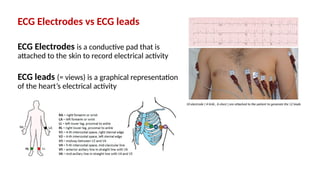
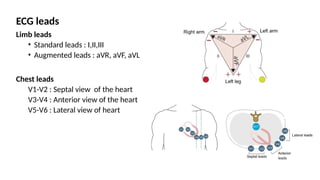
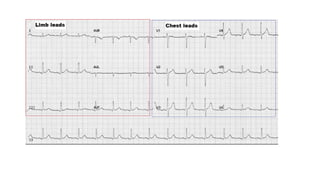
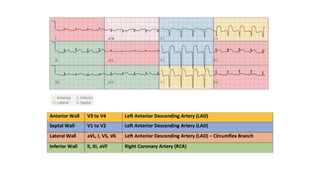
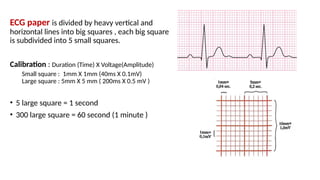
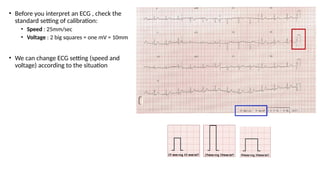
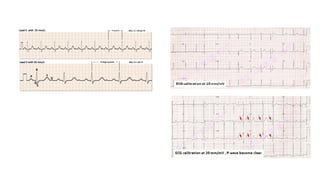
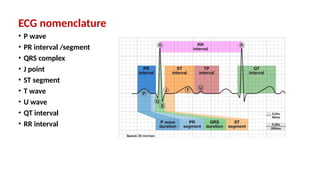
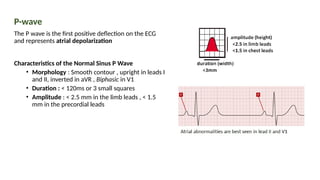
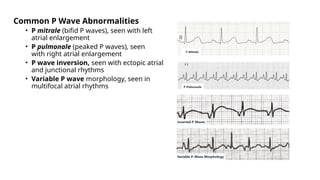
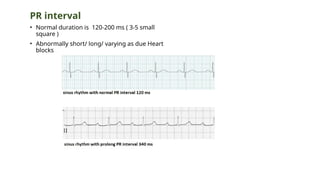
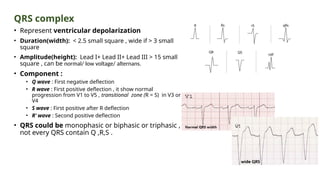
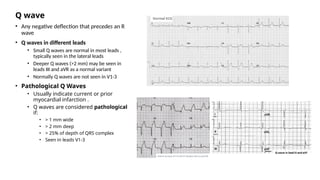
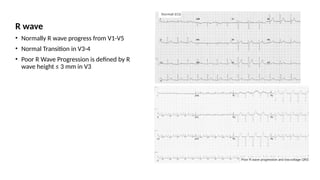
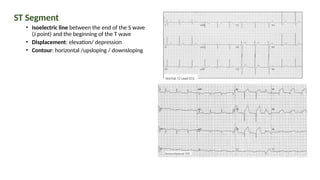
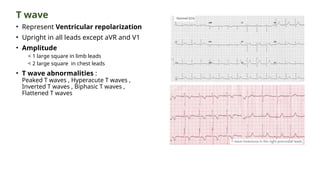
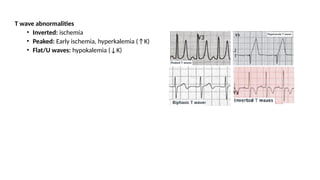
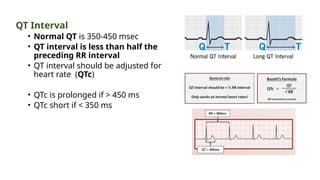
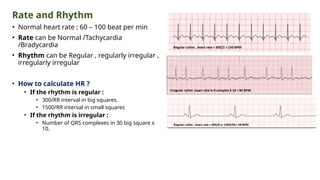
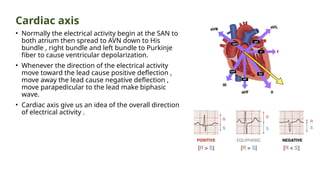
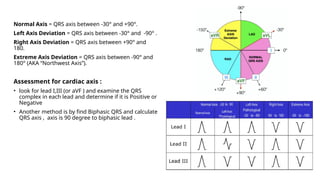
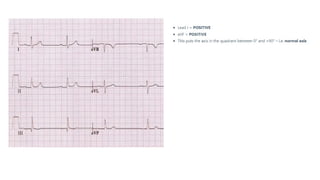
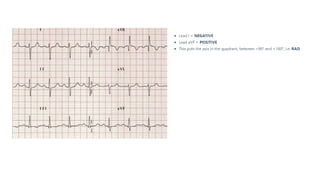
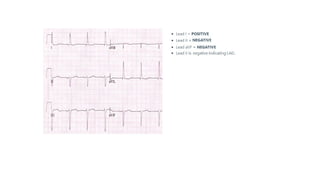
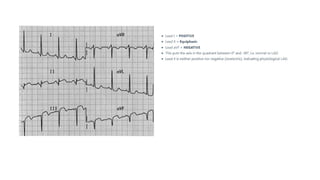
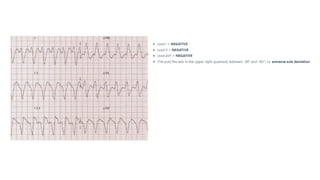
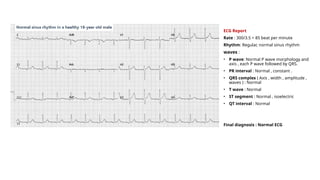
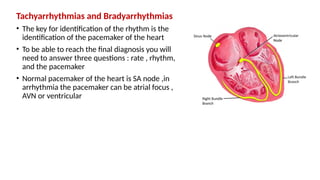
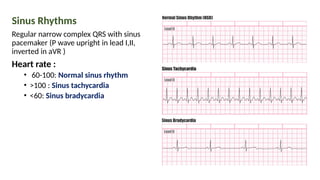
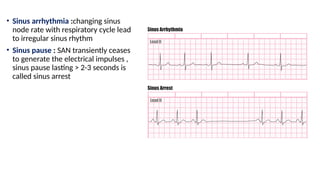
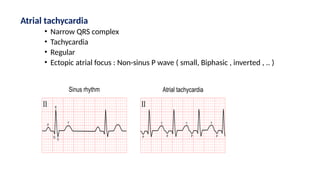
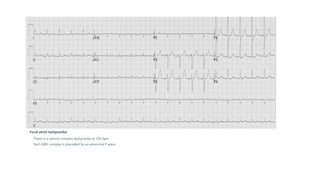
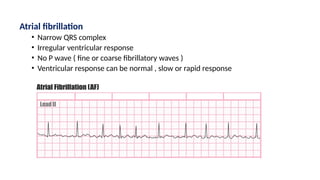
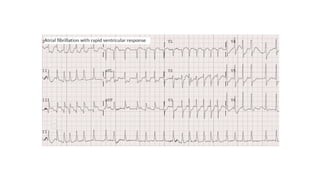
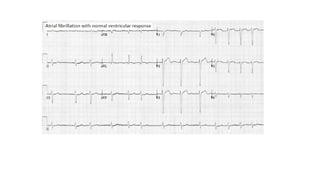
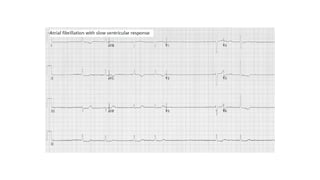
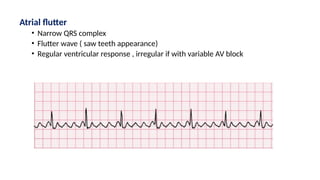
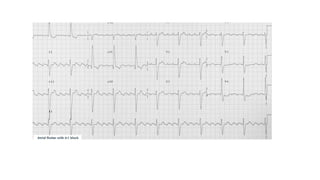
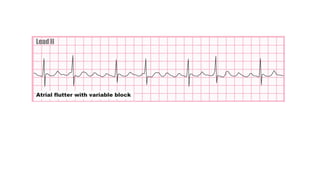
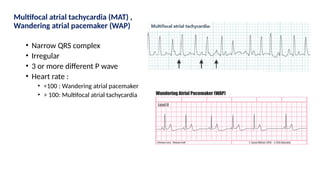
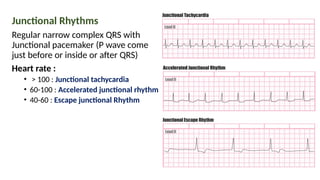
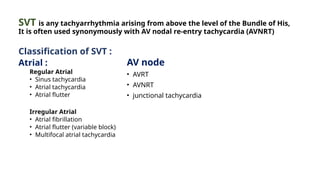
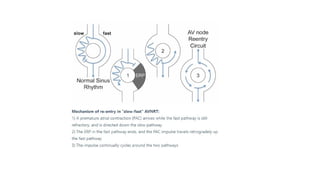
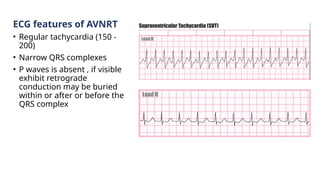
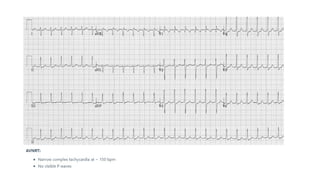
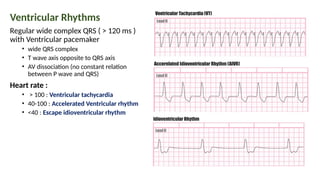
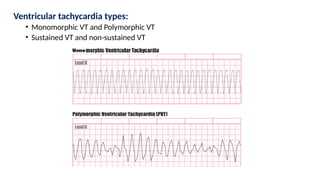
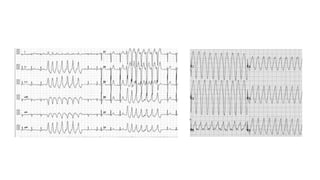
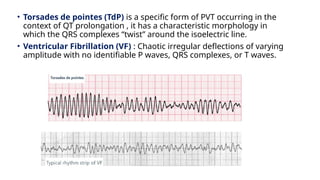
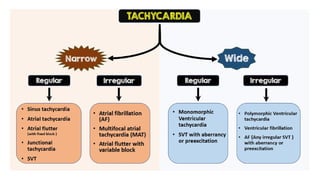
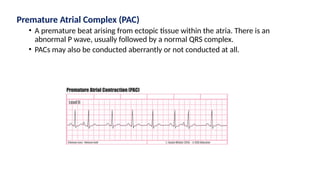
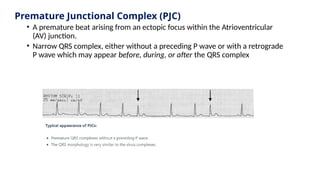
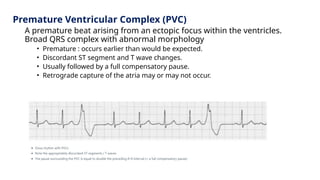
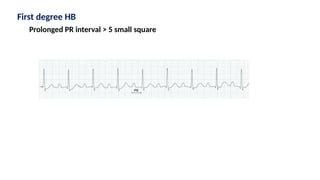
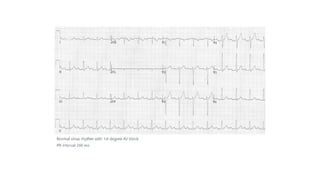
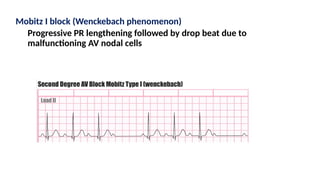
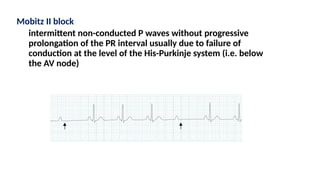
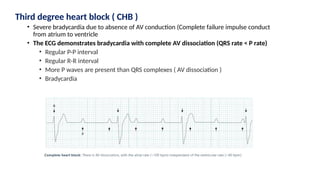
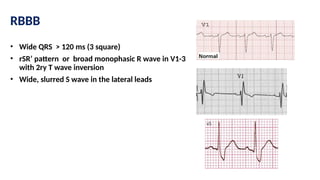
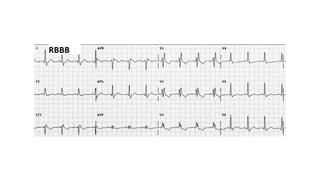
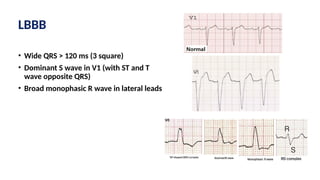
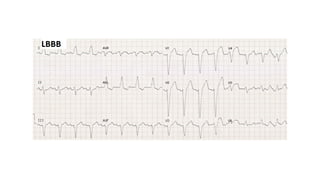
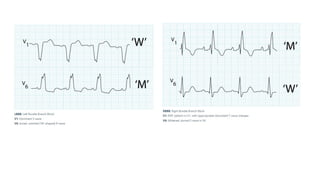
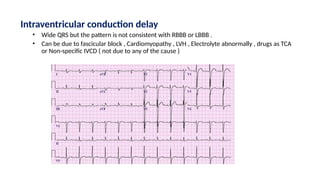
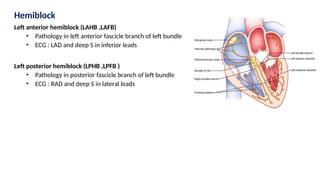
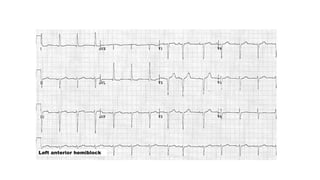
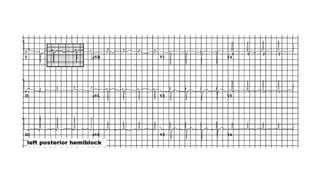
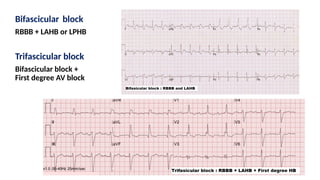
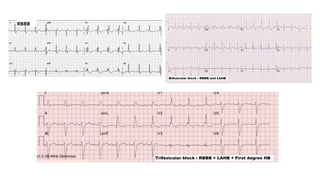
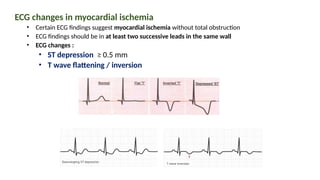
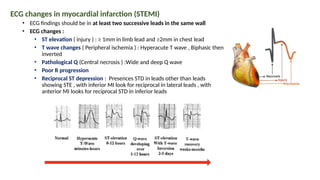
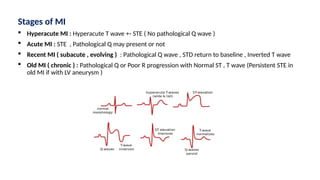
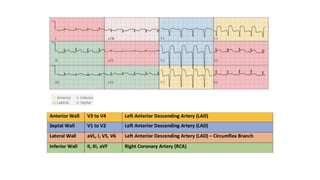
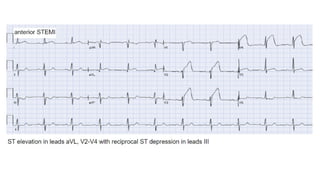
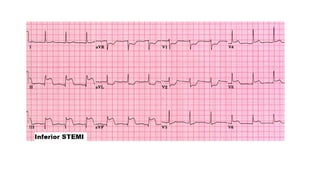
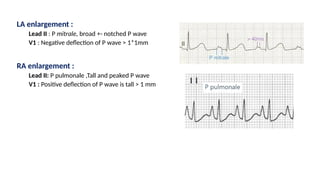
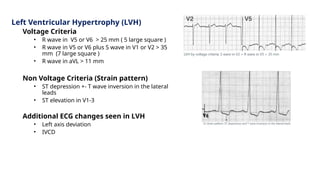
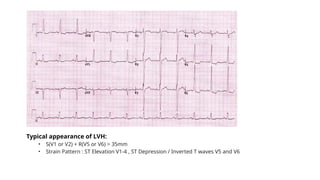
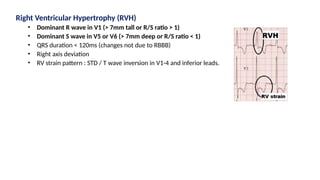
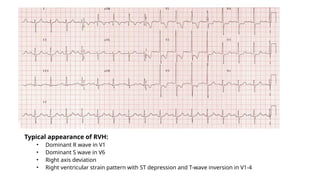
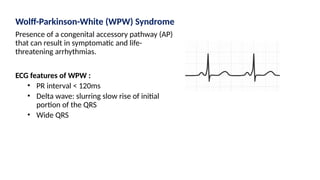
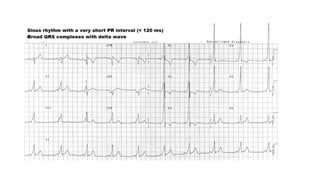
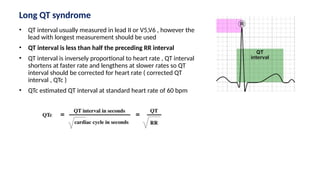
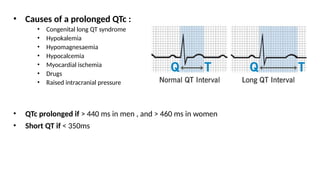
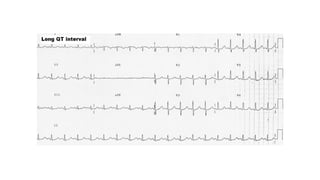
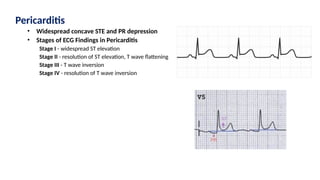
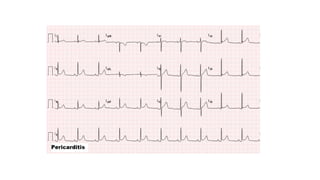
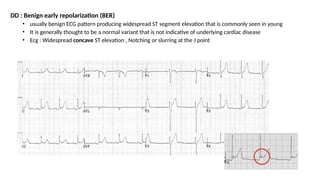
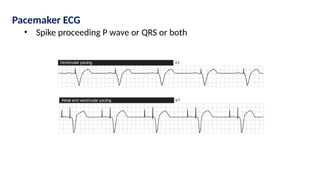
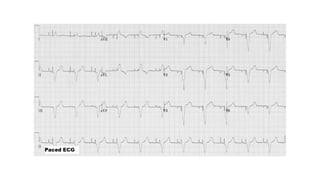
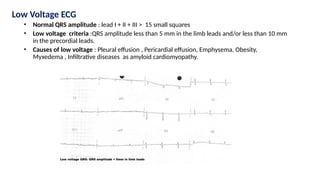
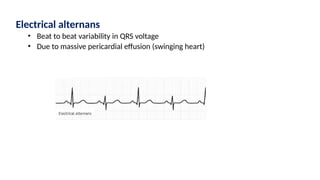
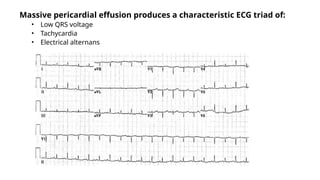
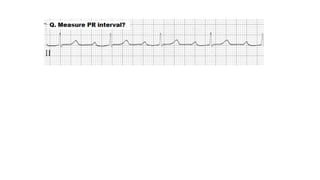
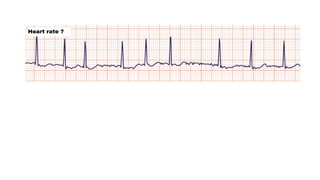
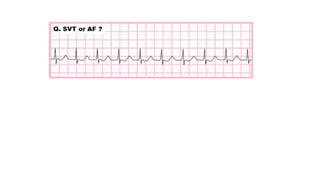
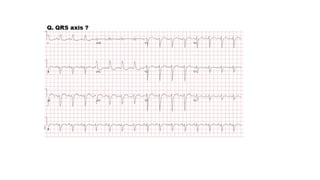
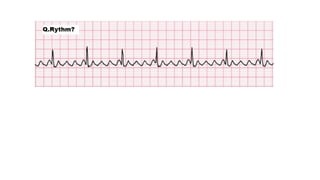
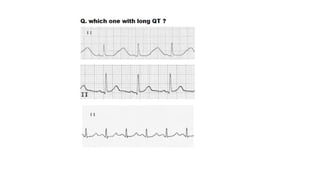
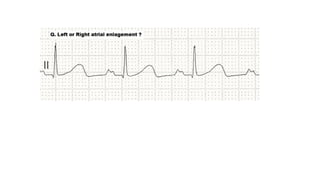
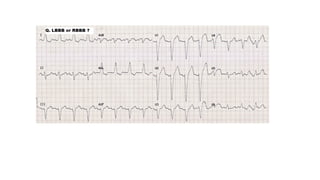
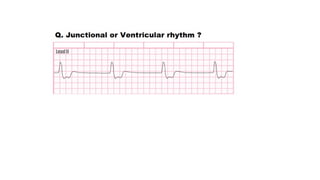
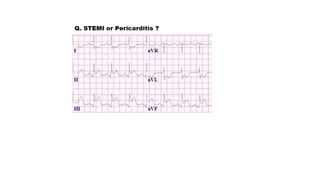
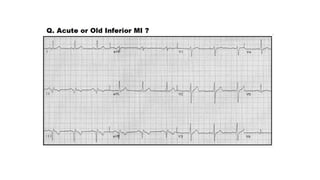
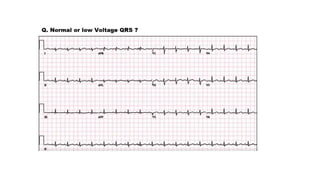
The document provides an extensive overview of the electrocardiogram (ECG), detailing its function, nomenclature, and various waveforms associated with cardiac electrical activity. It explains the key components of an ECG, including the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave, as well as the assessment of heart rate, rhythm, and pathological conditions. Additionally, it discusses abnormal ECG findings, heart blocks, and arrhythmias, offering guidelines on how to interpret and report ECG results.