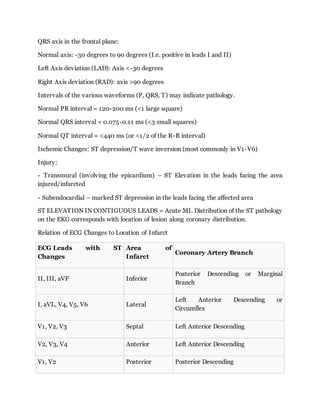
The ECG represents the electrical activity of the heart. Key things to assess include the rate, rhythm, intervals, axis, and any ischemic or injury changes. The standard ECG reports the QRS axis in the frontal plane from -30 to 90 degrees. ST elevation in contiguous leads indicates an acute MI, and the distribution of ST changes corresponds to the location of blockage in the coronary arteries. Characteristic sequential changes occur over time with an evolving MI.