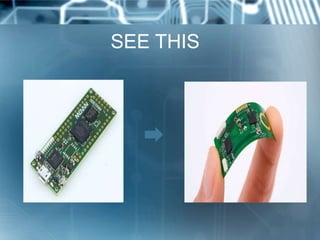
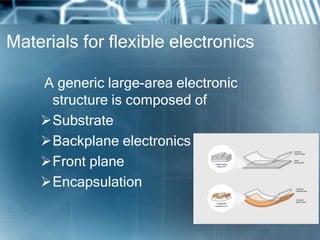
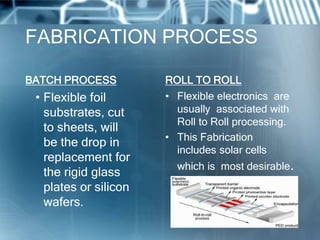
Flexible electronics are a new type of electronics that are flexible like human skin, unlike traditional rigid circuits. They are made by mounting electronic devices on flexible plastic substrates. Two main approaches to making them are transferring completed circuits to flexible substrates or directly fabricating circuits on flexible substrates. Flexible electronics have applications in smart cards, e-readers, displays, wearables and more. They are lighter weight and consume less energy than rigid circuits, though manufacturing precision is currently challenging. Researchers hope flexible electronics will create new opportunities and eventually be cheaper to produce than today's rigid electronics.