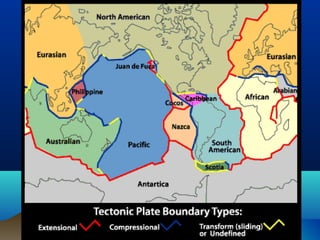
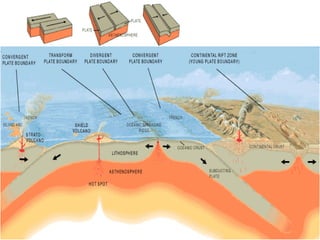
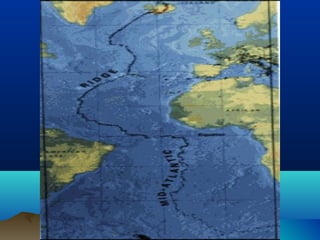
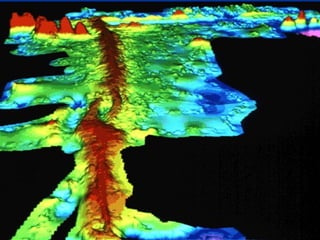
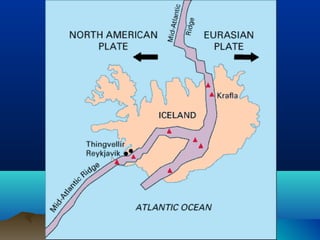
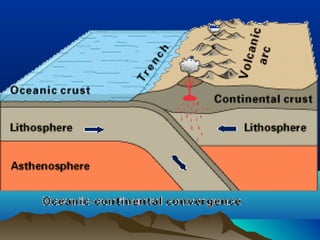
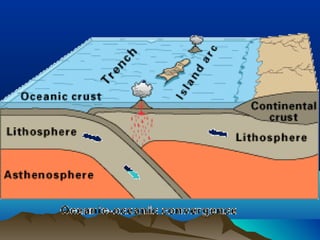
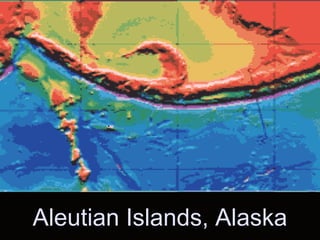
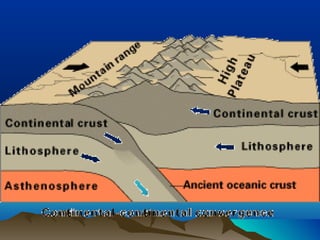
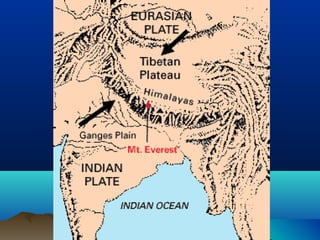
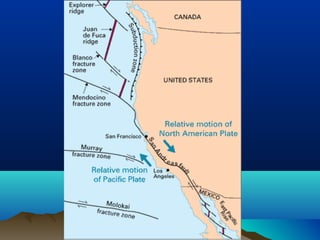
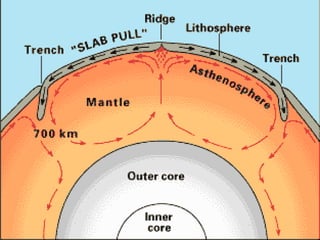
The theory of plate tectonics explains that Earth's outer layer is made up of plates that have moved throughout geological history. These plates float on top of the mantle and move at boundaries where they diverge, converge, or slide past one another. Convection currents in the upper mantle provide the driving force that causes plates to move over time.