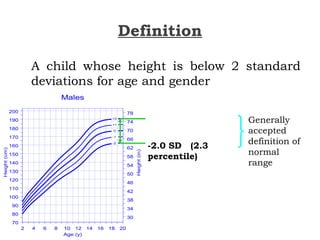
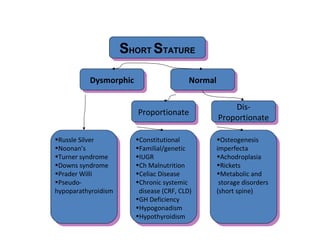
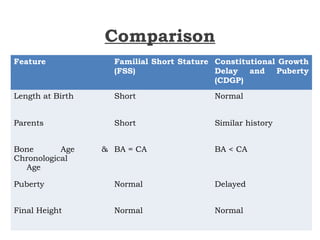
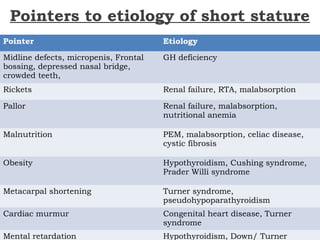
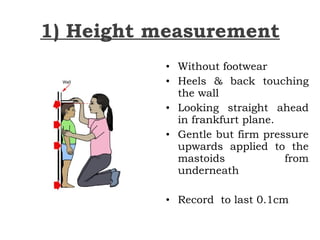
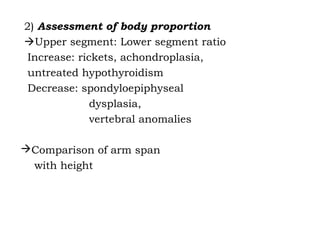
This document discusses short stature in children, defining it as height below 2 standard deviations for age and gender. It outlines factors that can affect height, including nutrition, hormones, and intrauterine growth. Short stature is classified as dysmorphic, proportionate, or disproportionate. Evaluation involves medical history, physical exam, auxiliary tests like bone age and growth hormone stimulation, and considering familial, constitutional, nutritional, endocrine, and genetic causes. Management depends on the underlying etiology and may include counseling, dietary changes, surgery, hormone replacement, or growth hormone therapy.