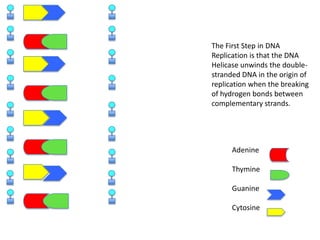
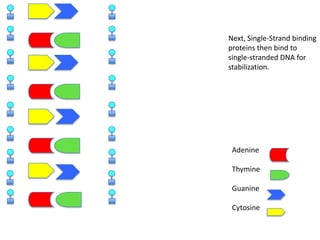
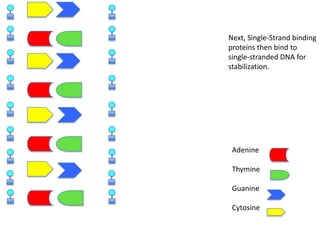
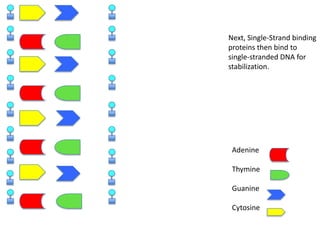
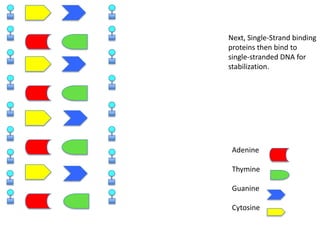
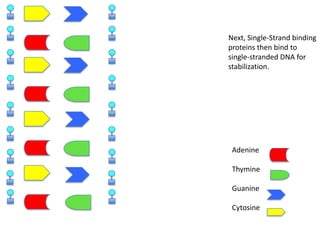
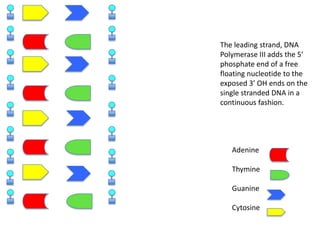
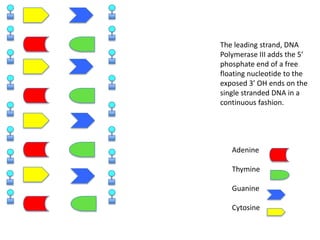
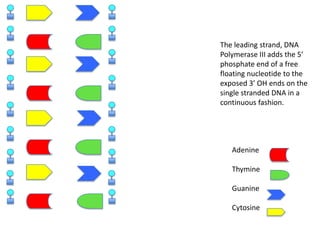
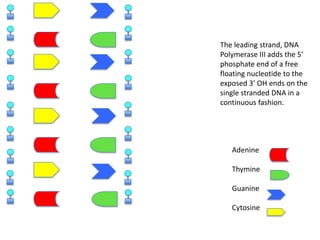
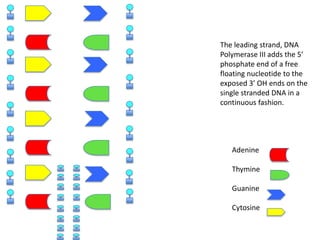
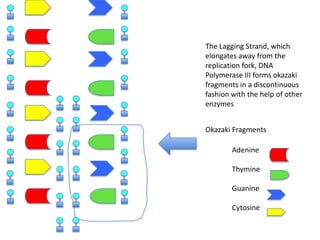
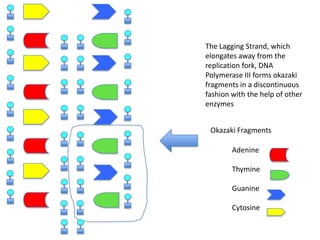
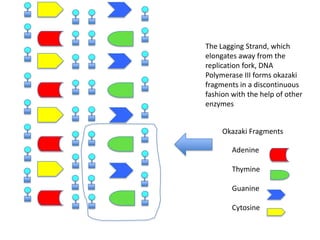
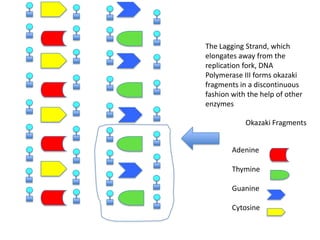
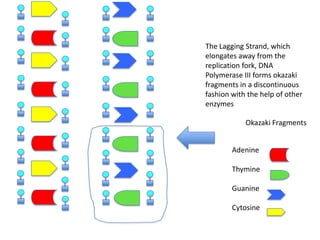
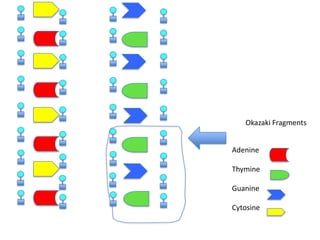
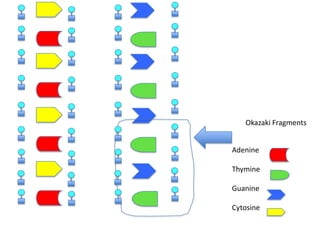
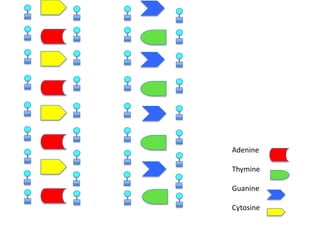
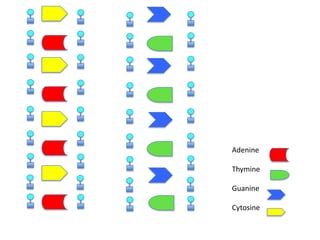
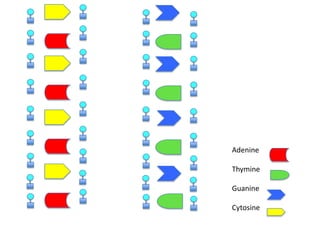
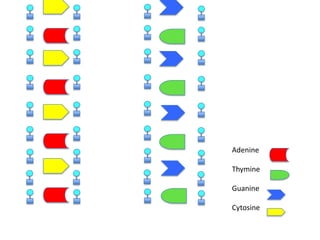
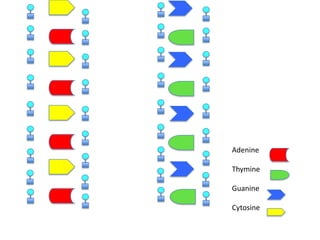
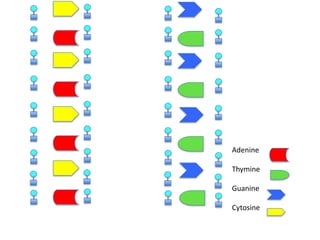
DNA replication is the process where DNA duplicates itself during cell division. It involves unwinding the double-stranded DNA at the origin of replication using the enzyme helicase. Single-strand binding proteins then stabilize the separated strands. DNA polymerase adds complementary nucleotides to each exposed strand in different ways, continuously for the leading strand but discontinuously in fragments called Okazaki fragments for the lagging strand.