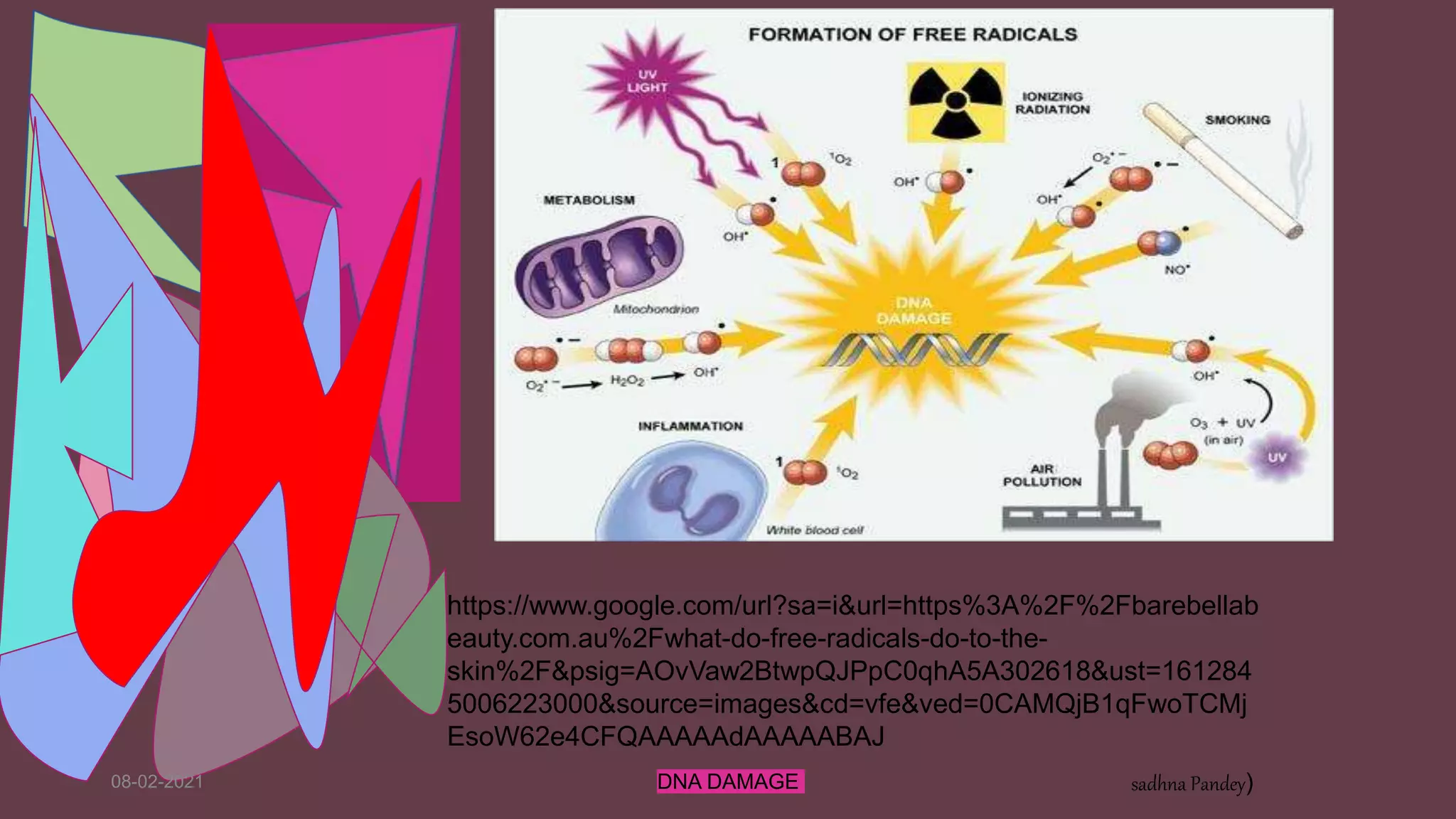
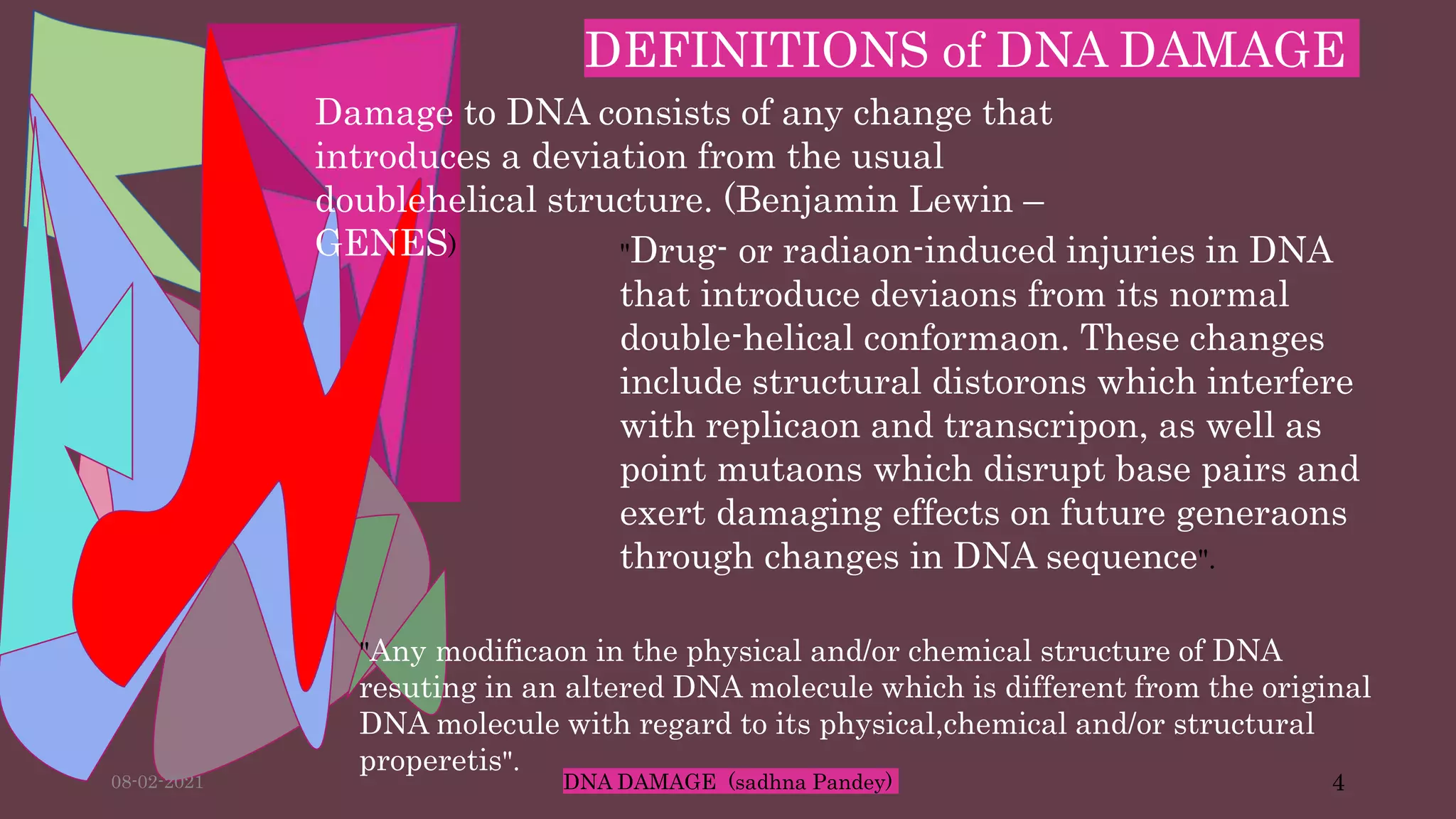
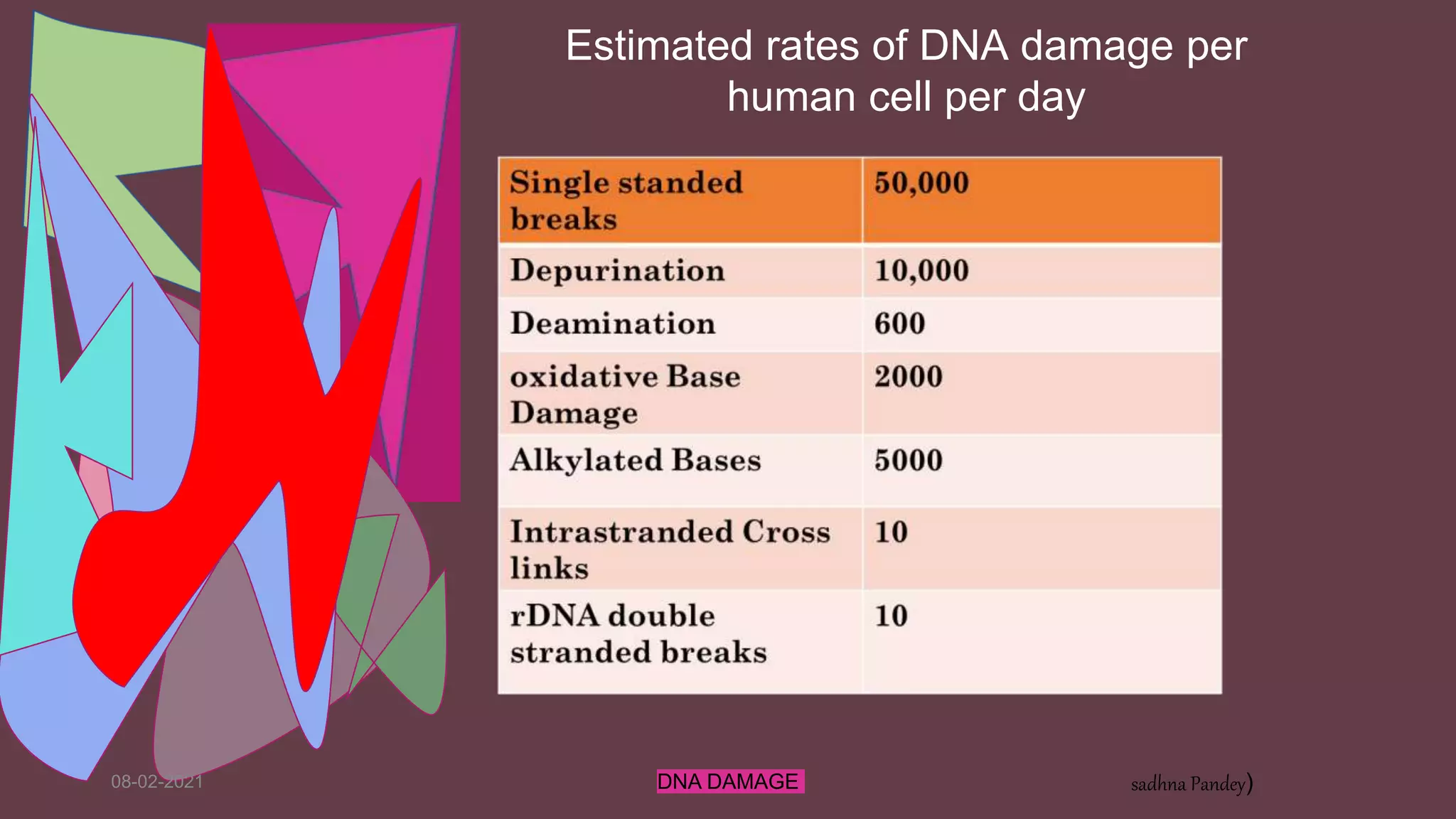
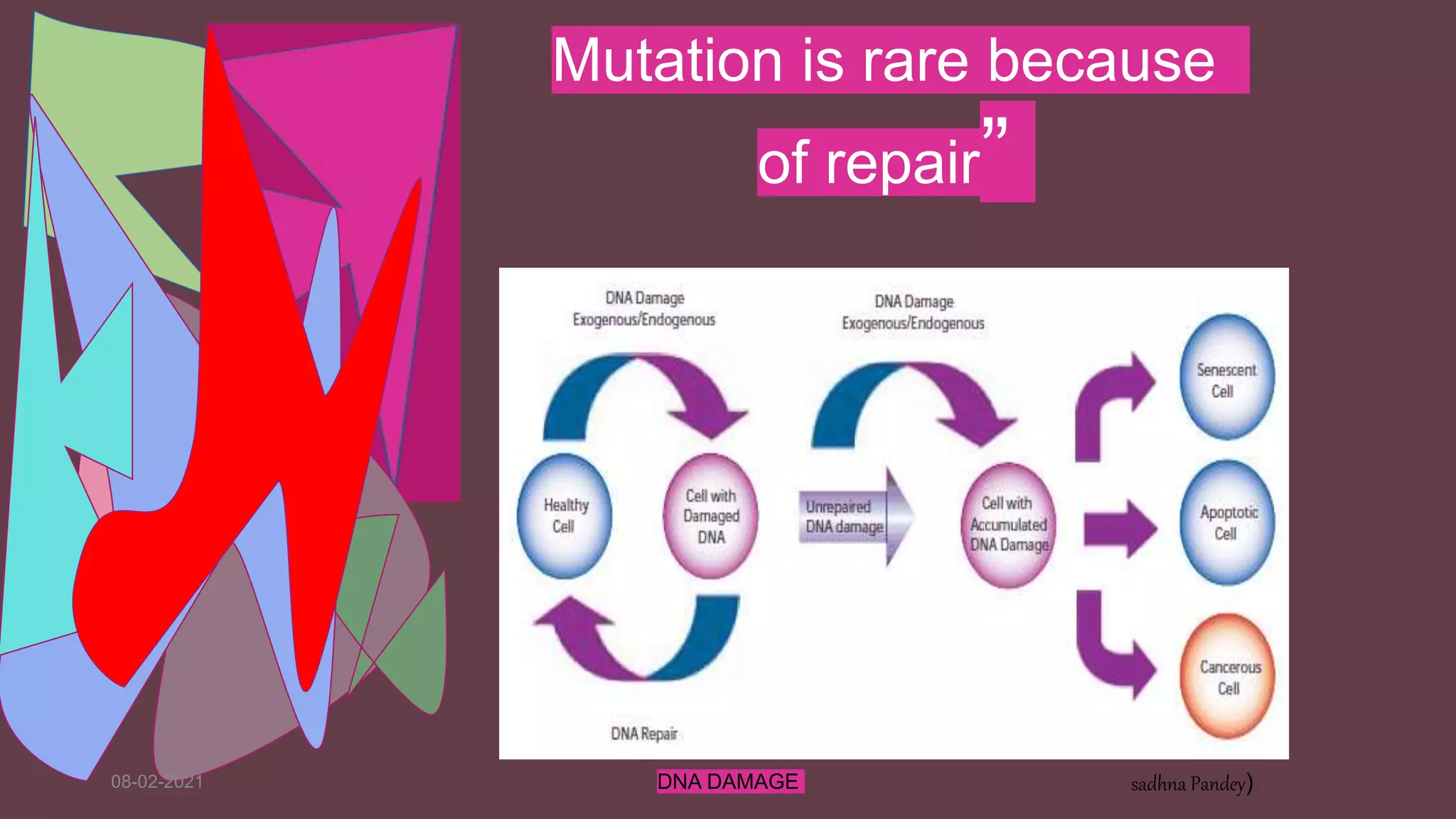
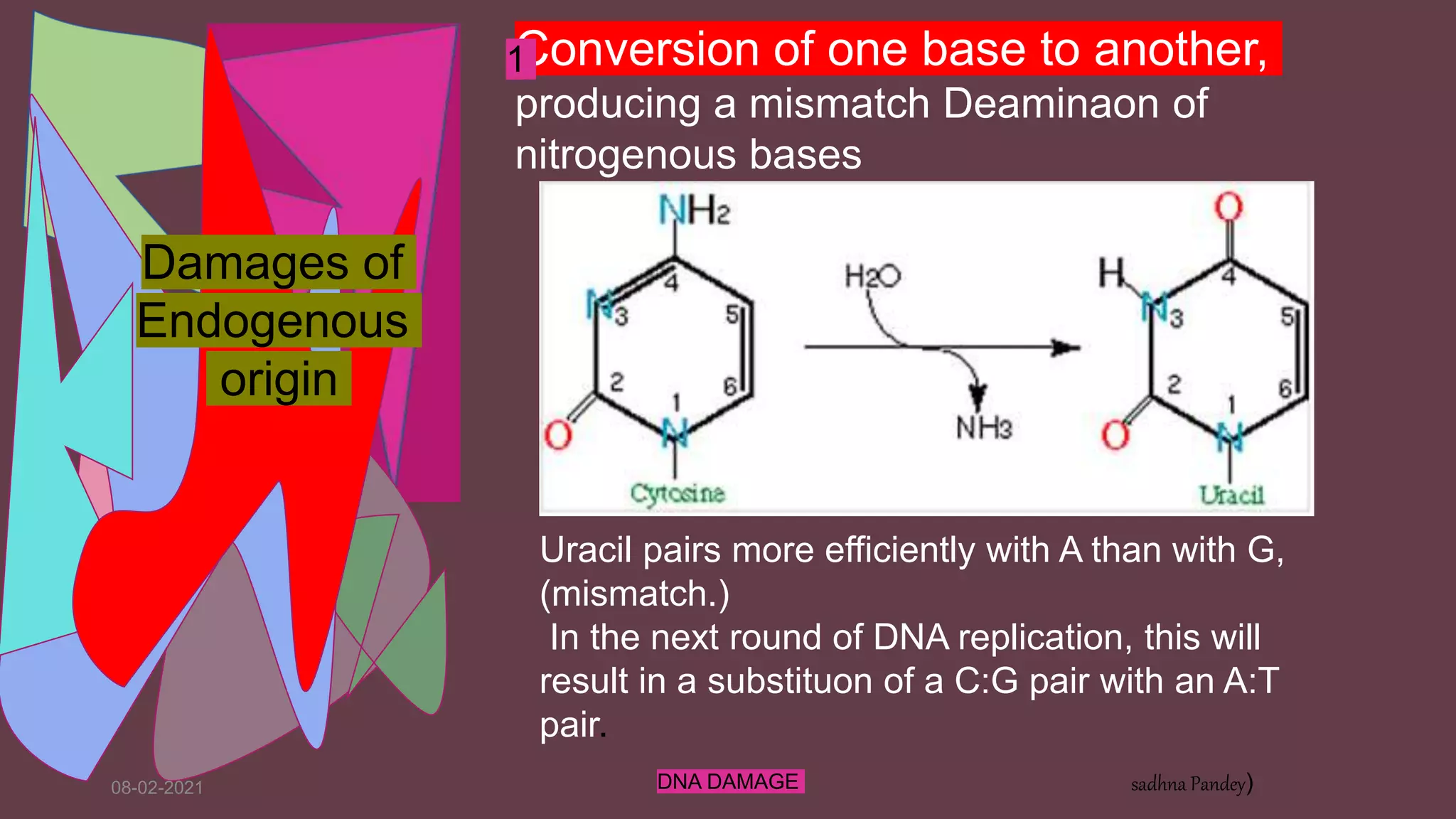
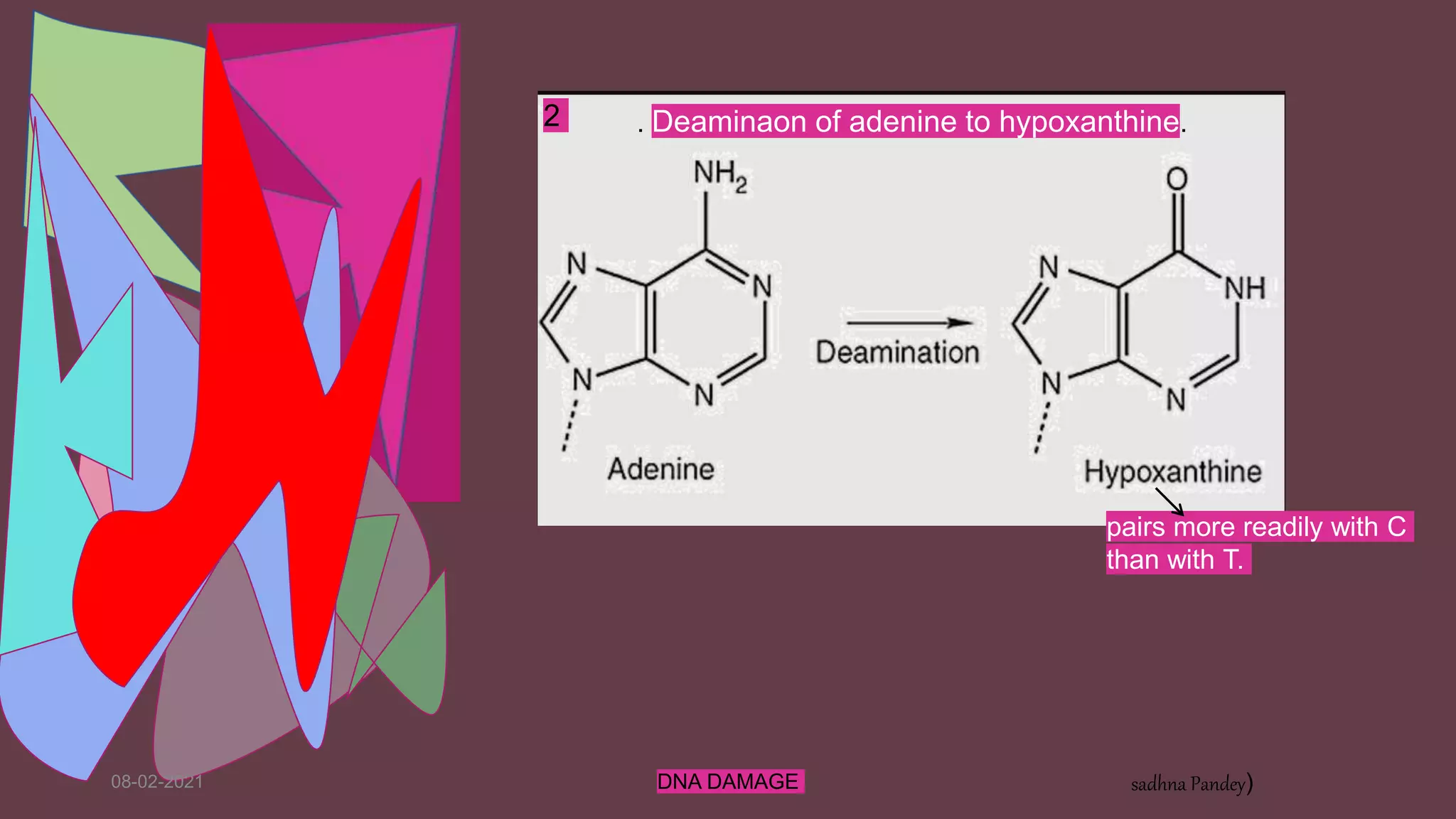
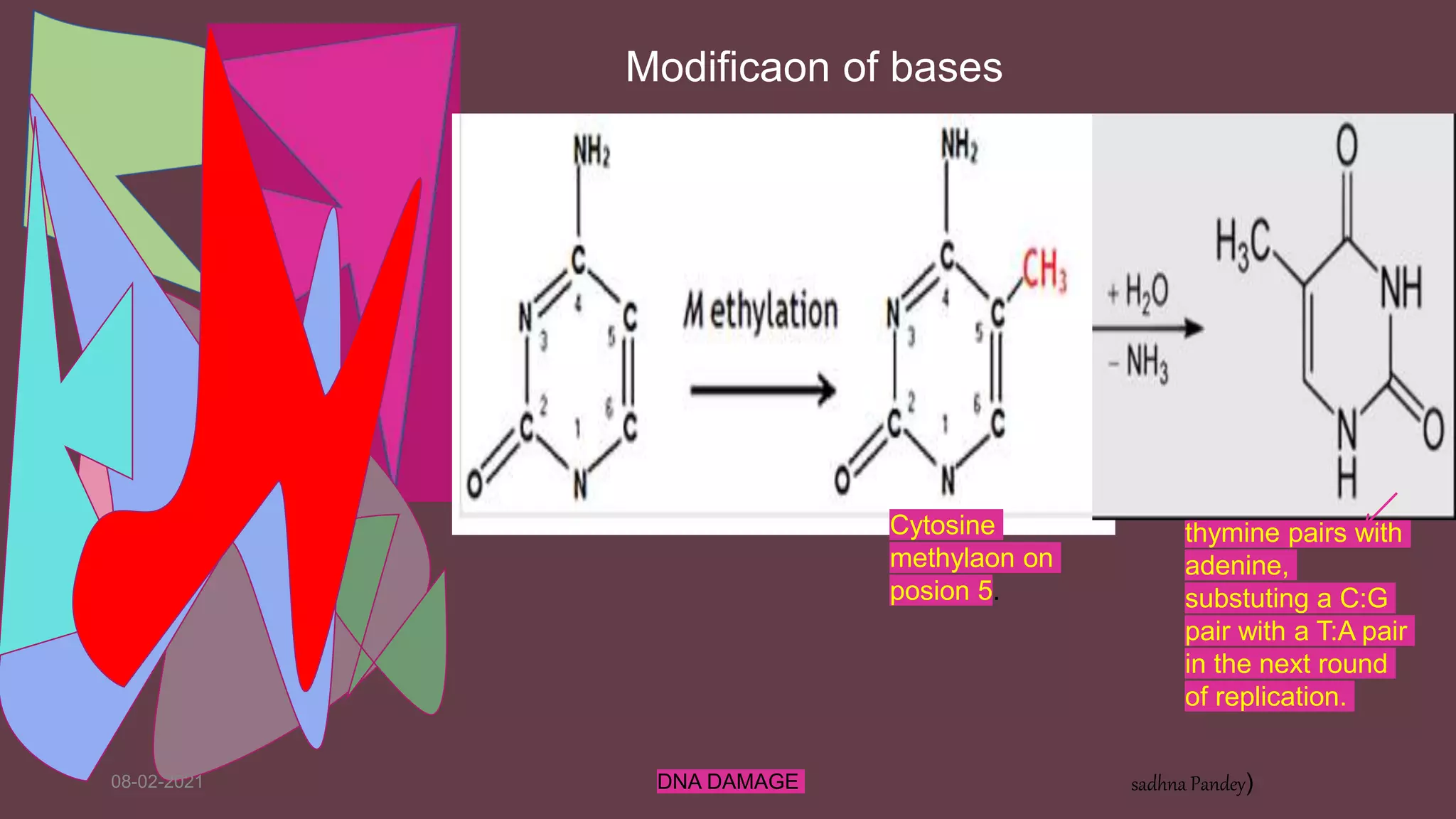
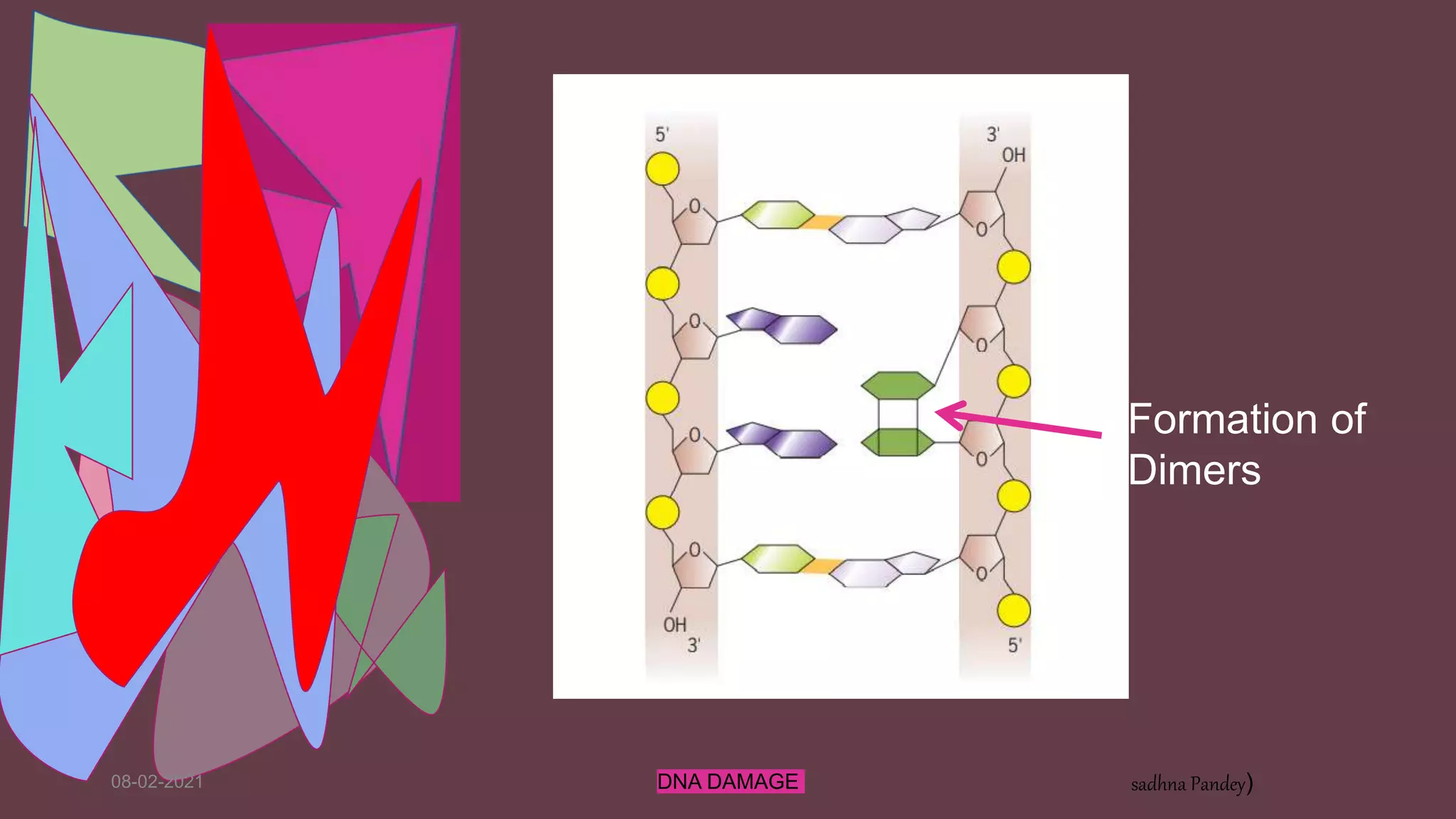
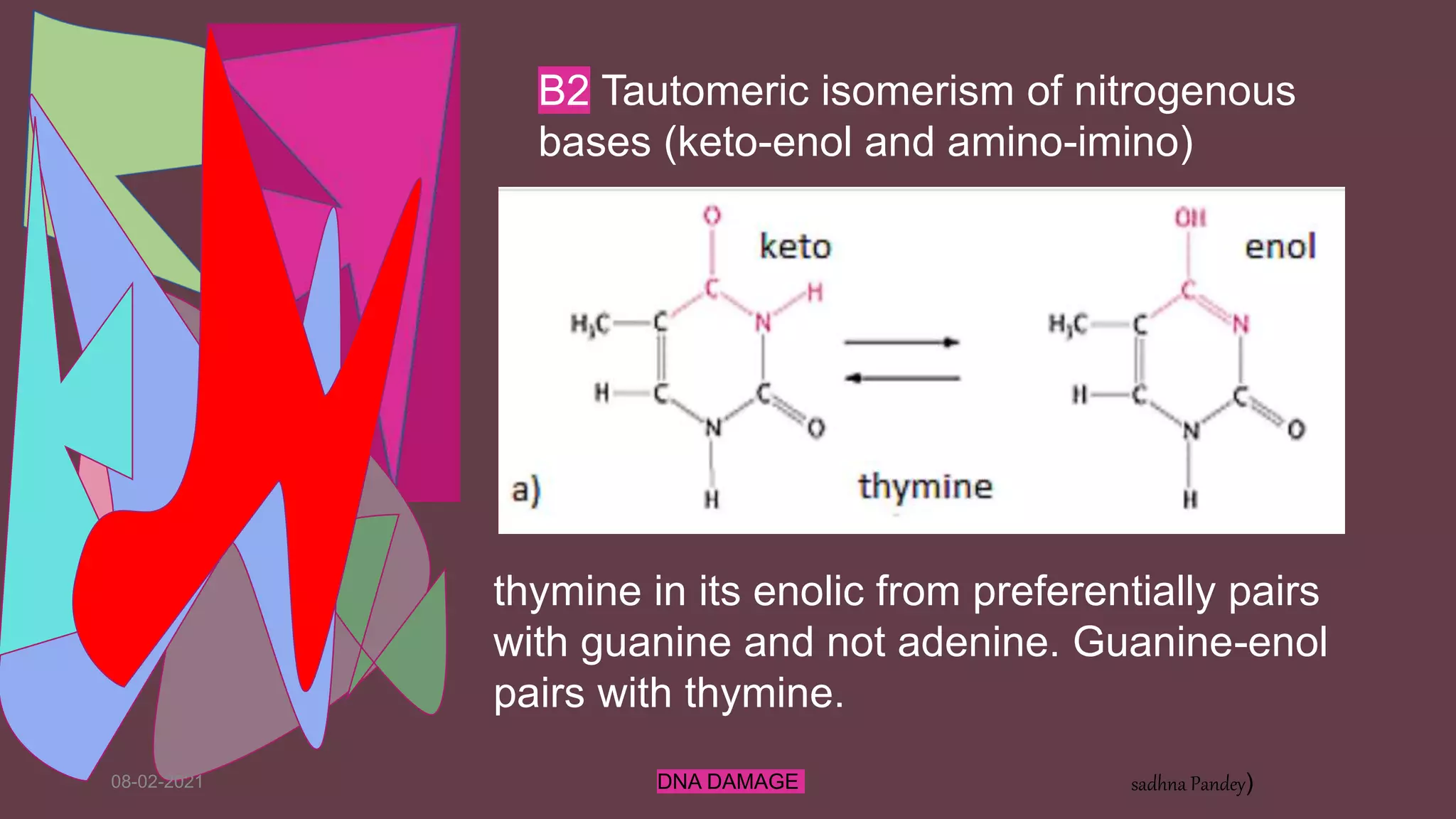
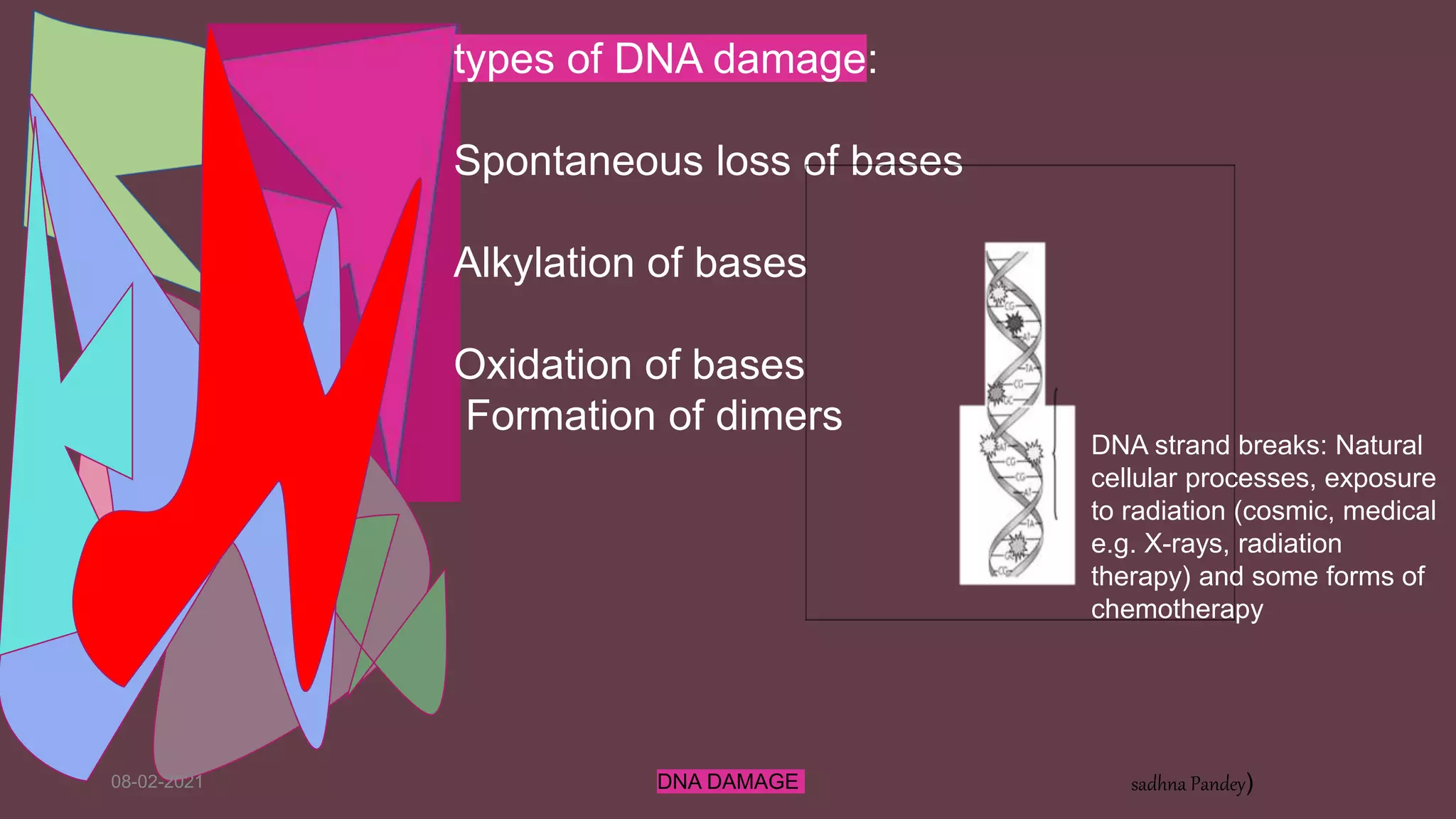
DNA can be damaged through various means, both endogenous and exogenous. Endogenous damage occurs as a result of normal cellular processes and metabolism, and includes deamination of bases, resulting in base mismatches during replication. Exogenous factors include physical agents like radiation which can cause base dimerization, and chemical agents that induce adducts and strand breaks. Unrepaired damage can lead to mutations being passed on if they affect the coding regions of genes. The cell has multiple repair pathways to prevent mutations from occurring and to maintain genomic integrity.