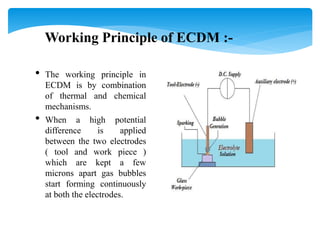
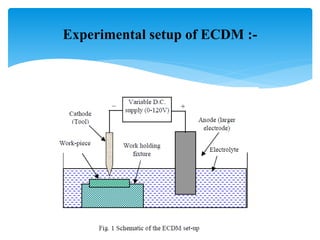
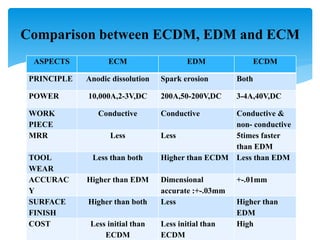
This document discusses electrochemical discharge machining (ECDM), which combines electrochemical machining (ECM) and electric discharge machining (EDM) to machine hard and brittle non-conductive materials like glass, quartz, and ceramics. It provides an introduction to ECDM, describes the working principle involving thermal and chemical material removal, lists the main subsystems of an ECDM setup, and compares ECDM to ECM and EDM in terms of material removal rate, accuracy, surface finish, and other factors. Key application areas of ECDM include micro-holes, grooves, and complex shapes in non-conductive materials for industries like turbines, filters, electronics, and