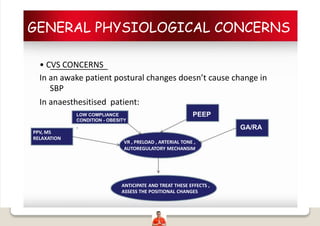
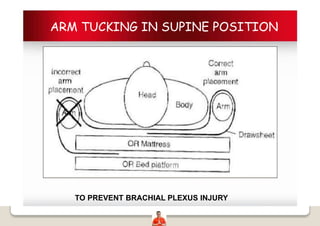
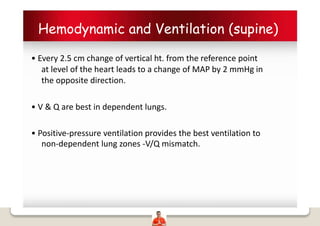
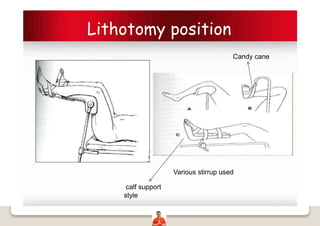
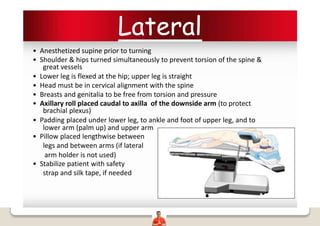
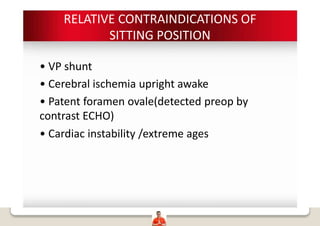
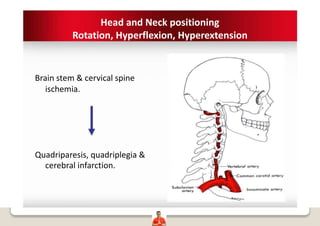
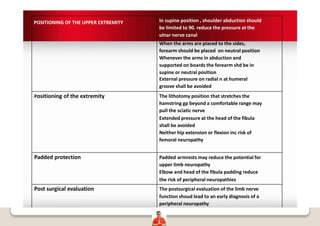
Patient positioning is a joint responsibility of the surgeon and anesthesiologist to balance surgical needs and risks to the patient. Key factors to consider include the procedure, patient characteristics, and physiological impacts of different positions. Common positions include supine, lateral, lithotomy and prone, each with benefits and risks requiring precautions like padding pressure points. The team must plan positioning prior to surgery based on these considerations.