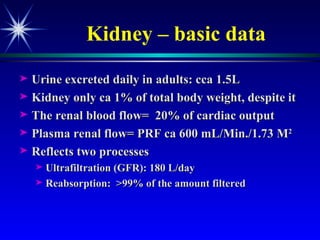
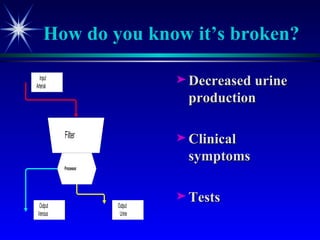
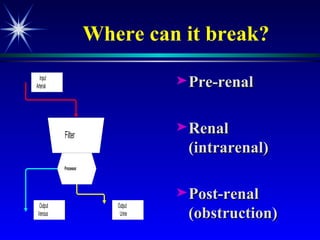
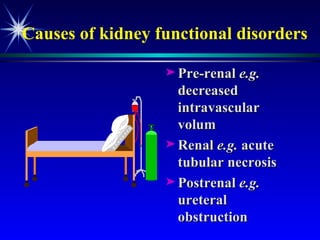
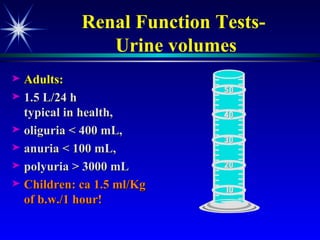
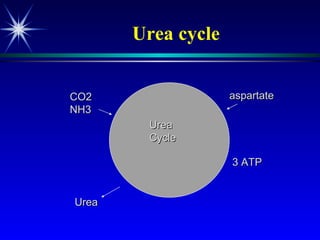
The document discusses various tests used to evaluate renal function, including tests of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and clearance tests. It describes how the kidney regulates water, electrolytes, and acid-base balance and produces hormones. Laboratory tests discussed include measures of creatinine, urea, urine output, protein, and osmolality. Causes of impaired kidney function are categorized as pre-renal, renal, or post-renal.







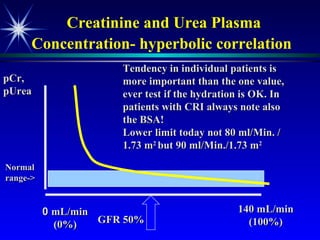




![Plasma creatinine vs. GFR not linear, hyperbolic correlation! GFR [pCreat] 140 mL/min (100%) 0 mL/min (0%) Change within an individual patient is usually more important than the absolute value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/renalfunctionsinchildren-100330004306-phpapp02/85/Renal-Functions-In-Children-22-320.jpg)