- Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl performed an experiment in 1958 using isotopes of nitrogen (N15 and N14) to track DNA replication in E. coli bacteria.
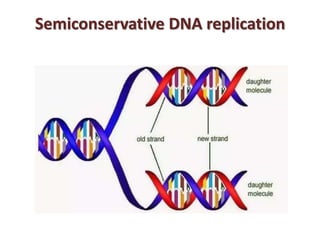
- They found that after one round of replication, the parental and newly synthesized DNA strands had an intermediate density, supporting Watson and Crick's semiconservative model where each new DNA molecule contains one original and one new strand.
- Subsequent experiments by Meselson and Stahl and others confirmed that DNA replication is semiconservative, with the two strands of the double helix separating and each acting as a template for synthesis of a new complementary strand.














![• DNA extracted from the culture after another
generation [that is after 40 minutes, II
generation] was composed of equal amounts of
this hybrid DNA and of ‘light’ DNA.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dnareplicationandtranscriptionunit-201211171046/85/DNA-replication-and-transcription-unit-17-320.jpg)



































