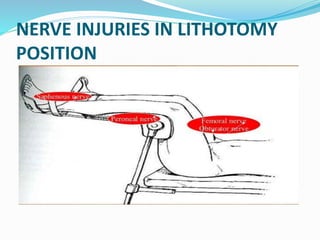
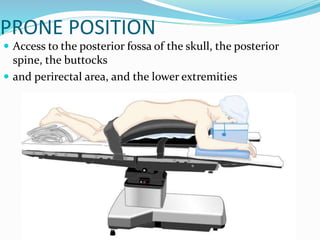
Patient positioning during anesthesia and surgery requires careful consideration of anatomical and physiological factors to prevent injury. The surgical position, procedure details, and patient characteristics and risks must be assessed to choose a position that allows procedure access while avoiding interference with breathing, circulation, nerve compression, or pressure points. Common positions like supine, lithotomy, lateral, and prone each have specific techniques, considerations, and potential risks that the anesthesia team must understand and address.