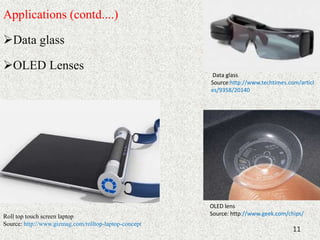
The document presents an overview of organic electronics, highlighting its applications such as OLED, OFET, and organic solar cells. Advantages of organic electronics include flexibility, low cost, and lightweight design compared to traditional inorganic electronics. Future prospects include smart textiles and enhancements in everyday technology, indicating a growing demand for organic solutions.





![OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode)[2]
First developed in early 1950’s.
Multiple organic layer sandwiched between two
electrodes marked as cathode and transparent anode.
Principle: Electroluminescence.
Doesn’t require any backlight; self emitting
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/applicationsoforganicelectronics-140901065449-phpapp02/85/Applications-of-organic-electronics-7-320.jpg)



![OFET(Organic Field-Effect Transistor)[1]
First OFET in 1987
Aromatic hydrocarbons based on linearly arranged benzene
rings
Tendency to form highly ordered films at low temperatures
12
OFET
Source: http://www.dileepnanotech.com/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/applicationsoforganicelectronics-140901065449-phpapp02/85/Applications-of-organic-electronics-12-320.jpg)



![OSC(ORGANIC SOLAR CELL)[3]
Conductive organic polymers and organic molecule
photovoltaic effect.
Rollable organic solar cell.
16
Rollable solar cell
Source:http://www.scorigin.com/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/applicationsoforganicelectronics-140901065449-phpapp02/85/Applications-of-organic-electronics-16-320.jpg)



![REFERENCE
[1]Hagen marien,Michel S.J.Steyaert’’On the applications of organic electronics on
foil’’IEEE solid state circuit magazine 2012.
[2] Ananth Dodabalapur ’’organic and polymer transistor for electronics’ The University
of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX 78733, USA 2006.
[3] Simon Forge and Colin Blackman, Sven Lindmark,’’ OLEDs and E-PAPER: Their
Disruptive Potential for the European Display Industry’’, EUR 23989 EN 2009.
[4] Tom J. Savenije’’ Organic solar cells’’ Tom J. SavenijeDelftChemTech, Faculty of
Applied Sciences Delft University 2010.
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/applicationsoforganicelectronics-140901065449-phpapp02/85/Applications-of-organic-electronics-20-320.jpg)
