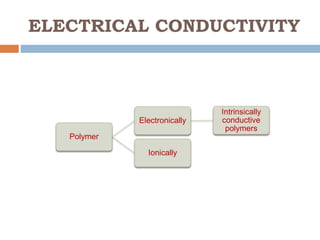
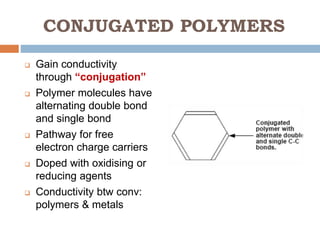
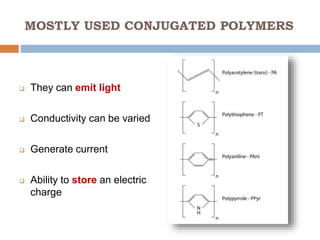
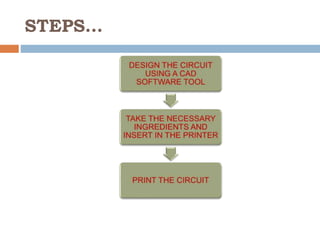
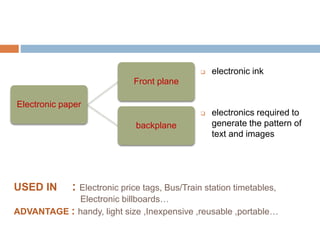
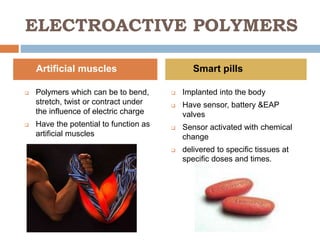
This document discusses polytronics, which involves making plastics electrically conductive by doping them with impurities. Certain plastics have inherent conductive and light-emitting properties. Conjugated polymers can also gain conductivity through chemical doping and have alternating double and single bonds along the polymer chain. This allows for applications like electronic paper, plastic batteries, artificial muscles using electroactive polymers, and OLED displays using organic thin films. Polytronics provides opportunities for cheap, flexible and lightweight electronic products printed on plastic substrates.