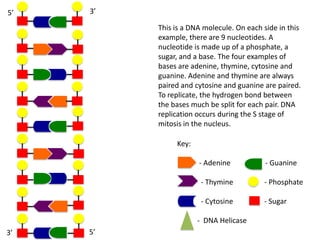
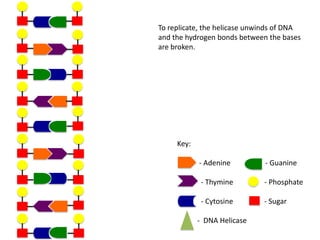
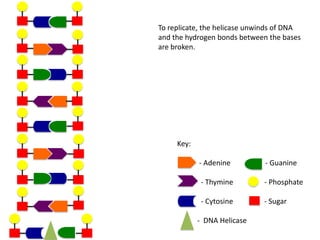
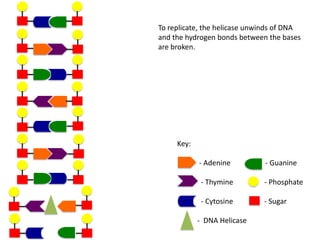
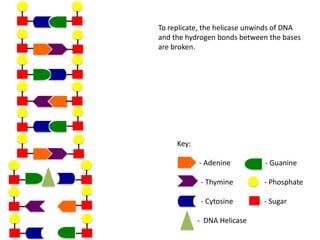
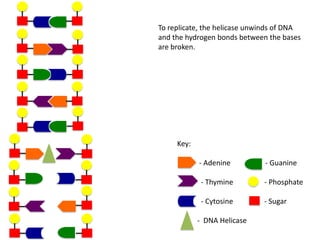
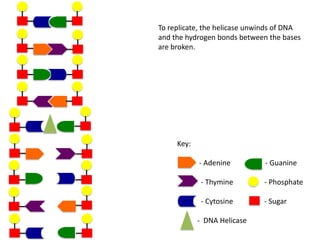
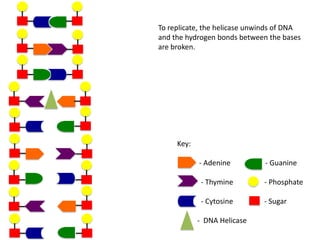
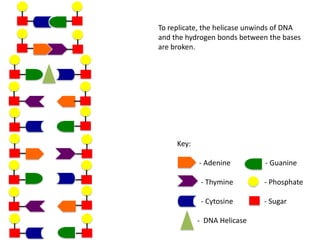
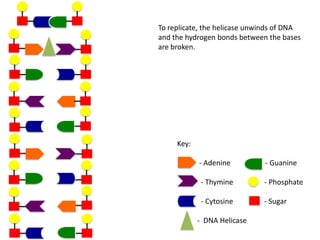
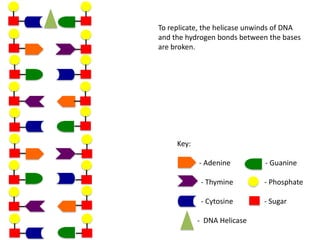
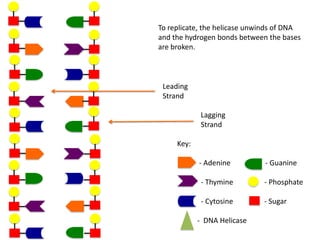
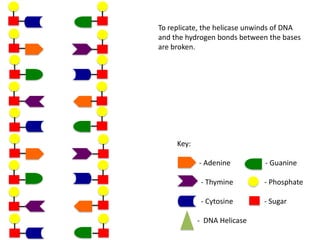
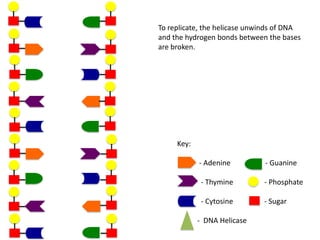
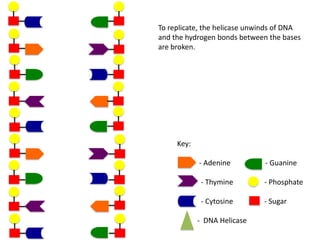
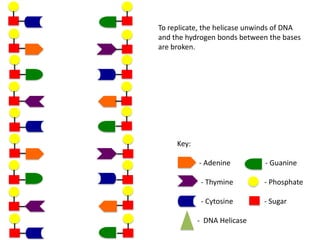
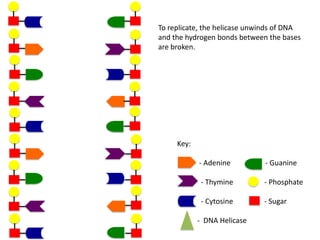
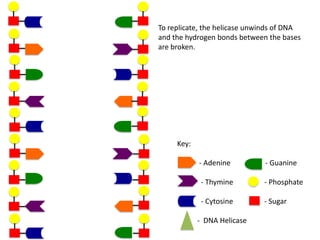
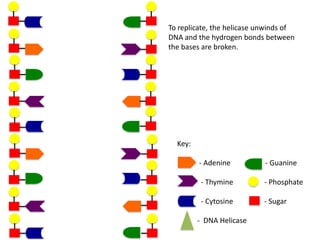
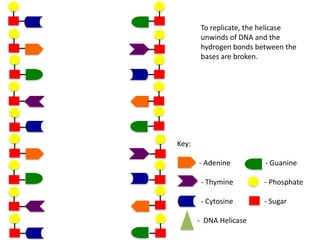
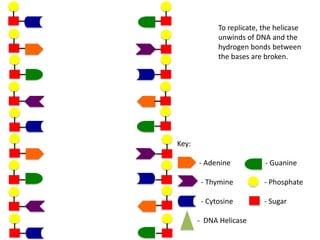
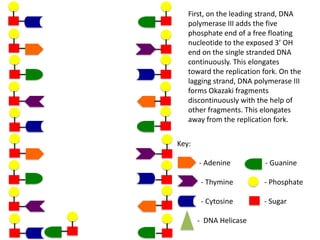
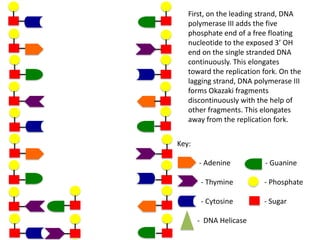
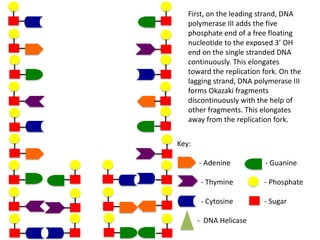
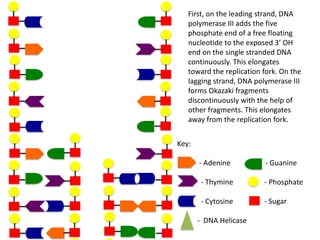
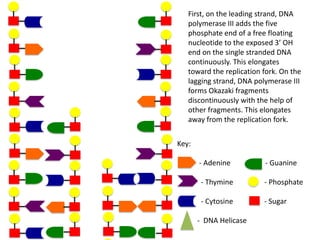
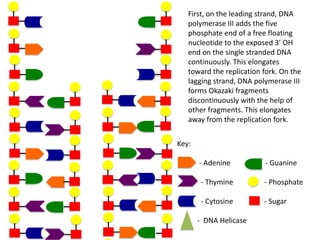
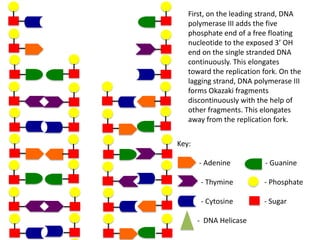
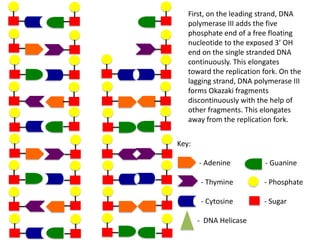
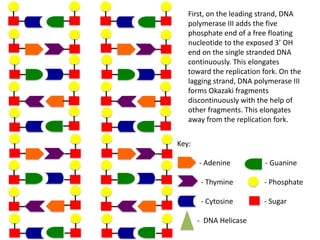
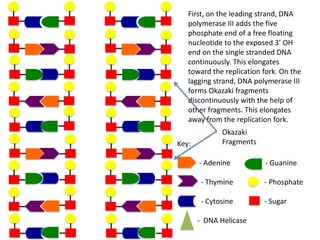
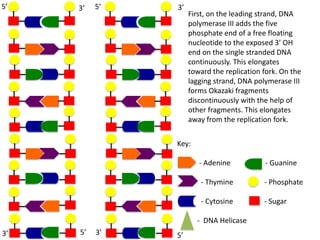
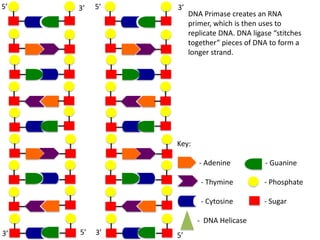
The document describes the process of DNA replication. It begins with DNA helicase unwinding the double helix structure and breaking the hydrogen bonds between nucleotide base pairs. On the leading strand, DNA polymerase continuously adds nucleotides to form the new strand in the 5' to 3' direction as the replication fork moves away. On the lagging strand, DNA polymerase forms Okazaki fragments in the opposite direction that are later joined by DNA ligase. DNA primase synthesizes RNA primers to initiate DNA replication.