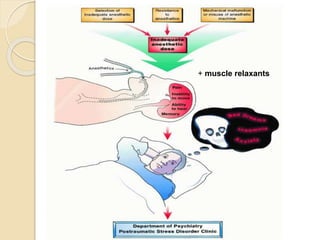
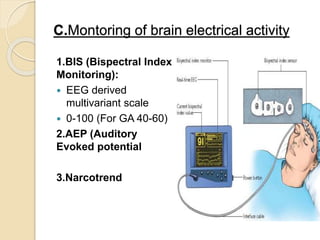
Anesthesia awareness occurs when a patient becomes conscious during a surgical procedure performed under general anesthesia and has recall of events. The incidence is 0.1-0.2% but higher for certain procedures like cardiac surgery. Patients at risk include women, those under 60, long surgeries, and prior awareness. Causes include light anesthesia, increased anesthetic requirements, and equipment errors. Patients commonly recall sounds and paralysis. Aftereffects may include PTSD. Prevention strategies include preoperative evaluation, proper equipment use, and intraoperative monitoring like BIS monitoring to maintain anesthesia levels.












![REFERENCES
Effects of different methods of general anesthesia on intraoperative
awareness in surgical patients Haijiao Yu, PhD and Di Wu, PhD∗
Posttraumatic stress disorder in aware patients from the B-aware
trial.Leslie K, Chan MT, Myles PS, Forbes A, McCulloch TJ Anesth
Analg. 2010 Mar 1; 110(3):823-8.
Chung HS. Awareness and recall during general anesthesia. Korean
J Anesthesiol 2014;66:339–45.
Awareness during anesthesia: how sure can we be that the patient
is sleeping indeed? G Kotsovolis1 and G Komninos2
[An anesthetized anesthesiologist tells his experience of waking up
accidentally during the operation].Peduto VA, Silvetti L, Piga M
Minerva Anestesiol. 1994 Jan-Feb; 60(1-2):1-5.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/anesthesiaawareness-190113140647/85/Anesthesia-awareness-19-320.jpg)