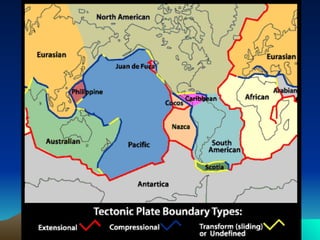
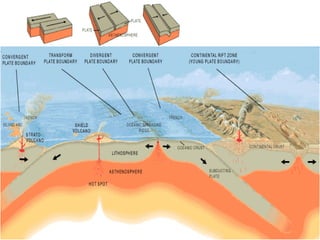
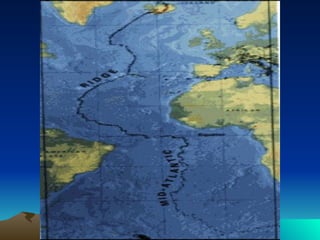
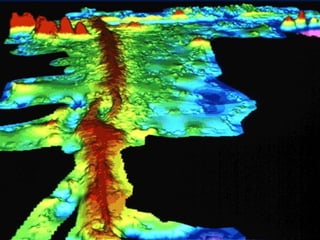
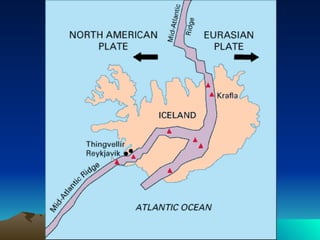
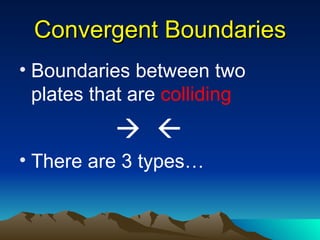
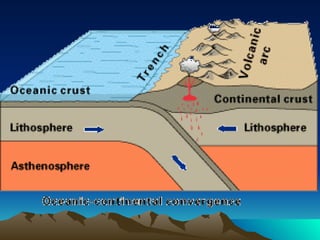
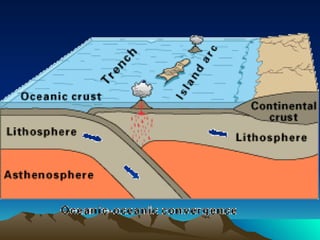
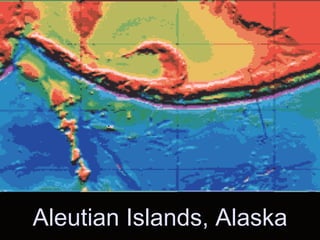
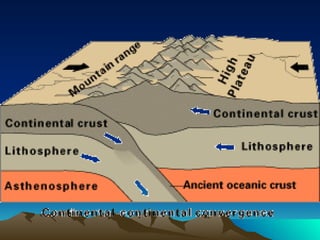
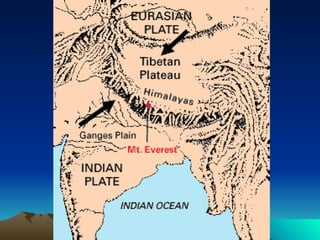
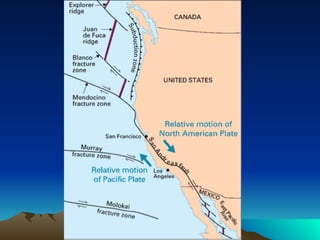
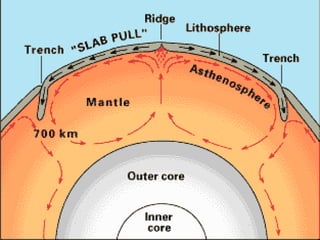
The document discusses plate tectonics, including that the Earth's crust is broken into plates that move atop the mantle. There are two types of plates - oceanic and continental. Plates interact at three types of boundaries: divergent boundaries where plates separate and new seafloor is created, convergent boundaries where plates collide resulting in subduction zones or mountain building, and transform boundaries where plates slide past one another causing earthquakes. Convection currents in the underlying mantle are cited as the cause of plate tectonic movement.