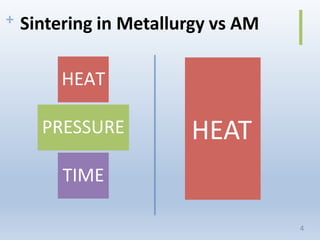
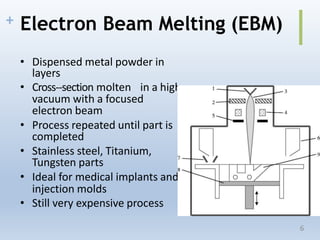
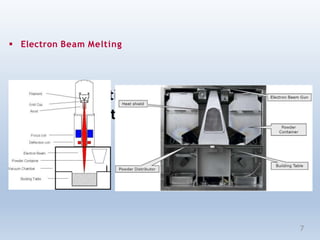
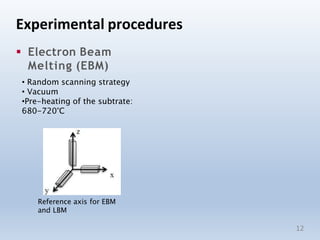
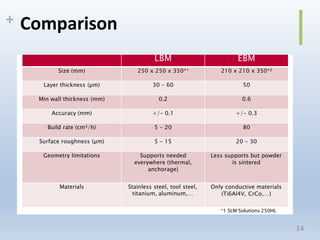
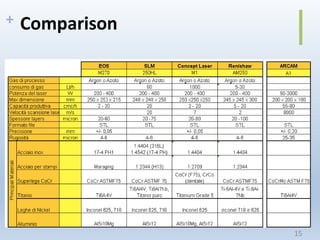
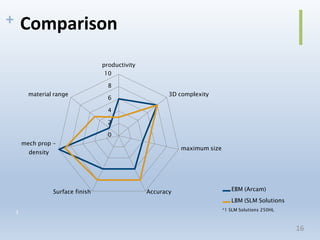
This document discusses electron beam melting (EBM), a type of additive manufacturing that uses an electron beam to melt and fuse metal powder layers together to build parts. EBM produces fully dense, void-free metal parts. It differs from conventional sintering used in powder metallurgy by fully melting layers instead of just bonding powders. The document compares EBM to laser beam melting (LBM), noting EBM's advantages as higher productivity, ability to build larger parts, and capability to build with electrically conductive materials like titanium alloys. Drawbacks include longer cooling times between builds and challenges removing powder from internal channels.