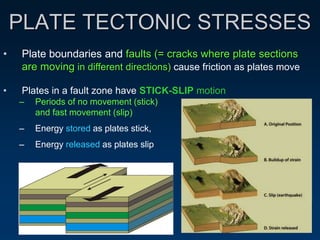
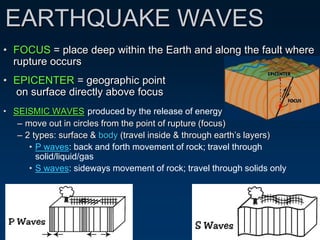
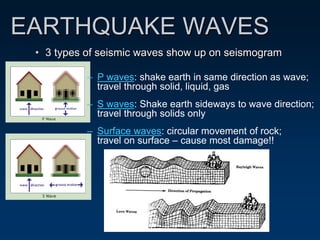
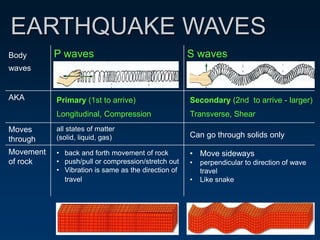
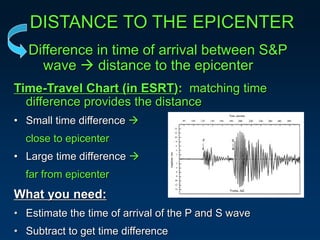
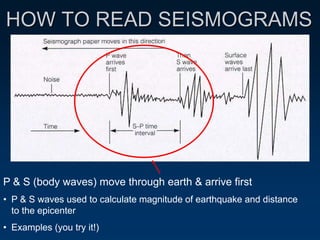
Earthquakes are caused by the sudden movement or breakage of the Earth's crust along plate boundaries and faults. Plate tectonic stresses build up as plates stick together over time, storing energy. When the stresses exceed the strength of the rocks, the plates slip rapidly, releasing stored energy in the form of seismic waves. There are three main types of seismic waves - P waves, which move rock back and forth; S waves, which move rock sideways; and surface waves, which cause the most earthquake damage as they travel along the Earth's surface. Seismograms record these wave arrivals and amplitudes, which can provide information about the distance to the earthquake epicenter.