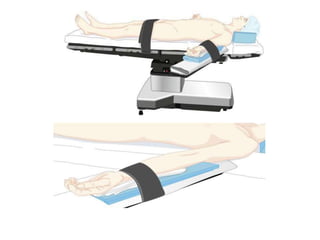
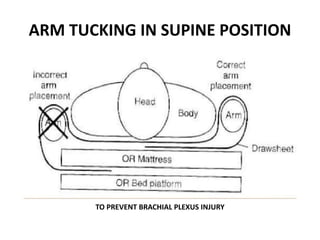
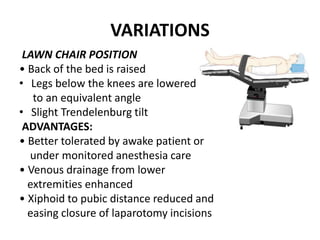
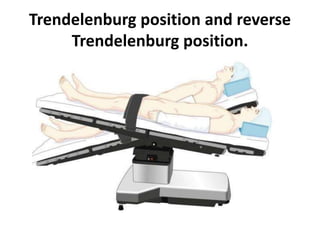
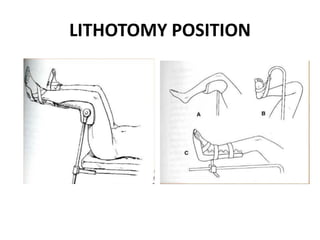
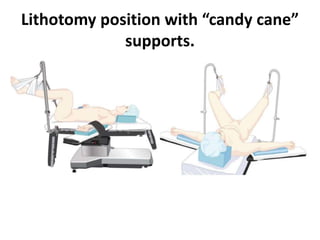
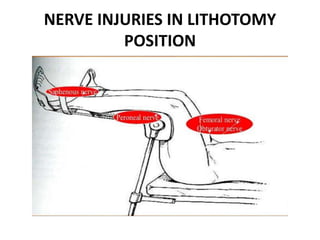
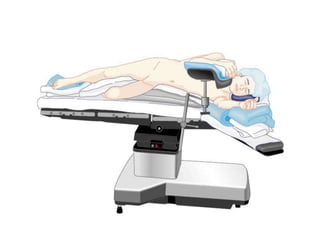
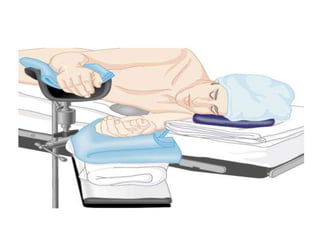
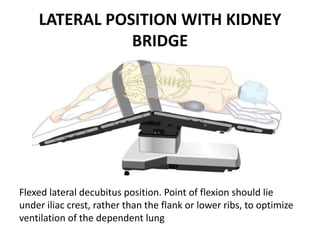
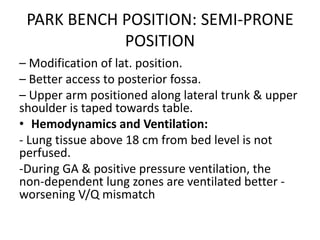
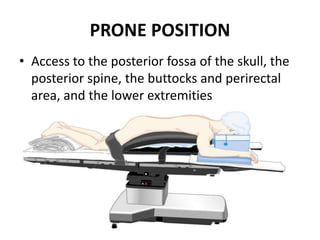
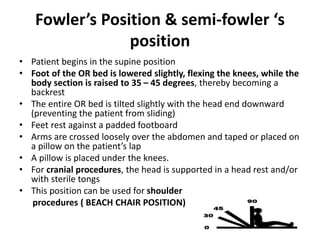
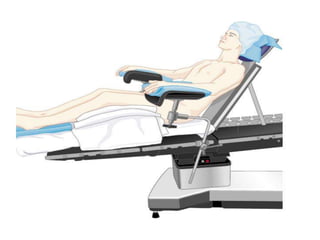
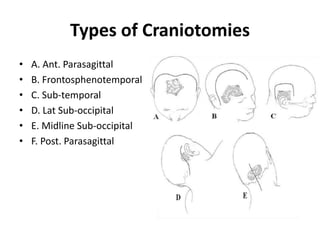
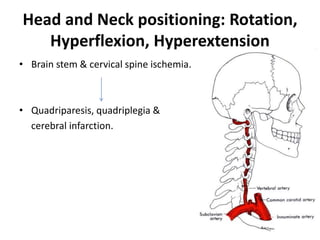
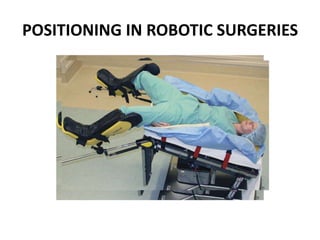
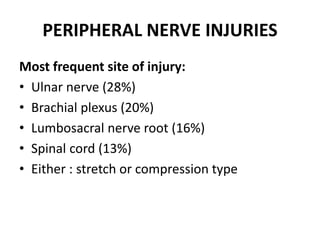
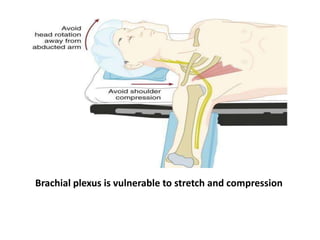
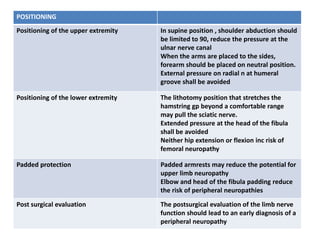
Patient positioning during anesthesia is crucial for ensuring surgical comfort while minimizing potential risks associated with different positions. Each surgical position, including supine, lateral, prone, lithotomy, and variations like Trendelenburg, has specific physiological implications and risks that need to be assessed based on individual patient requirements and procedure type. Awareness and careful planning can prevent complications such as nerve injuries and impaired circulation during anesthetic care.