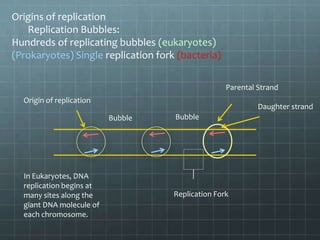
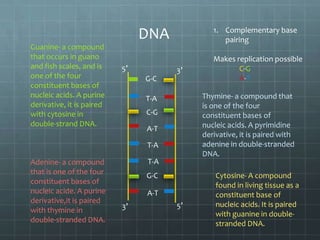
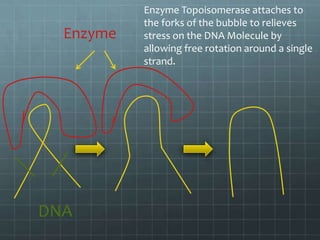
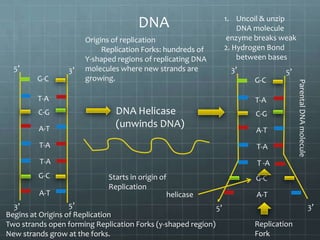
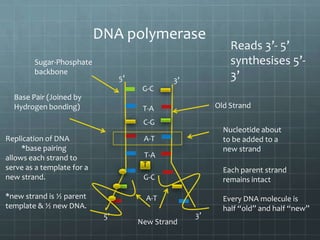
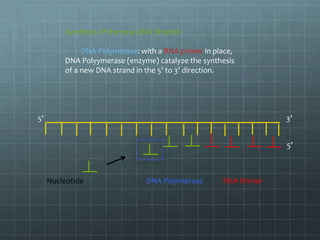
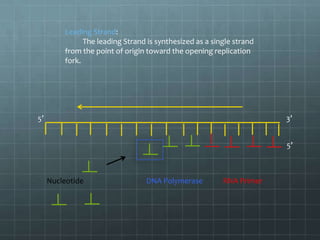
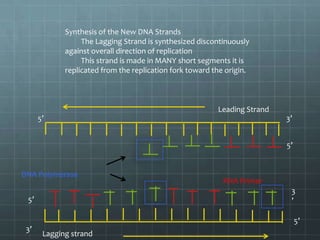
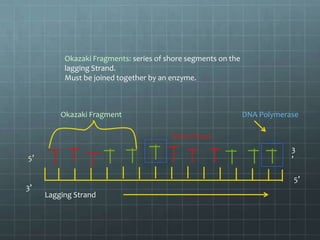
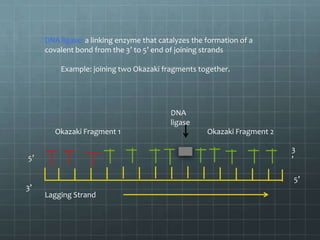
DNA replication occurs through a semi-conservative process where the parental double helix unwinds and each strand serves as a template to produce two new DNA molecules, each with one original and one new strand. Replication begins at multiple origins of replication and proceeds bidirectionally. Enzymes such as helicase unwind the DNA and single-strand binding proteins stabilize the separated strands. DNA polymerase adds complementary nucleotides to the 3' ends of the new strands which grow toward each other, producing daughter strands. The leading strand is continuous while the lagging strand is synthesized discontinuously in short Okazaki fragments later joined by DNA ligase.