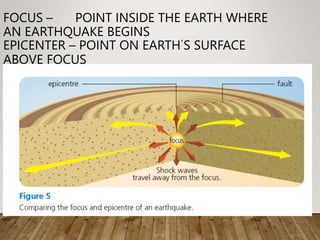
1) Earthquakes are caused by the release of energy along faults in the Earth's crust due to the buildup of pressure.
2) There are three main types of seismic waves that radiate out from the earthquake focus: primary (P) waves, secondary (S) waves, and surface waves.
3) Earthquakes are measured using the Richter Scale, which quantifies the amount of energy released by the earthquake. The strongest earthquake ever recorded was magnitude 9.5.