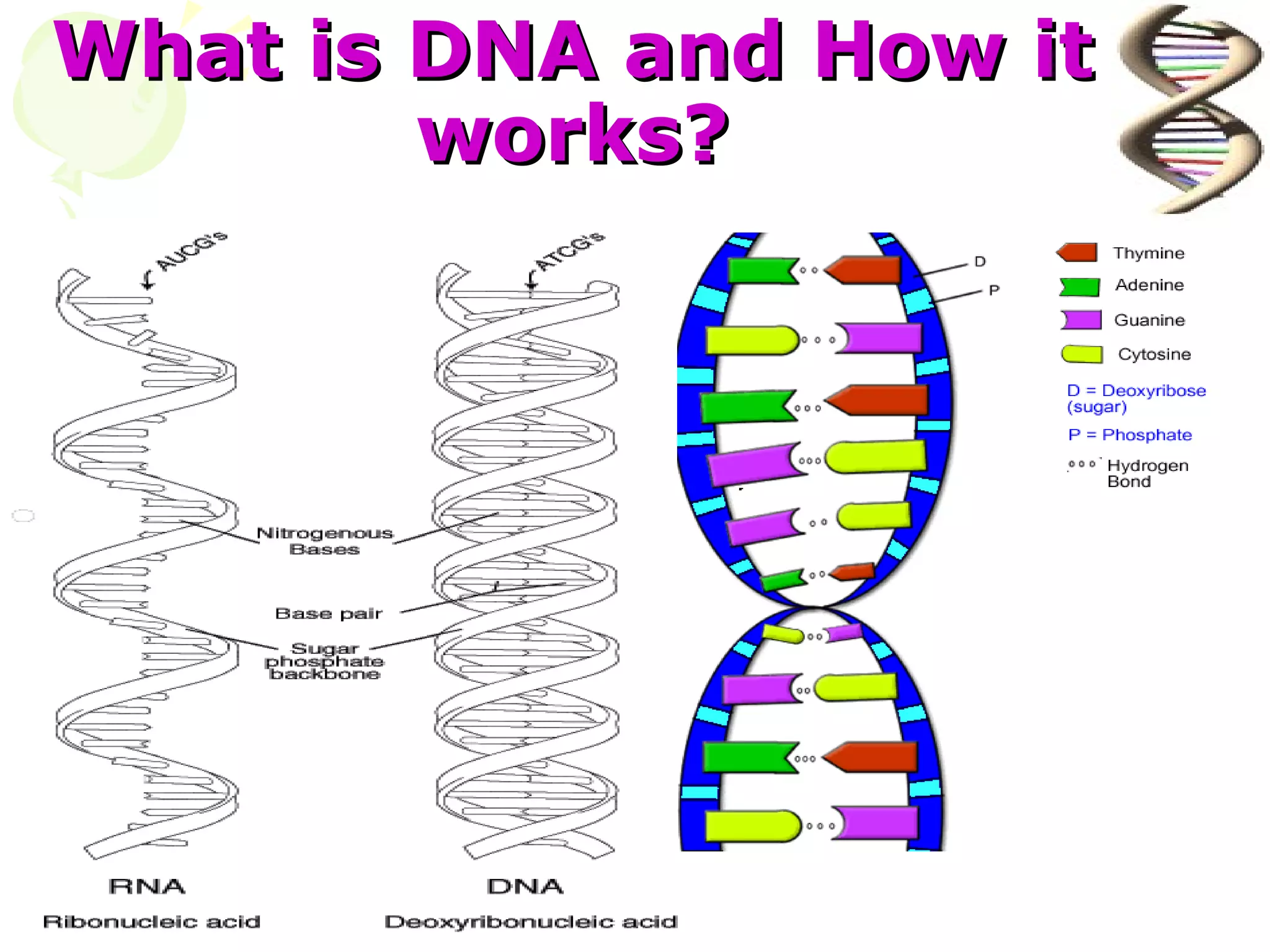
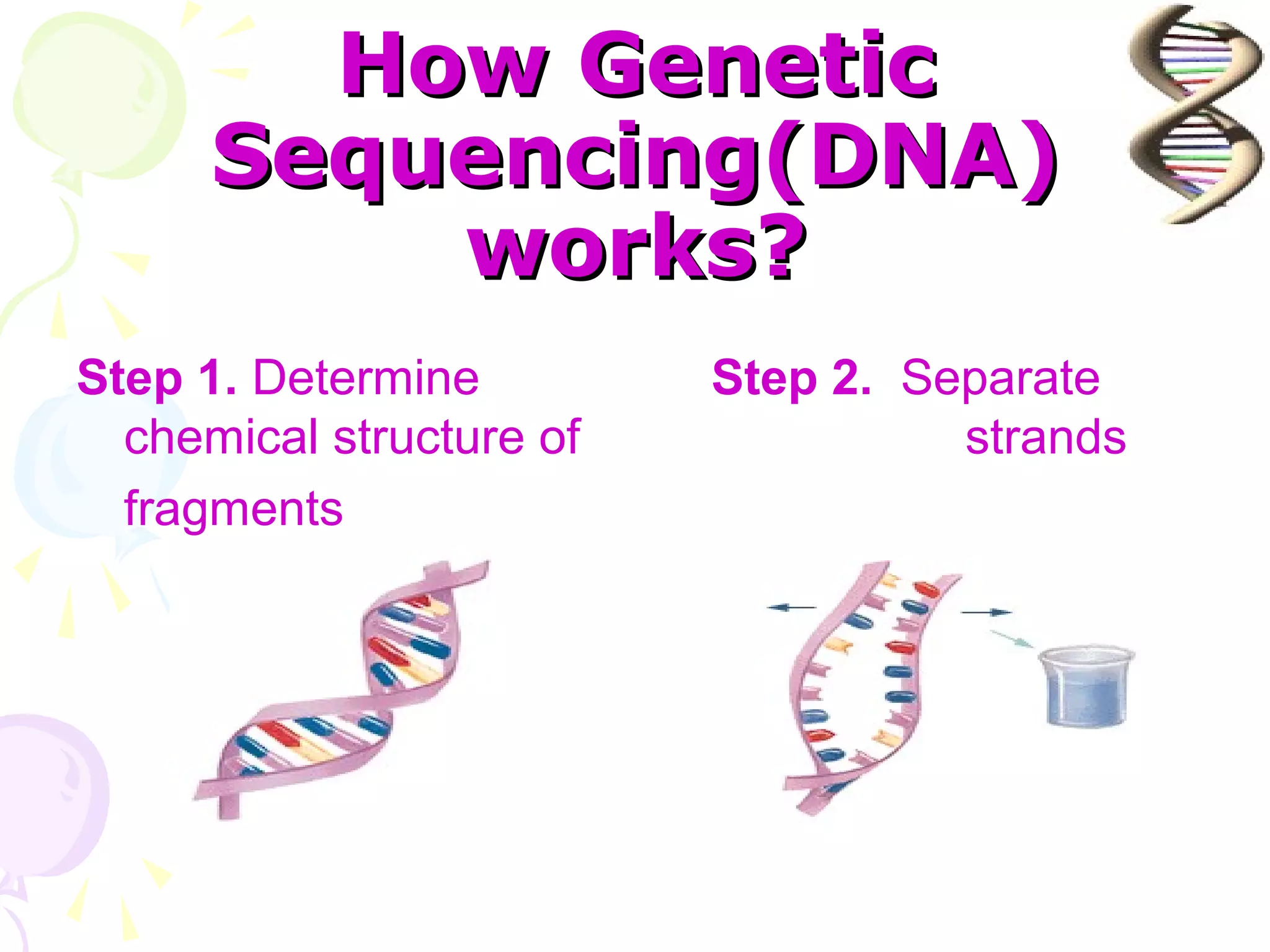
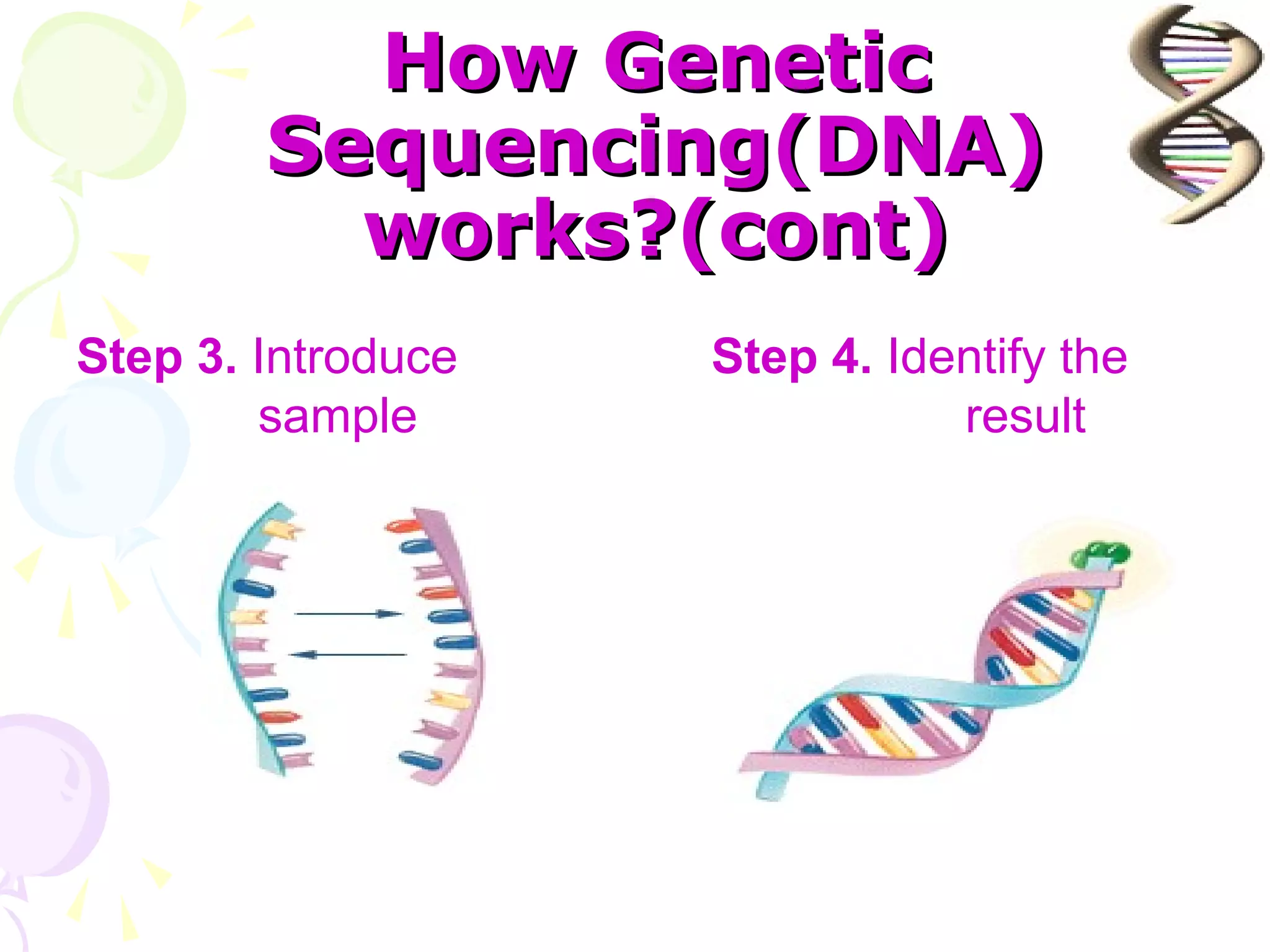
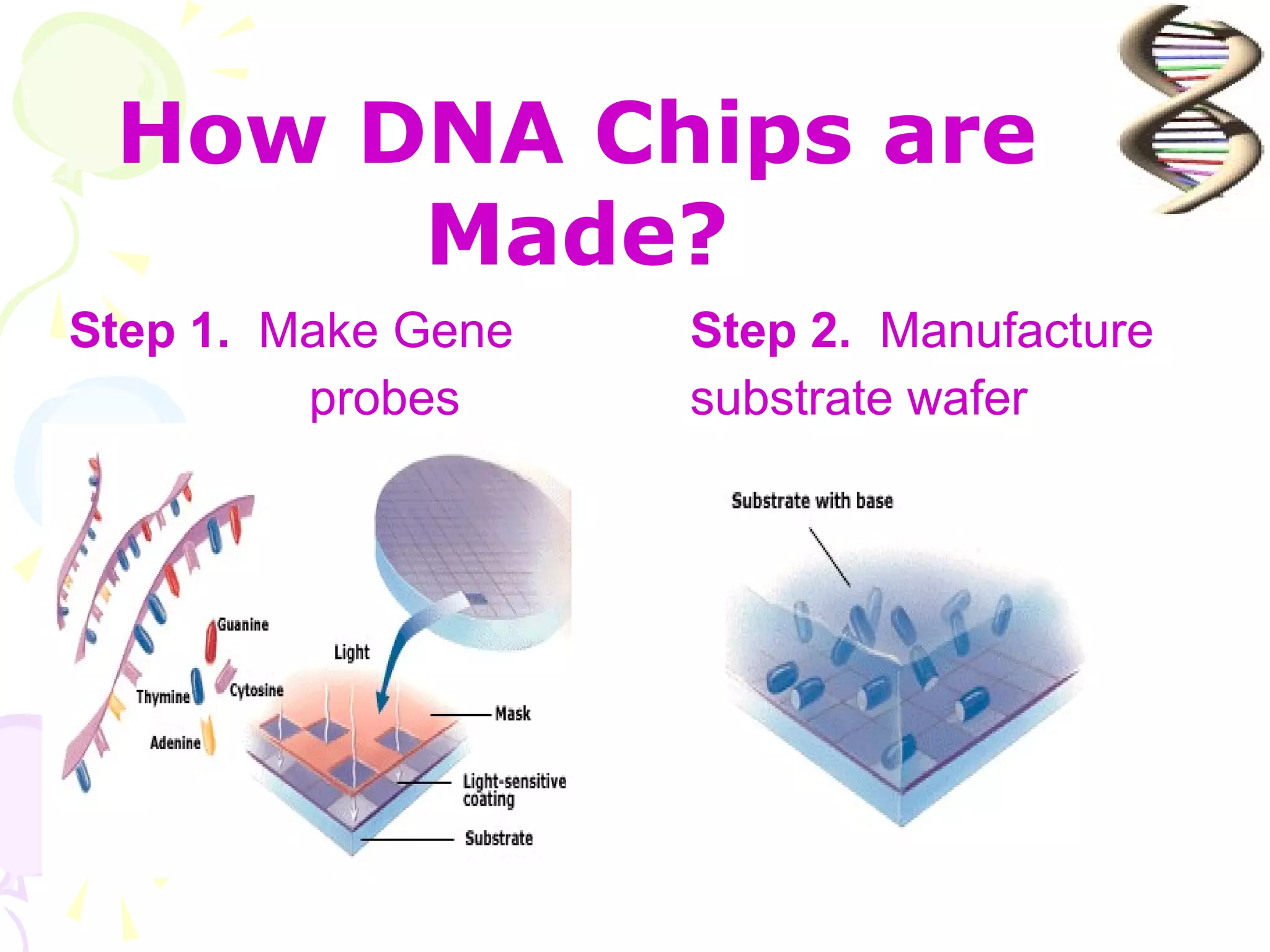
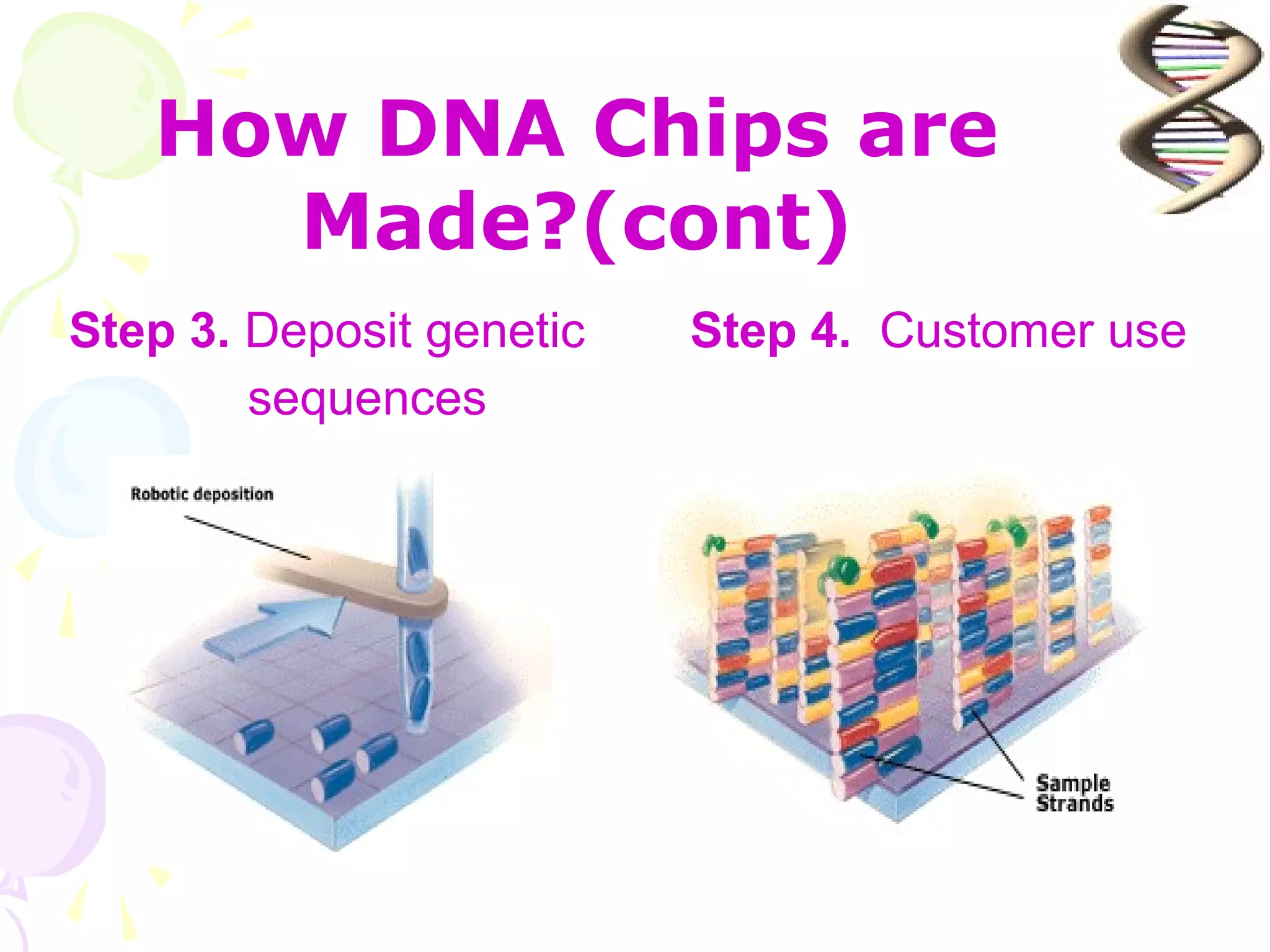
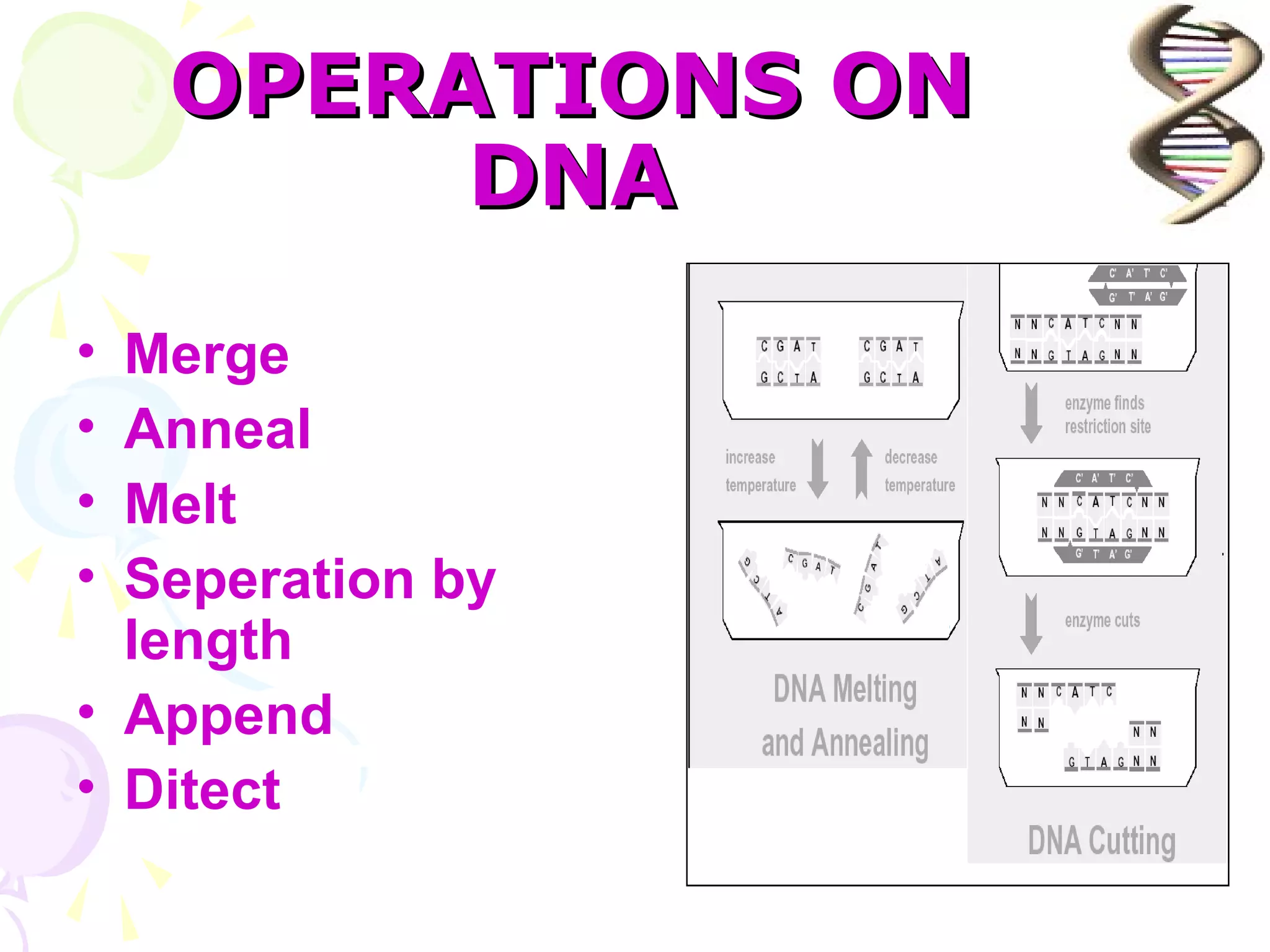
DNA computing is a novel approach that uses DNA, genetic material, and biochemical processes to solve computational problems. DNA computers have significant potential advantages over traditional silicon-based computers, including massive parallelism, large storage capacity, and low energy usage. However, DNA computing also faces challenges such as slow operation speeds and reliability issues that need to be addressed through ongoing research.