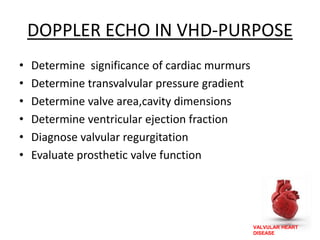
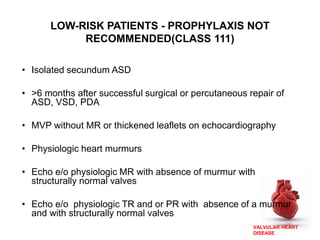
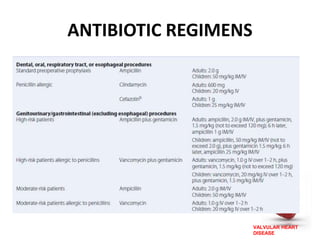
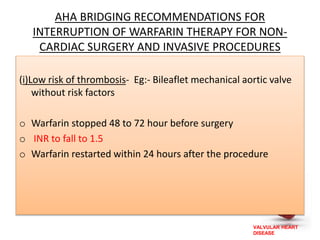
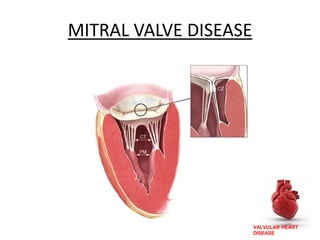
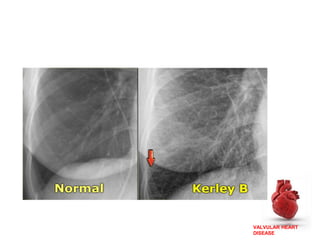
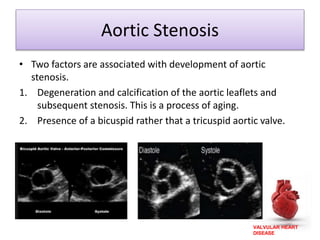
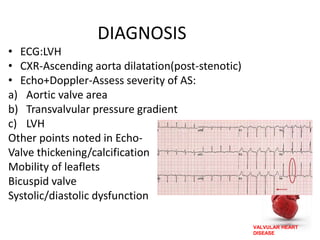
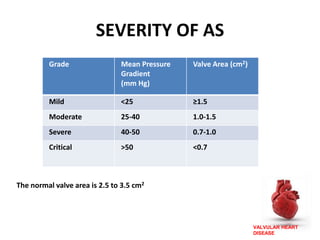
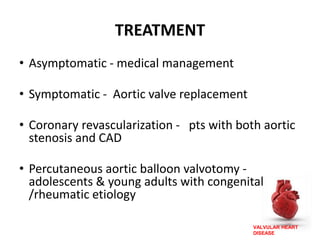
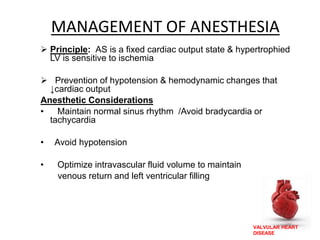
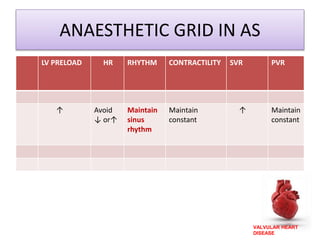
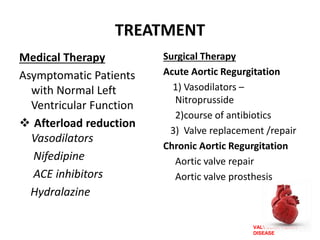
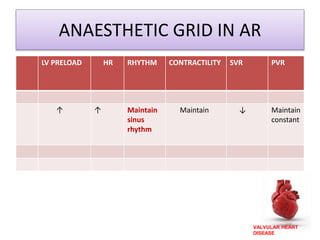
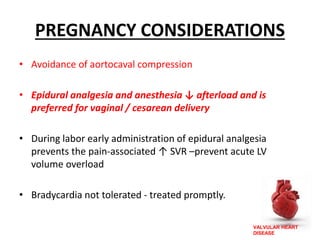
Valvular heart disease, specifically mitral stenosis, places a hemodynamic burden on the heart over time. The disease results in a narrowed mitral valve opening that obstructs blood flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle. This obstruction can lead to elevated left atrial pressure and pulmonary hypertension. Symptoms include breathlessness and fatigue. Echocardiography is used to evaluate the severity based on mitral valve area and pressure gradients. Treatment involves managing symptoms medically or surgically replacing/repairing the valve. Anesthetic management focuses on maintaining preload, controlling heart rate, and avoiding pulmonary vasoconstriction.