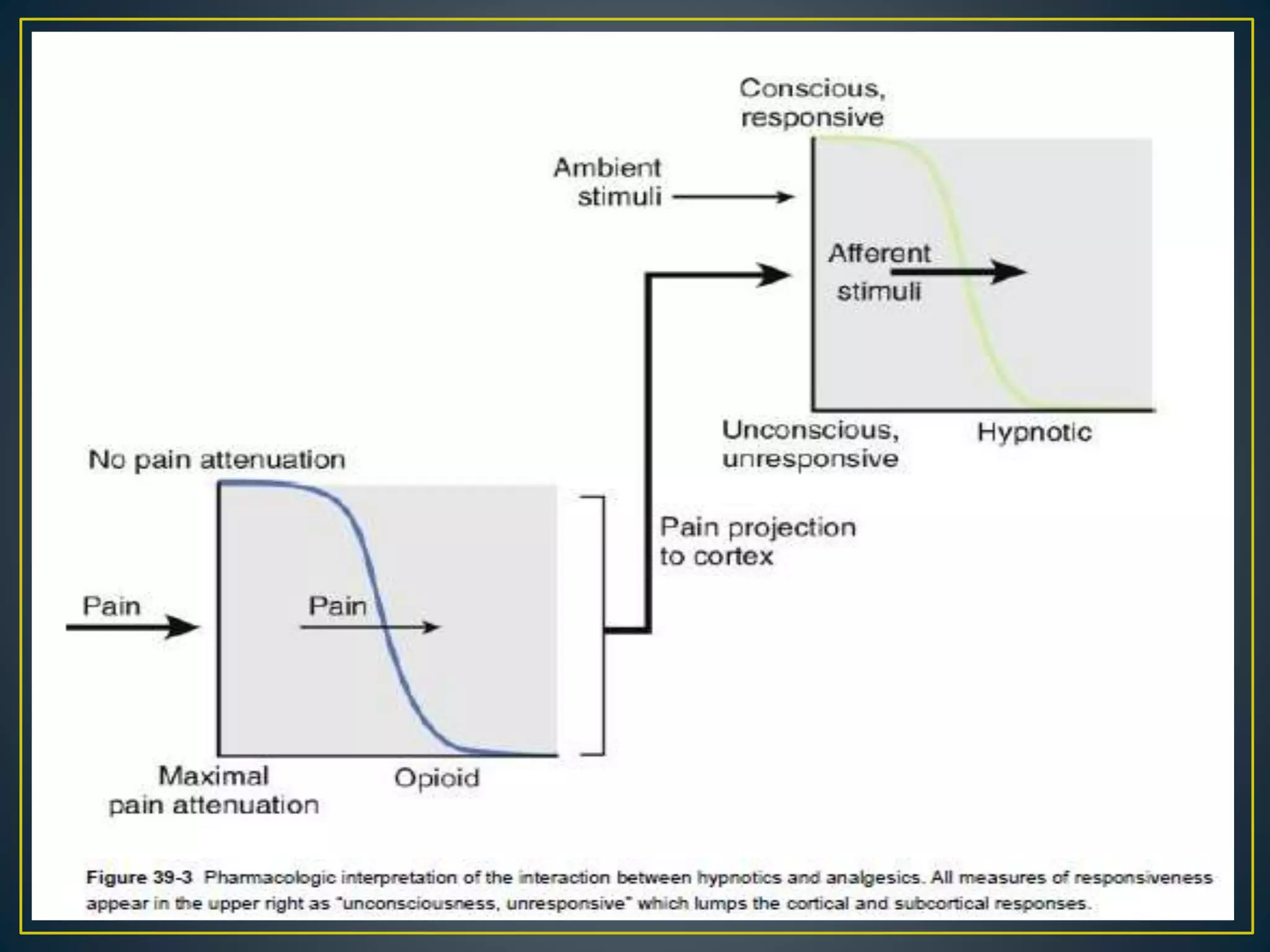
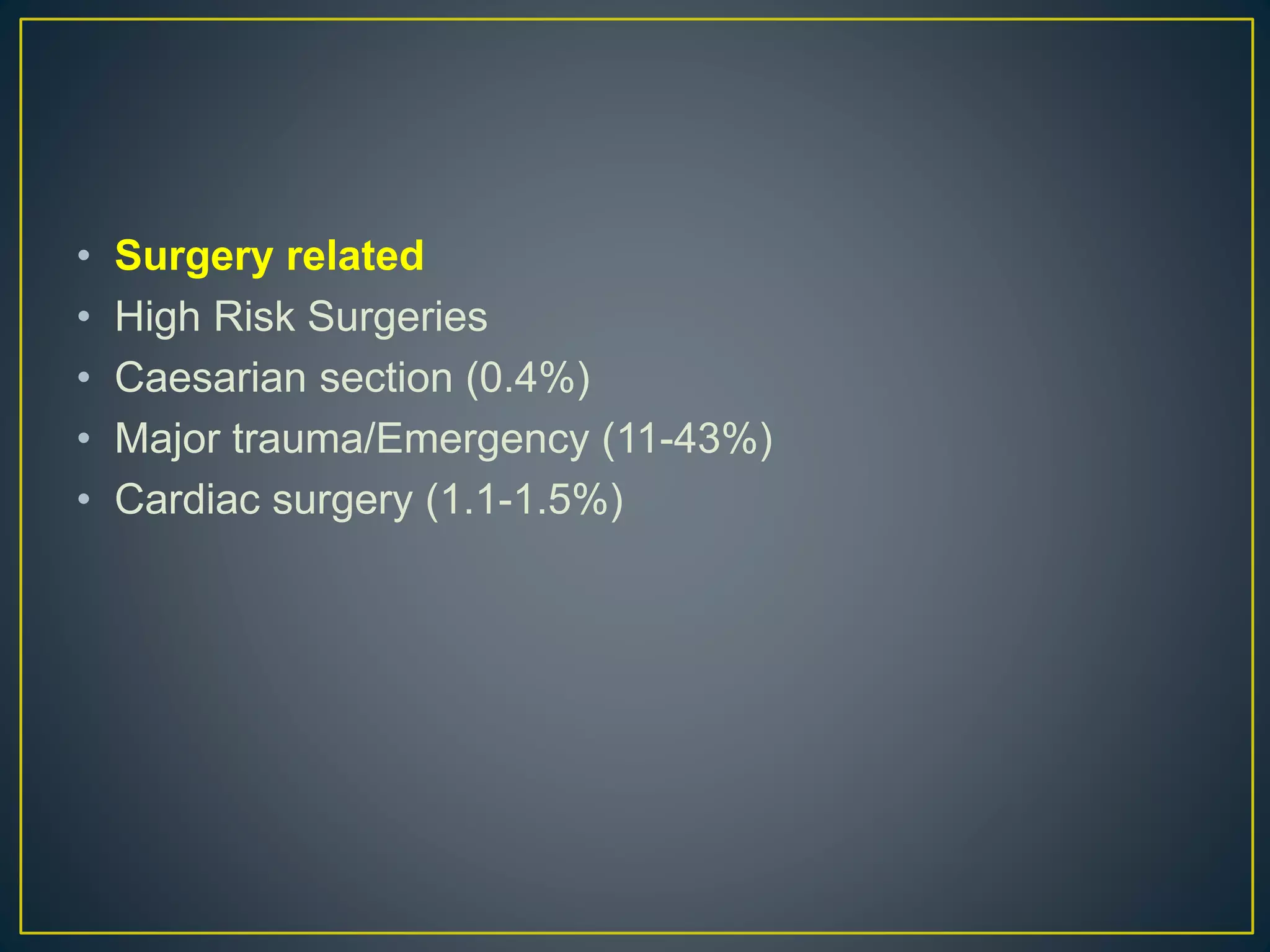
This document provides information about general anesthesia and intraoperative awareness. It discusses what general anesthesia is, how its depth is determined, and the different stages of awareness and memory formation. It also covers risk factors for awareness, its incidence and impact on patients. Monitoring techniques like BIS, entropy and EEG patterns are described. Finally, it discusses approaches to preventing and managing cases of intraoperative awareness.