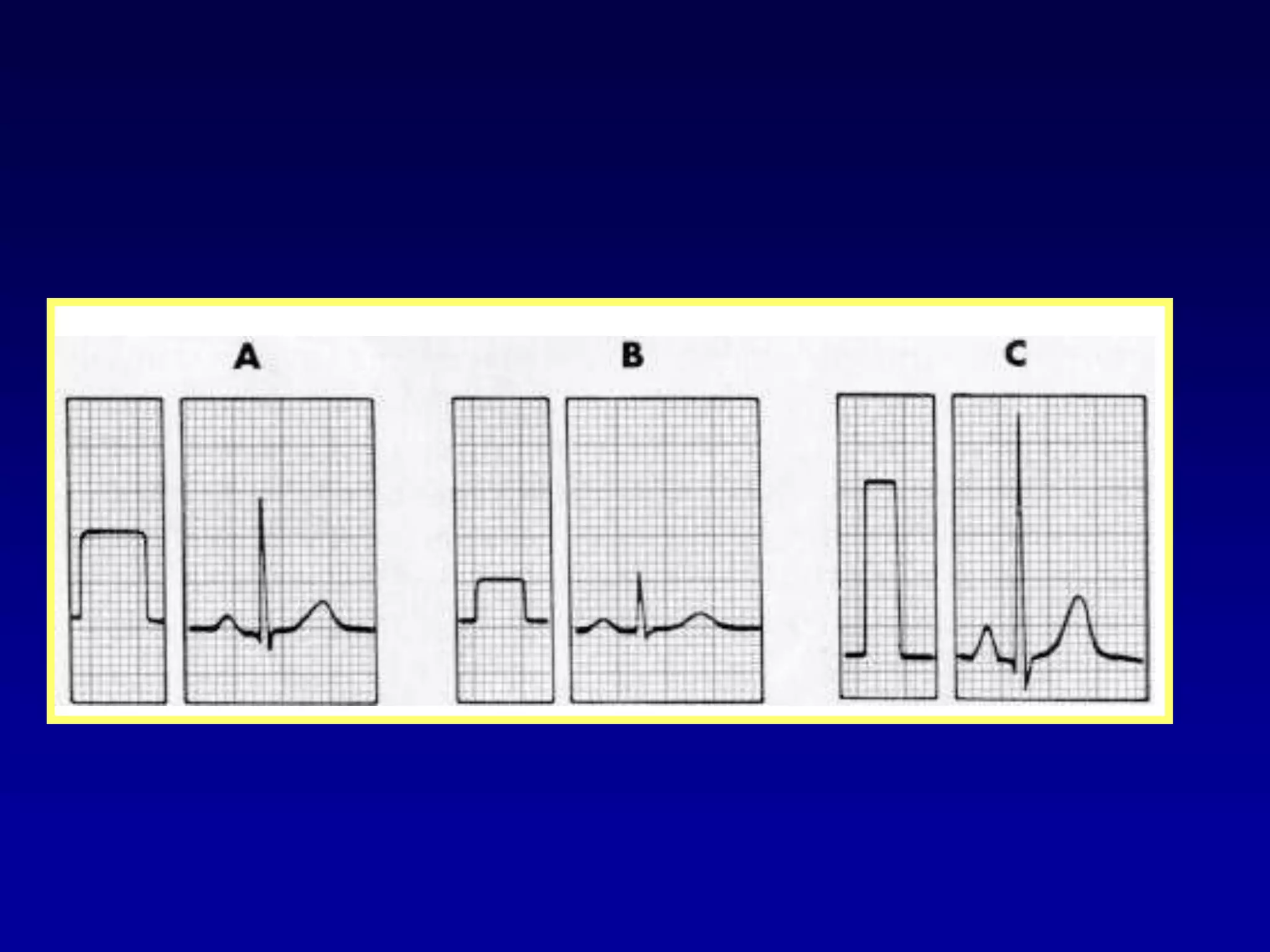
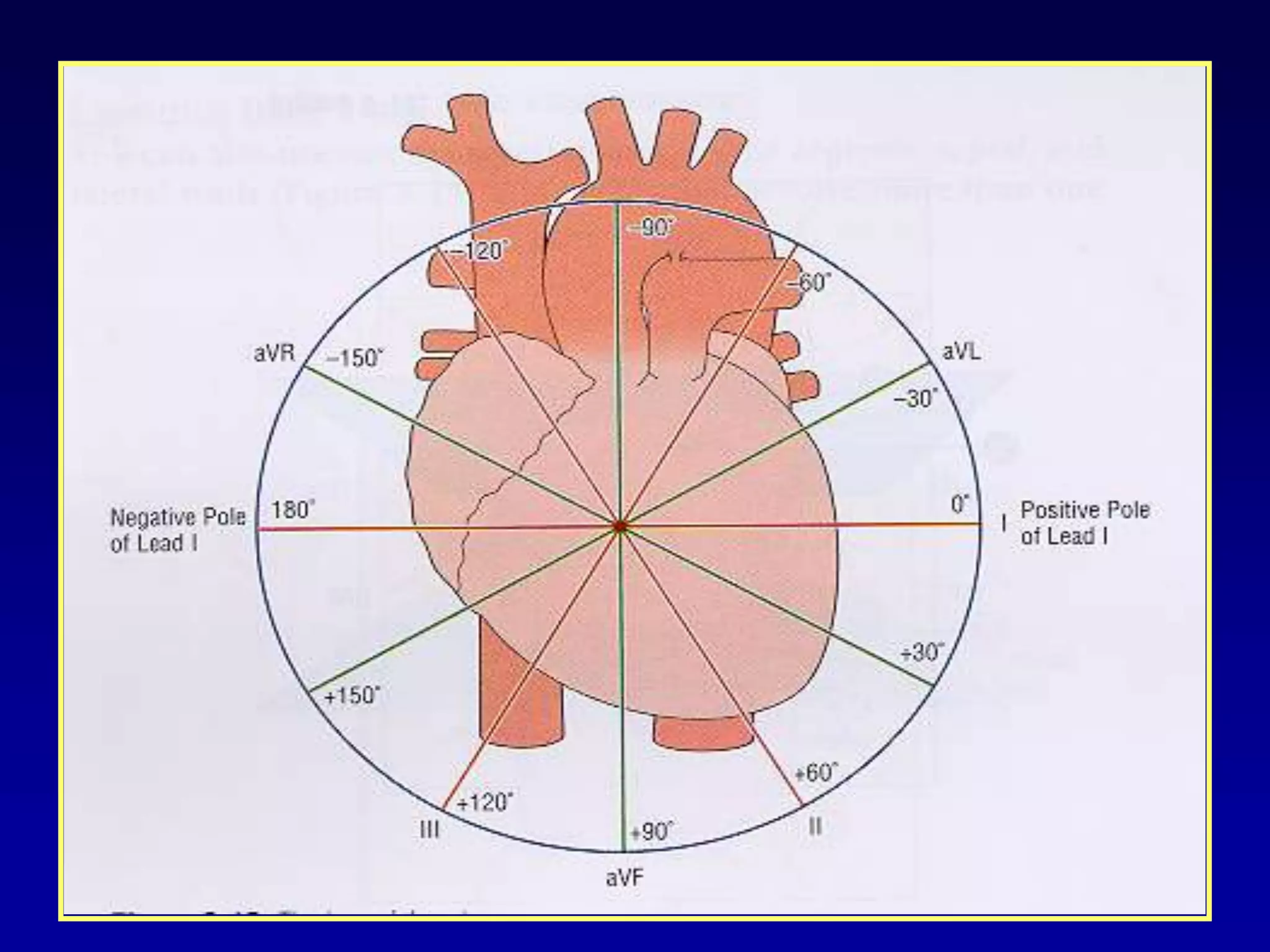
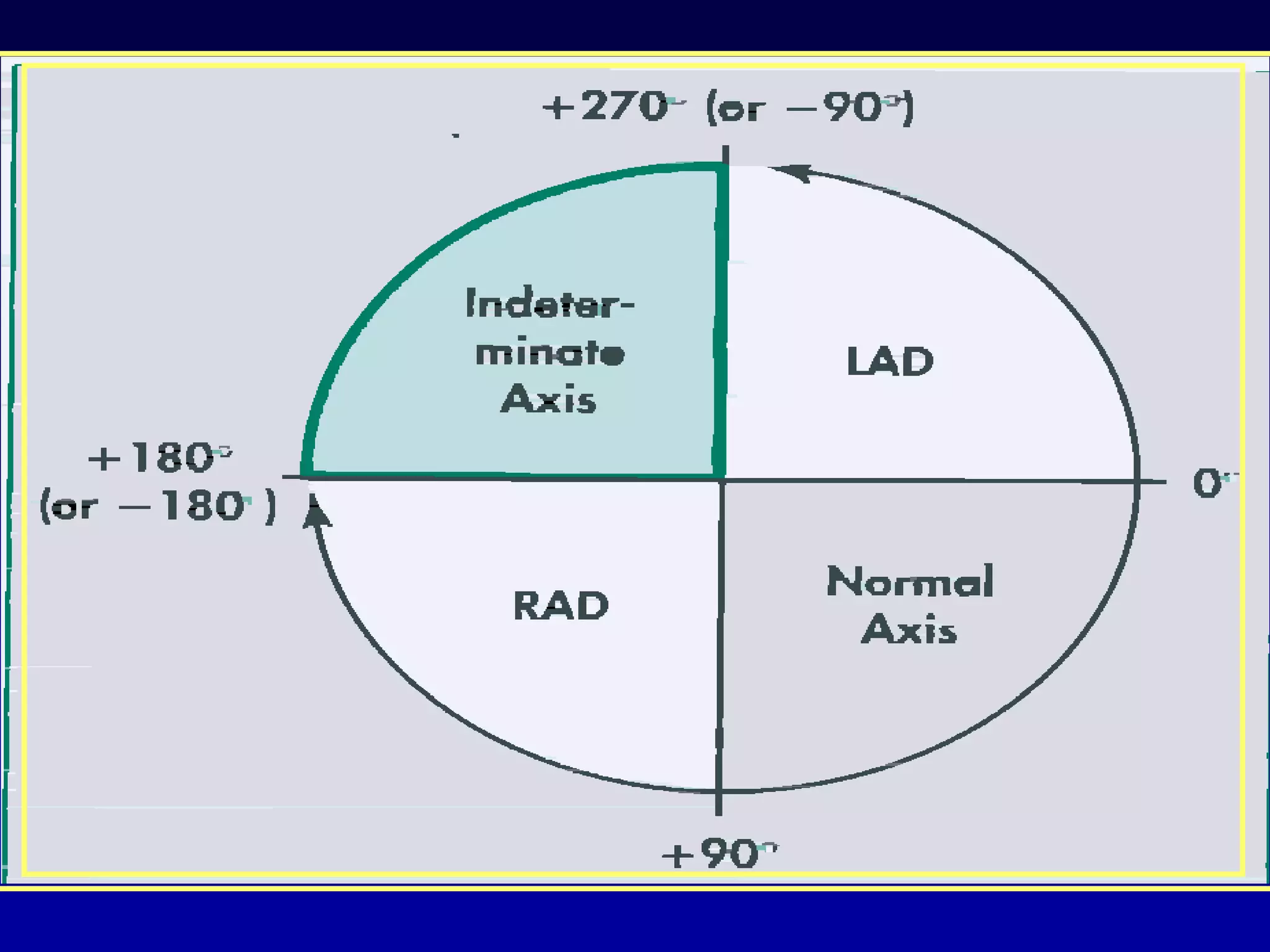
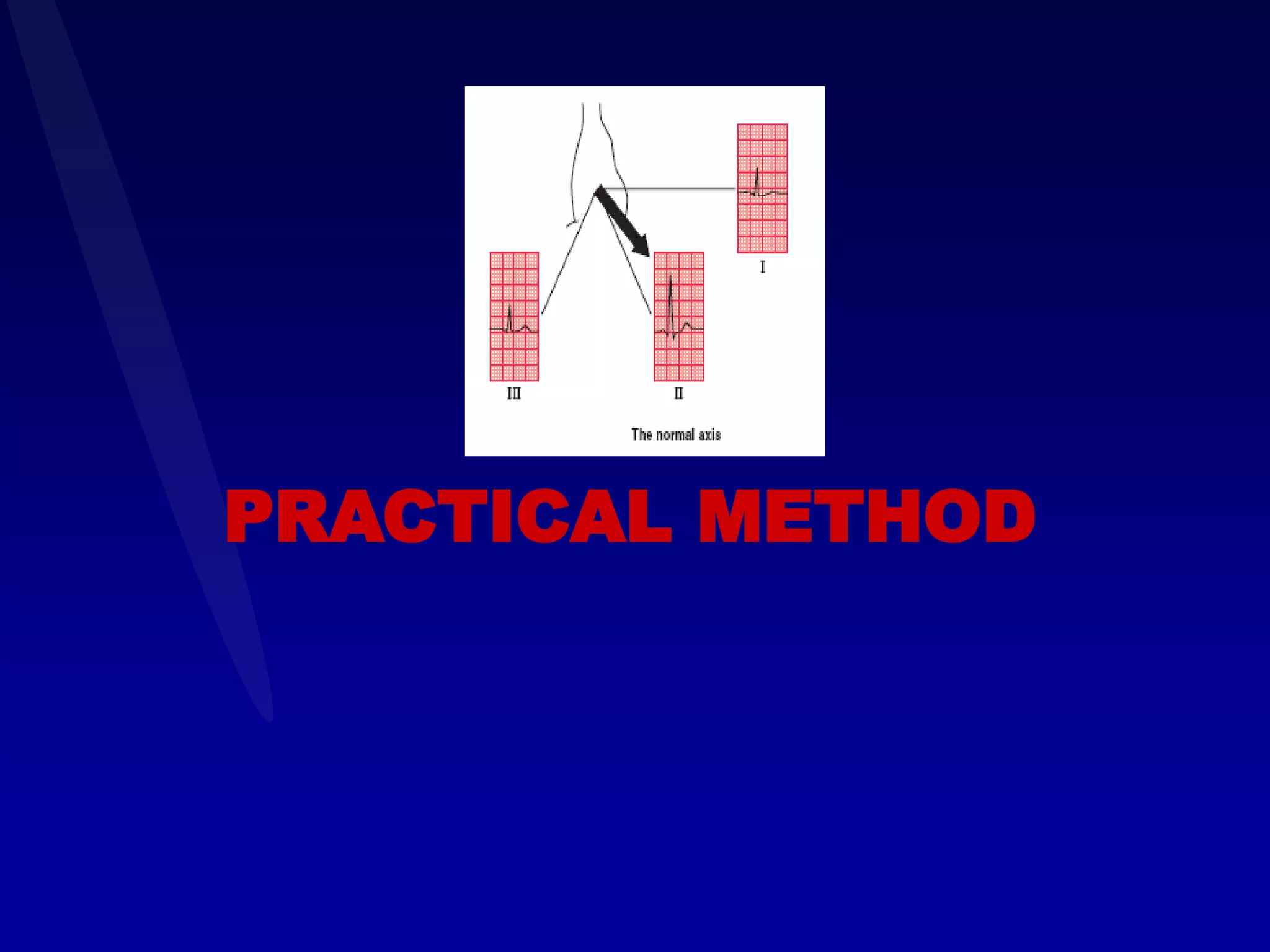
The document provides information on electrocardiography (ECG) including:
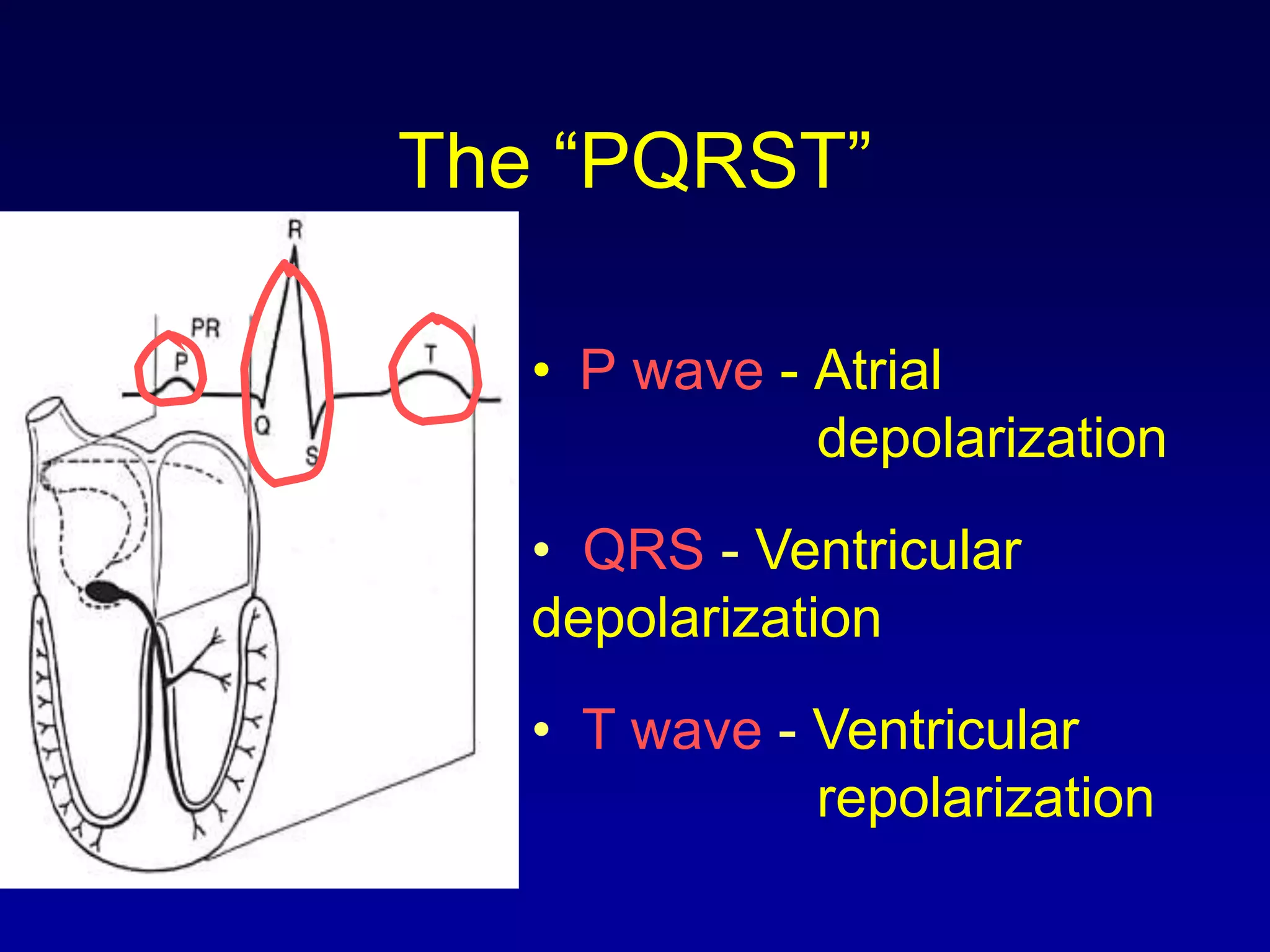
1. It describes the normal conduction system of the heart and how it relates to the ECG waves and intervals.
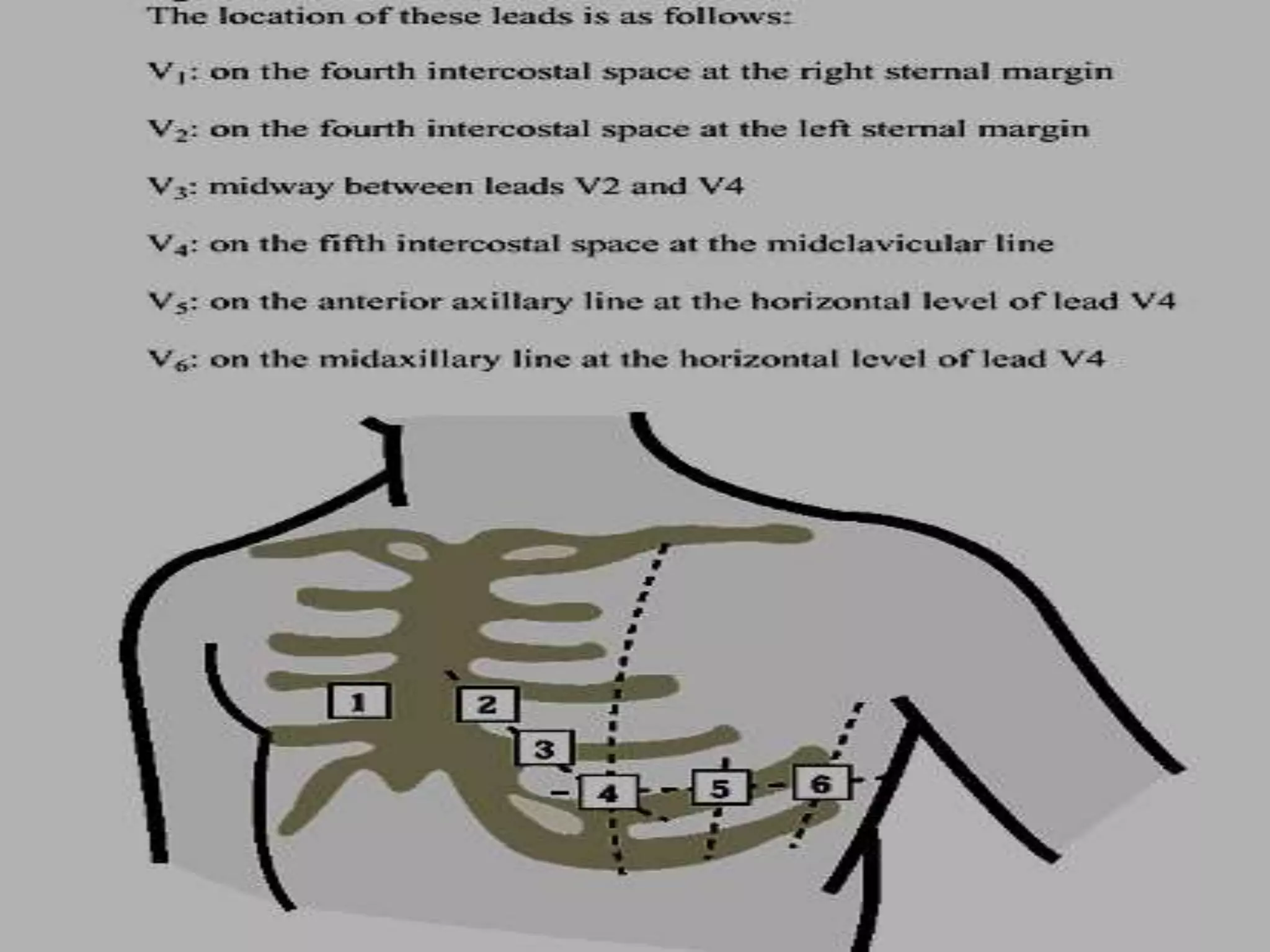
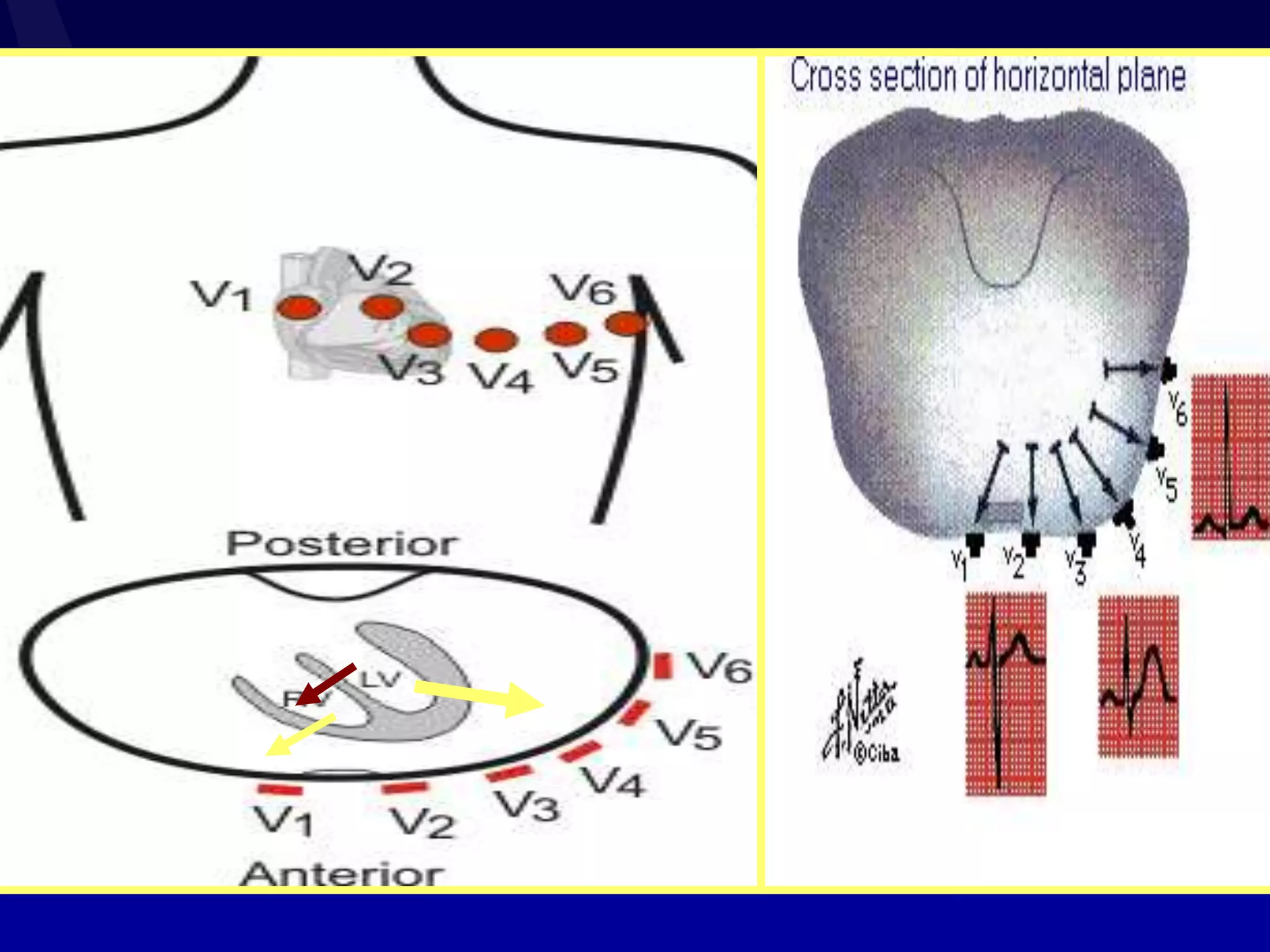
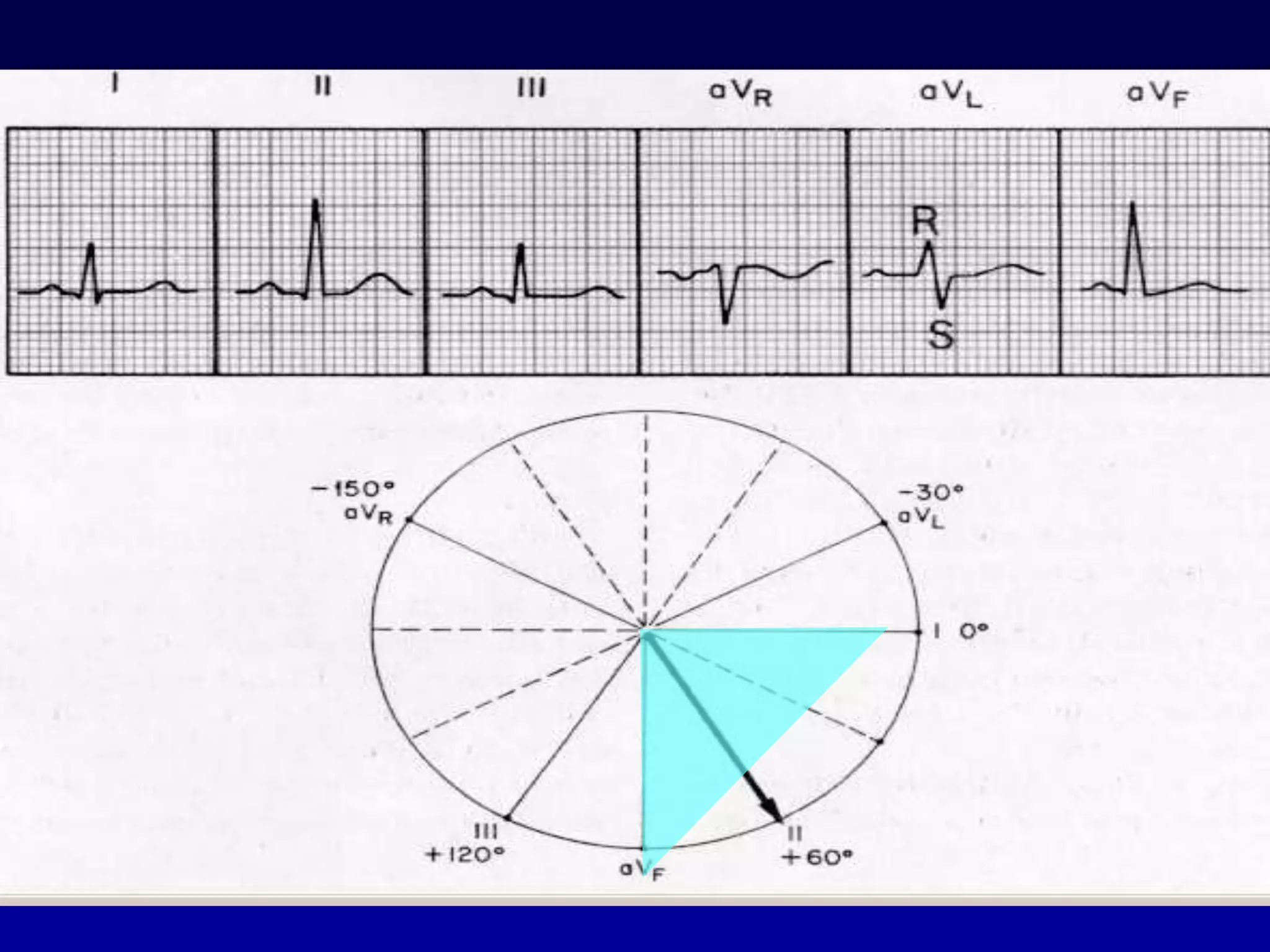
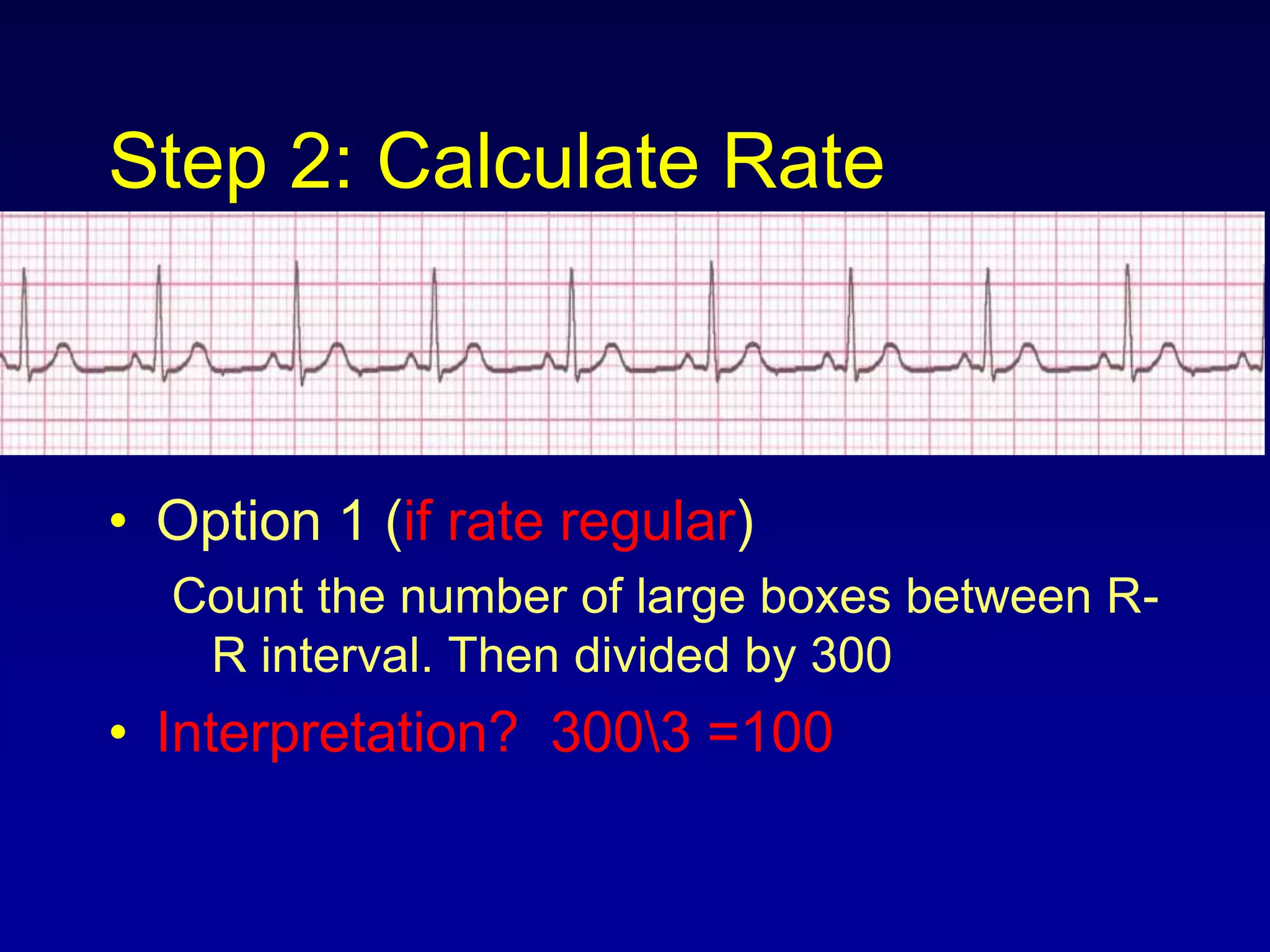
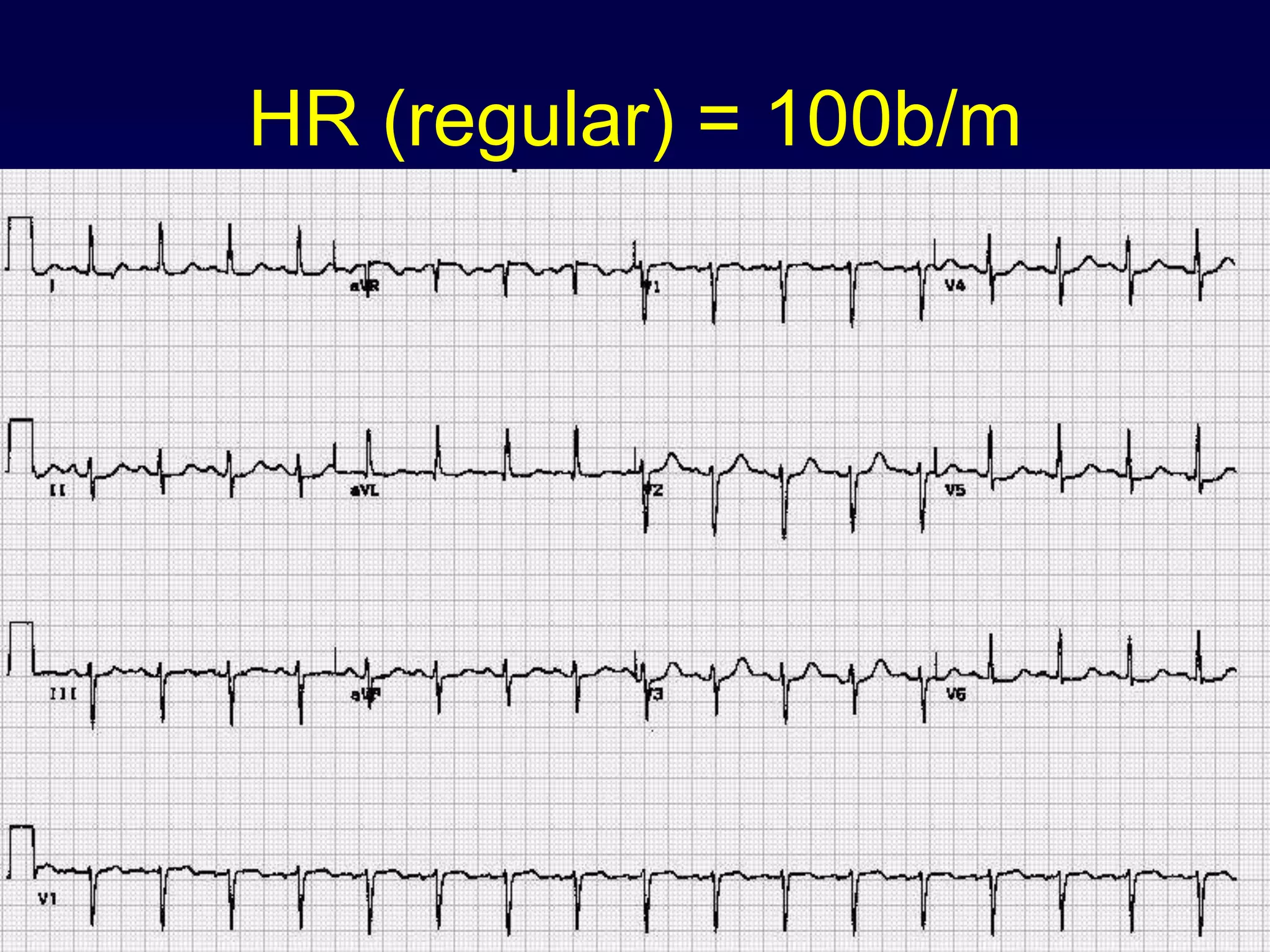
2. It explains the basics of reading an ECG such as determining the heart rate, analyzing waves, segments, and intervals, and identifying abnormalities.
3. It discusses ECG findings associated with various cardiac conditions like myocardial infarction, left ventricular hypertrophy, bundle branch blocks, and cardiac arrhythmias.