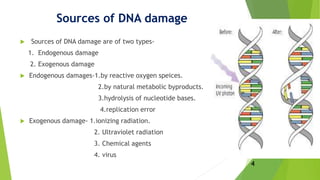
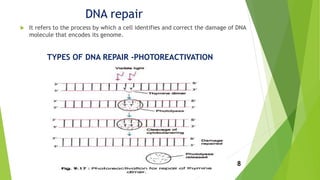
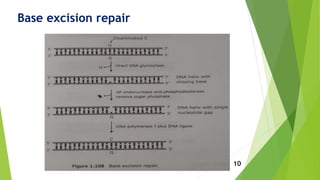
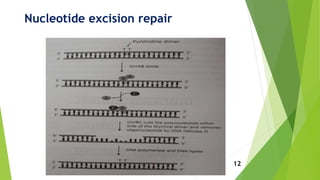
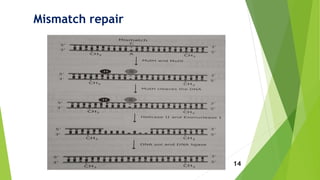
This document discusses DNA damage and repair mechanisms. It begins by introducing DNA damage and its sources, including endogenous sources like reactive oxygen species and exogenous sources like radiation. It then describes different types of DNA damage such as single base alterations, double base alterations, chain breaks, and cross-linkages. The document proceeds to explain four main DNA repair pathways: photoreactivation, base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair, and mismatch repair. Each repair pathway involves specific enzymes to identify and remove damaged DNA and allow for new DNA synthesis. In summary, the document provides an overview of DNA damage sources and types as well as the key repair mechanisms cells use to correct DNA damage.